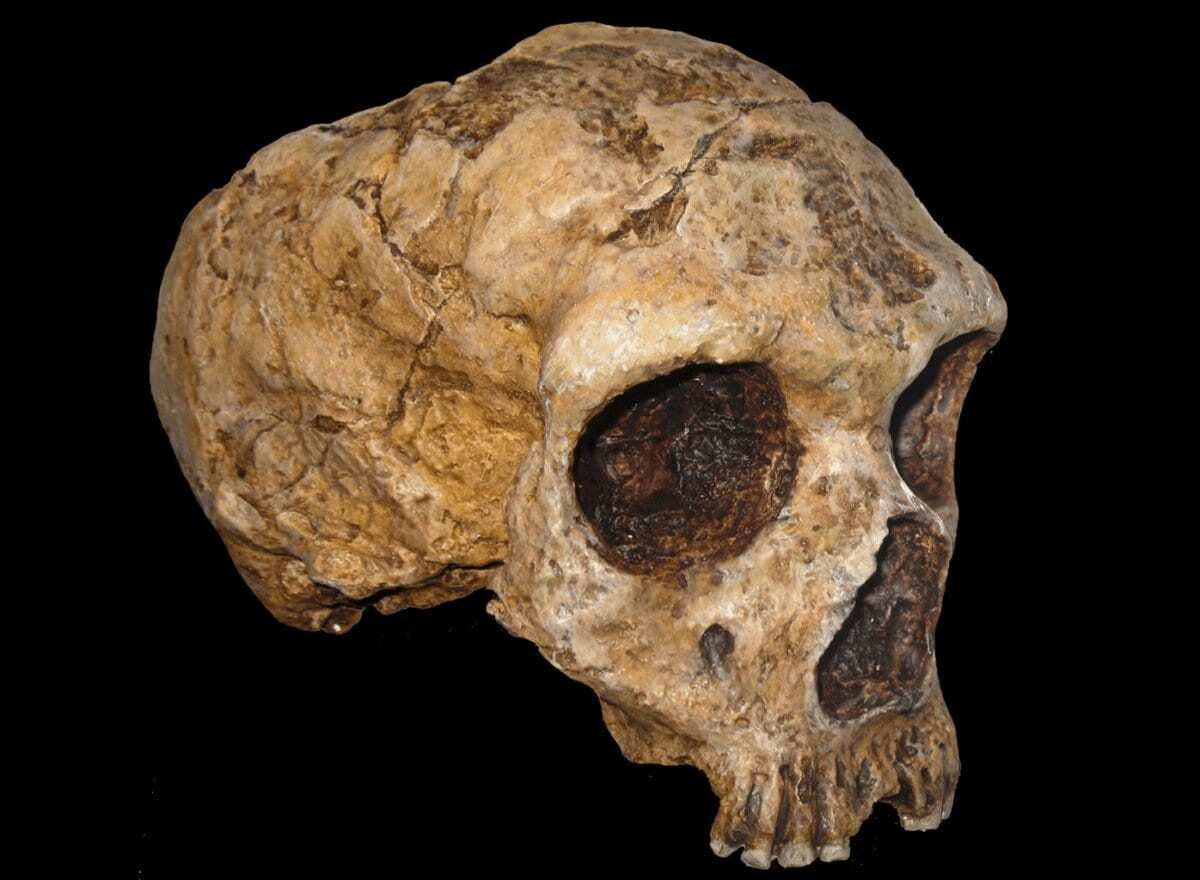
The Paleoneurobiology group at the National Center for Research on Human Evolution (CENIEH), led by Emiliano Bruner, has just published a morphological analysis of the brain of Neanderthals and modern humans, the results of which suggest that the “Roundness” of our brain is due in part to the fact that the parietal lobes are, on average, larger and more bulky.
In particular, two regions could be more developed in our species. The first is the posterior and dorsal part of the upper parietal lobe, and the second is the intermediate zone of the intraparietal groove, in the lower parietal lobe, as noted by Sofía Pereira, who has coordinated this study in collaboration with the Max Planck Institute in Leipzig ( Germany).
Three-dimensional spatial models have been created to compare the brain shape of 52 modern humans with the brain shape of 8 Neanderthals, based on the endocranial molds and the traces left by the brain grooves in the surface of the cranial cavity.
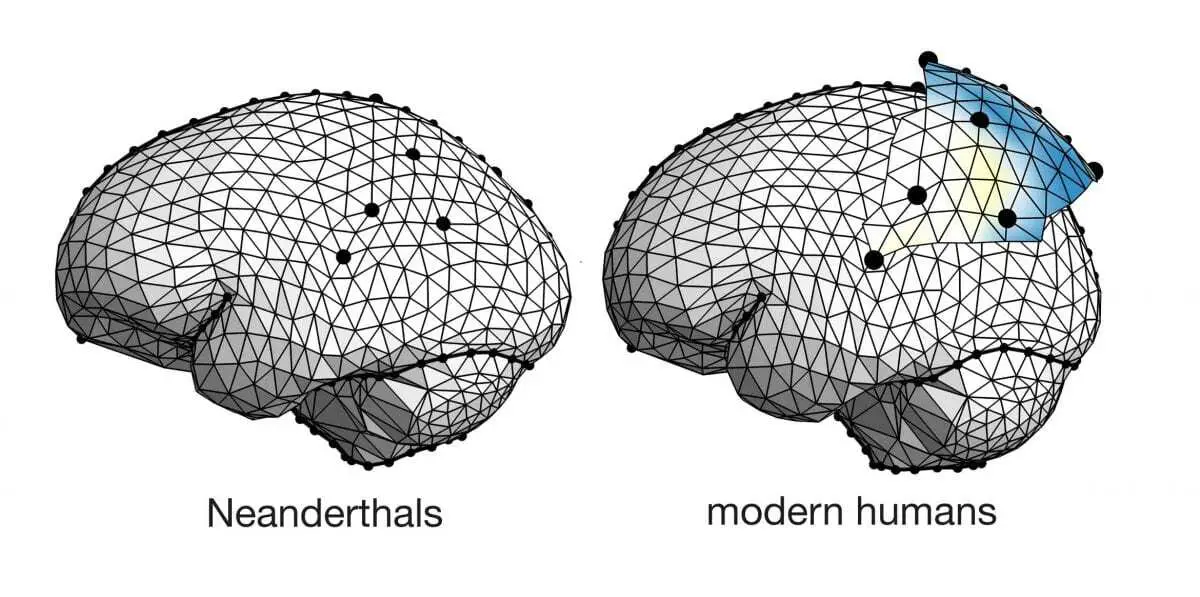
The geometric model used includes not only information about the general shape of the brain, but also the specific location of the parietal anatomy.
The parietal lobes are involved in visuo-spatial integration functions such as visual imagination or manipulation, and in general in all those cognitive aspects that concern the coordination between brain, body and external environment, including the relationship between eye and hand, and between hand and tools.
Header Image Credit : Anagoria





