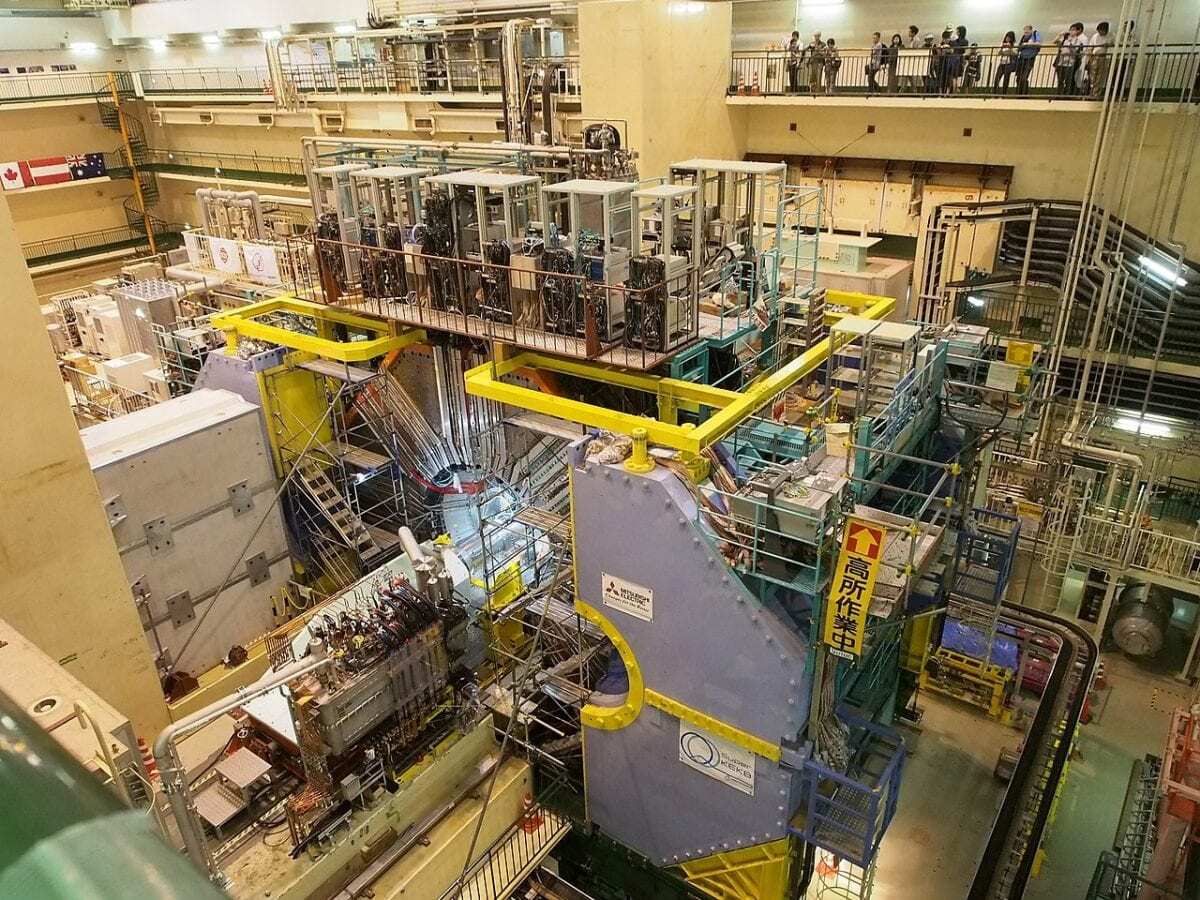
The Belle II experiment has been collecting data from physical measurements for about one year now.
After several years of rebuilding work, both the SuperKEKB electron-positron accelerator and the Belle II detector have been improved compared with their predecessors in order to achieve a 40-fold higher data rate. Scientists at 12 German research institutions are involved in constructing and operating the detector, developing evaluation algorithms, and analyzing the data. Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) supported this project by developing and programming special electronics for monitoring the pixel vertex detector.
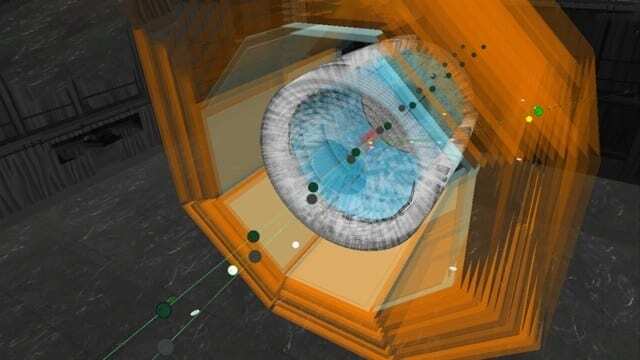
With the help of Belle II, scientists are looking for traces of new physics that can be used to explain the unequal occurrence of matter and anti-matter and the mysterious dark matter. One of the so far undiscovered particles that the Belle II detector is looking for is the Z? boson – a variant of the Z boson, which acts as an exchange particle for the weak interaction.
As far as we know, about 25 percent of the universe consists of dark matter, whereas visible matter accounts for just under 5 percent of the energy budget. Both forms of matter attract each other through gravity. Dark matter thus forms a kind of template for the distribution of visible matter. This can be seen, for example, in the arrangement of galaxies in the universe.
Link between dark and normal matter
The Z’ boson may play an interesting role in the interaction between dark and visible matter, it could be in fact a kind of mediator between the two forms of matter). The Z’ boson can – at least theoretically – result from the collision of electrons (matter) and positrons (anti-matter) in the SuperKEKB and then decay into invisible dark matter particles.
The Z’ boson can thus help scientists to understand the behavior of dark matter. What’s more, the discovery of the Z’ boson could also explain other observations that are not consistent with the Standard Model, the fundamental theory of particle physics.
Important clue: Detection of muon pairs
But how can the Z’ boson be detected in the Belle II detector? Not directly – that much is sure. Theoretical models and simulations predict that the Z’ boson could reveal itself through interactions with muons, the heavier relatives of electrons. If scientists discover an unusually high number of muon pairs of opposite charge after the electron/positron collisions as well as unexpected deviations in energy and momentum conservation, this would be an important indication of the Z? boson. However, the new Belle II data has not yet provided any indication of the Z? boson. But with the new data, the scientists can limit the mass and coupling strengths of the Z? boson with previously unattainable accuracy.
These initial results come from the analysis of a small amount of data collected during the start-up phase of SuperKEKB in 2018. Belle II went into full operation on March 25, 2019. Since then, the experiment has been collecting data while continuously improving the collision rate of electrons and positrons. Once the experiment is perfectly tuned, it will provide considerably more data than in the recently published analyses. The physicists thus hope to gain new insights into the nature of dark matter and other unanswered questions.
JOHANNES GUTENBERG UNIVERSITAET MAINZ
Header Image Credit :





