Scientists have discovered the world’s oldest known example of a squid-like creature attacking its prey, in a fossil dating back almost 200 million years.
The fossil was found on the Jurassic coast of southern England in the 19th century and is currently housed within the collections of the British Geological Survey in Nottingham.
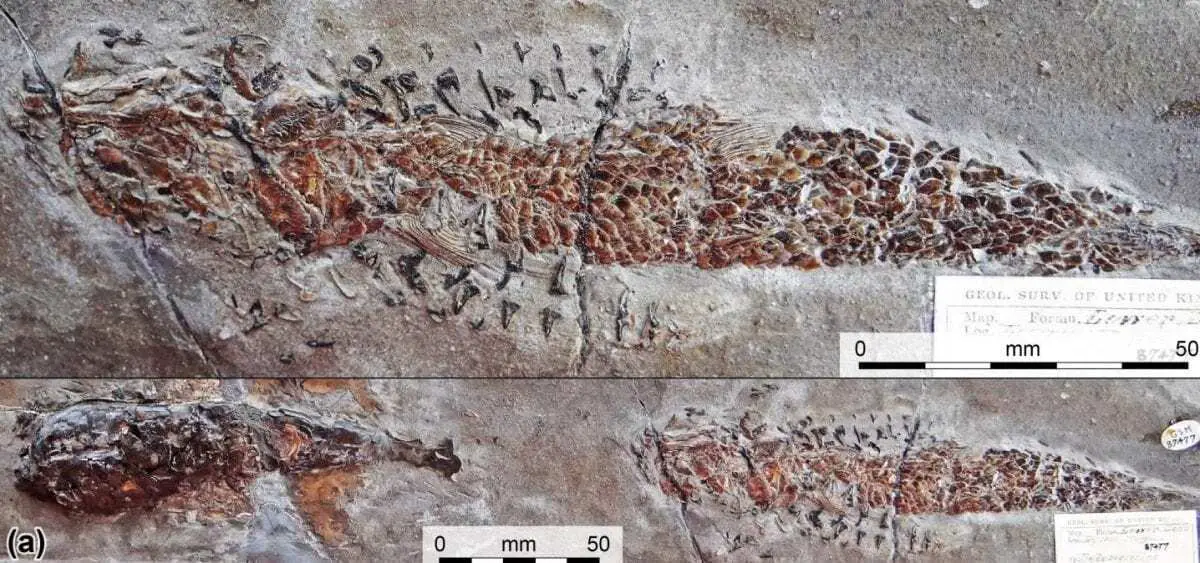
In a new analysis, researchers say it appears to show a creature – which they have identified as Clarkeiteuthis montefiorei – with a herring-like fish (Dorsetichthys bechei) in its jaws.
They say the position of the arms, alongside the body of the fish, suggests this is not a fortuitous quirk of fossilization but that it is recording an actual palaeobiological event.
They also believe it dates from the Sinemurian period (between 190 and 199 million years ago), which would predate any previously recorded similar sample by more than 10 million years.
The research was led by the University of Plymouth, in conjunction with the University of Kansas and Dorset-based company, The Forge Fossils.
It has been accepted for publication in Proceedings of the Geologists’ Association and will also be presented as part of Sharing Geoscience Online, a virtual alternative to the traditional General Assembly held annually by the European Geosciences Union (EGU).
Professor Malcolm Hart, Emeritus Professor in Plymouth and the study’s lead author, said: “Since the 19th century, the Blue Lias and Charmouth Mudstone formations of the Dorset coast have provided large numbers of important body fossils that inform our knowledge of coleoid palaeontology. In many of these mudstones, specimens of palaeobiological significance have been found, especially those with the arms and hooks with which the living animals caught their prey.
“This, however, is a most unusual if not extraordinary fossil as predation events are only very occasionally found in the geological record. It points to a particularly violent attack which ultimately appears to have caused the death, and subsequent preservation, of both animals.”
In their analysis, the researchers say the fossilised remains indicate a brutal incident in which the head bones of the fish were apparently crushed by its attacker.
They also suggest two potential hypotheses for how the two animals ultimately came to be preserved together for eternity.
Firstly, they suggest that the fish was too large for its attacker or became stuck in its jaws so that the pair – already dead – settled to the seafloor where they were preserved.
Alternatively, the Clarkeiteuthis took its prey to the seafloor in a display of ‘distraction sinking’ to avoid the possibility of being attacked by another predator. However, in doing so it entered waters low in oxygen and suffocated.
Header Image – An image showing the full fossil with the body of the squid on the left and its arms, with the trapped fish, to the right. Image Credit : Malcolm Hart, Proceedings of the Geologists’ Association