Climate change is leading to the retreat of mountain glaciers.
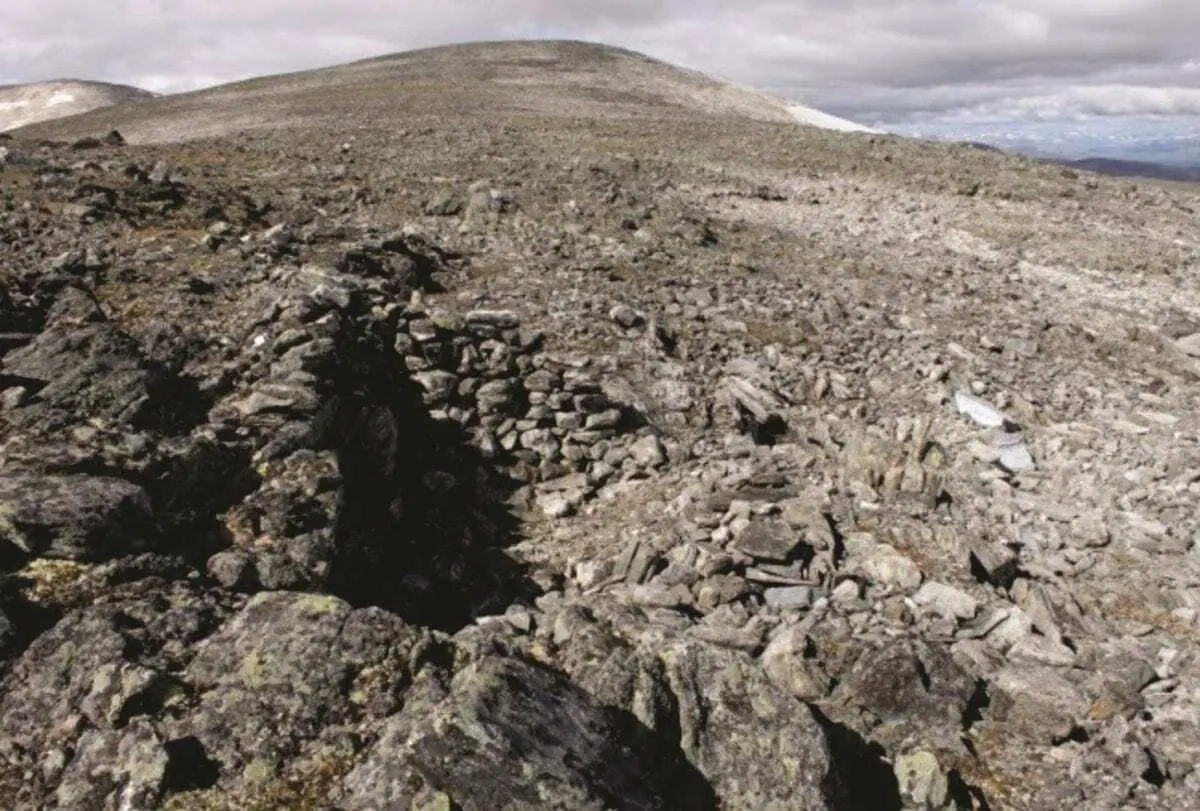
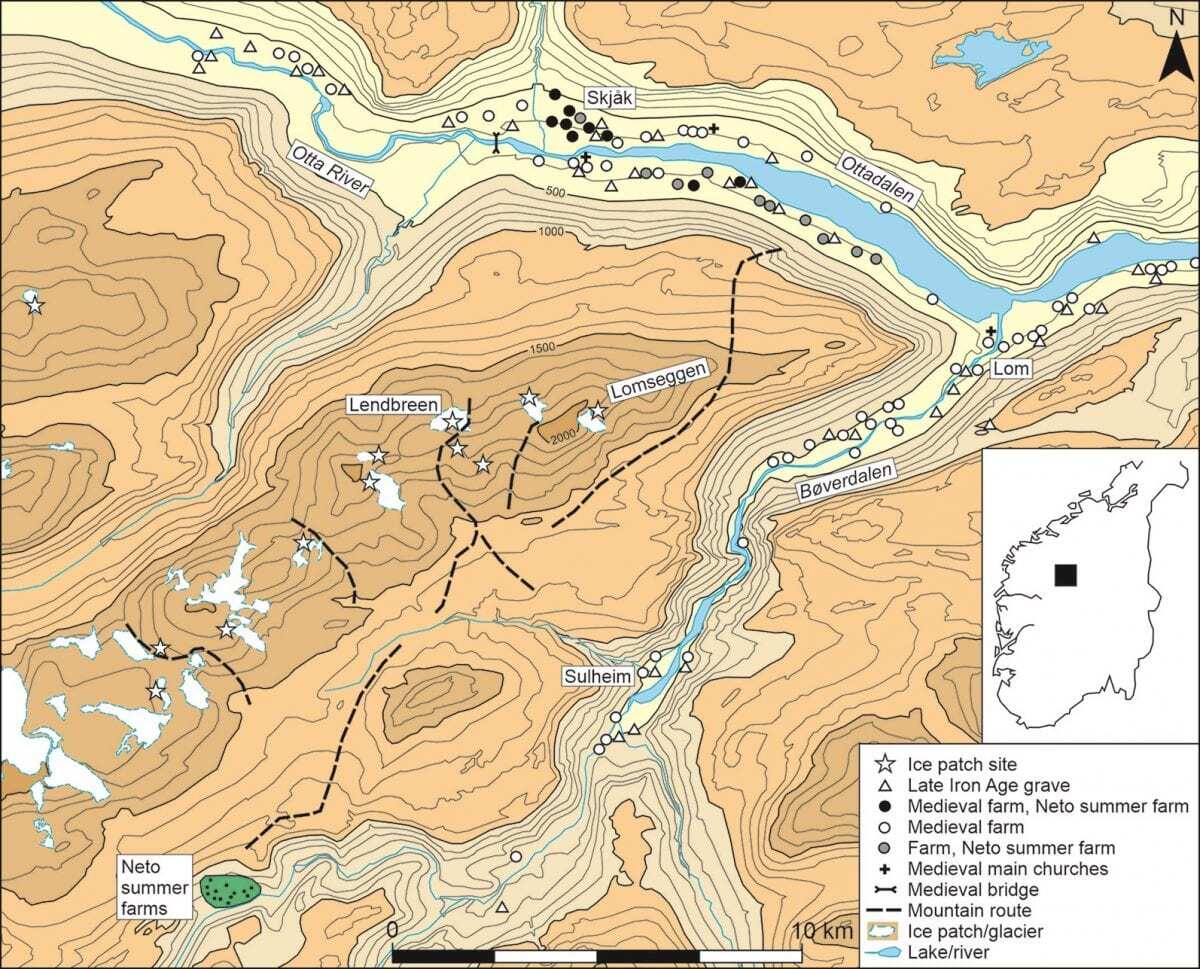
In Norway, hundreds of rare archaeological finds have been revealed by melting ice in a lost mountain pass at Lendbreen in Innlandet County.
The finds tell a remarkable story of high-altitude travel in the Roman Iron Age and the Viking Age.
