A team of researchers from Brown University and Brandeis University has discovered the lost ruins of a Maya capital in the backyard of a Mexican cattle rancher.
Associate professor of anthropology, Charles Golden and bioarchaeologist Andrew Scherer believe that the site (now named Lacanja Tzeltal) was the capital of the Sak Tz’i’ kingdom, located in what is today the state of Chiapas in south-eastern Mexico.
Sak Tz’i’ was a minor kingdom of the Maya, the ruins are certainly more modest when compared to the larger sites of Palenque and Chichén Itzá.
First settled around 750 BC, the city remained in continuous occupation for 1000 years and comprises of a royal palace, ball court and the ruins of several pyramids, the largest of which towers 45 feet high.
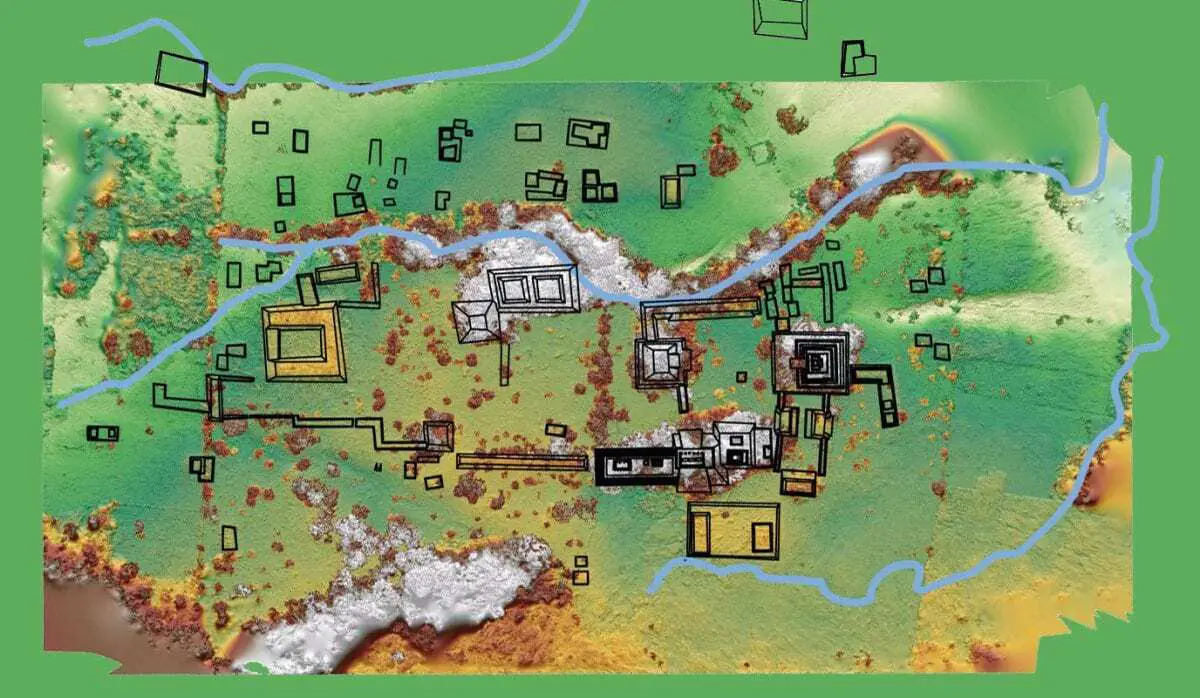
The team also discovered various domestic structures used by the city’s elite and religious sites used for rituals. In the centre of the city was the “Plaza Muk’ul Ton,” or Monuments Plaza, a 1.5-acre courtyard where the people gathered for ceremonies.
So far, dozens of sculptures have been found among the ruins, though many have been damaged by looters or degraded over the millennia by rain, forest fires and lush tropical vegetation.
With the permission of the Mexican government and the local community, Golden, Scherer and the rest of their team plan to return to Sak Tz’i’ in June 2020. The team will continue to survey the city using LIDAR (light detection and ranging) and scan beneath the dense jungle canopy. Read the full site report
Header Image – A map of the excavation site. The horseshoe-shaped structure to the left is the palace area. On the far right, center, is the Monuments Plaza. Credit: Charles Golden