“A lost mountain pass melting out of the ice is a dream discovery for us glacial archaeologists,” says Lars Pilo, first author of the study and co-director for the Glacier Archaeology Program.
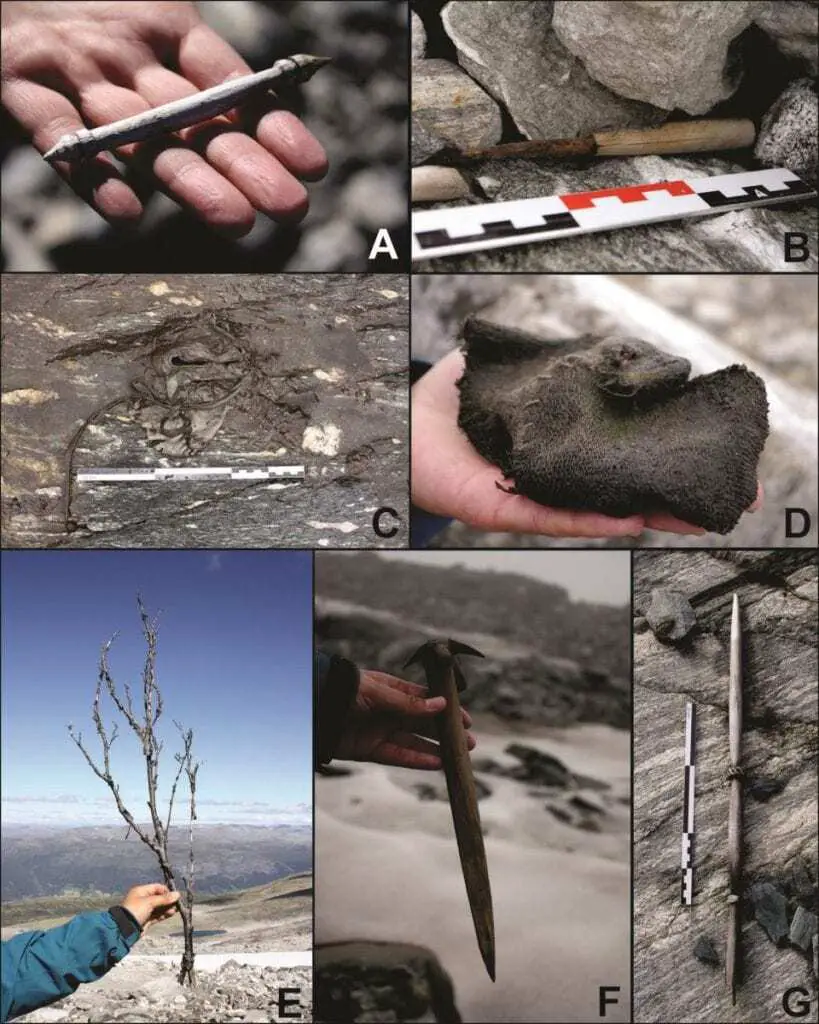

“In such passes, travellers lost many artefacts that became frozen in time by the ice. These incredibly well-preserved artefacts of organic materials have great historical value.”
Some of the hundreds of finds from Lendbreen derive from the actual transport through the pass – such as horseshoes, bones from packhorses, remains of sleds and even a walking stick with runic inscriptions.
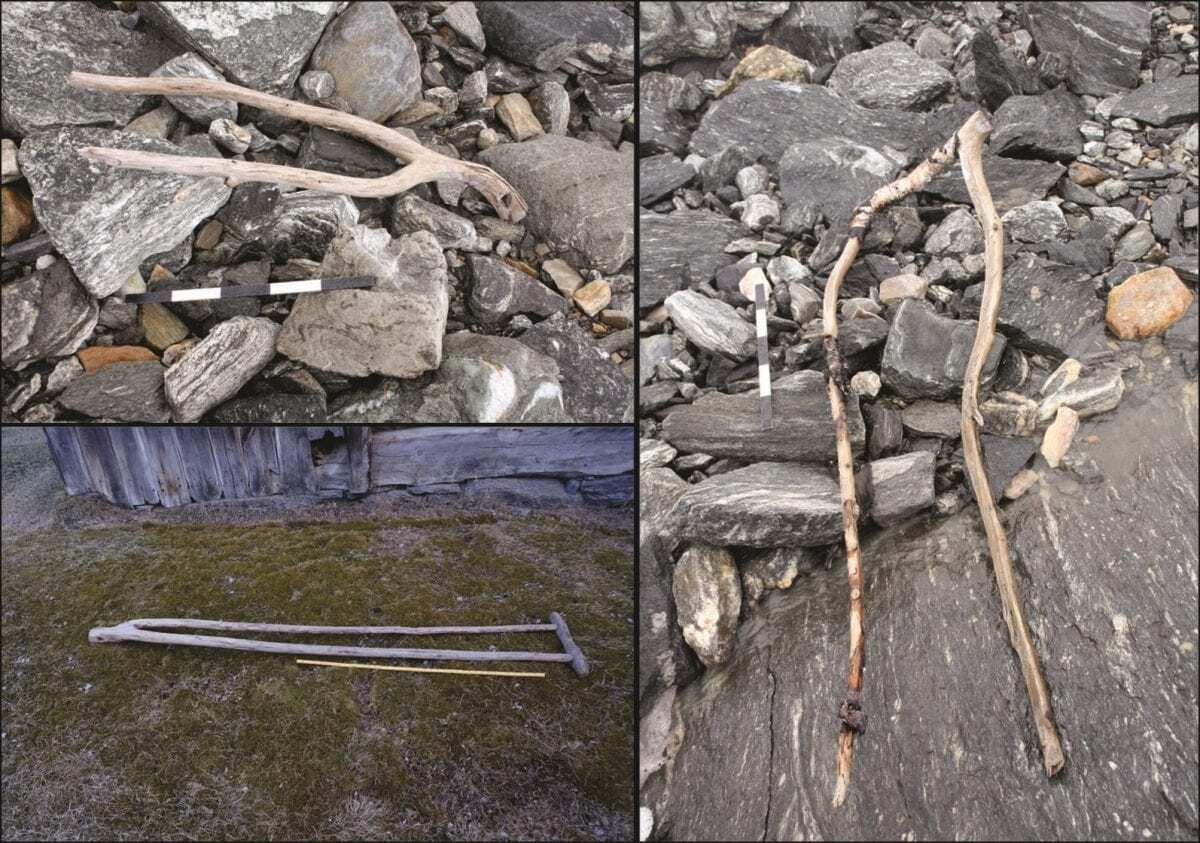

Other finds are items from daily life discarded by travellers such as a knife with a preserved wooden handle, a wooden distaff (for holding wool during hand-spinning) and a wooden whisk. Remains of clothing was also discovered that included a Roman Iron Age tunic, a Viking Age mitten and shoes. Other objects have no parallels in the archaeological record and their function is yet to be determined.
“The preservation of the objects emerging from the ice is just stunning” says Espen Finstad, co-author and co-director of the Glacier Archaeology program. “It is like they were lost a short time ago, not centuries or millennia ago.”

Sixty finds from Lendbreen have been radiocarbon-dated. They show when the pass was used, when the traffic was at its most intense and when traffic declined. They also revealed that the pass was mainly used in late winter/early summer when the rough terrain was covered by snow.
“Radiocarbon dates on the artefacts show that traffic through the pass started in the Roman Iron Age around AD300, peaking in the Viking Age around AD1000 and declined after this”, says corresponding author and program partner James J. Barret.
Header Image Credit : Antiquity Journal





