Many dinosaur species are known from scant remains, with some estimates suggesting 75% are known from five or fewer individuals.
Auroraceratops rugosus was typical in this regard when it was named in 2005 based upon a single skull from the Gobi Desert in northwestern China. But that is no longer the case.
In the intervening years, scientists have recovered fossils from more than 80 individual Auroraceratops, bringing this small-bodied plant-eater into the ranks of the most completely known dinosaurs. It is now one of the few very early horned dinosaurs known from complete skeletons. In a collection of articles appearing as Memoir 18 in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology this week, researchers from the University of Pennsylvania, Indiana University of Pennsylvania, the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Gansu Agricultural University, and other institutions describe the anatomy, age, preservation, and evolution of this large collection of Auroraceratops.
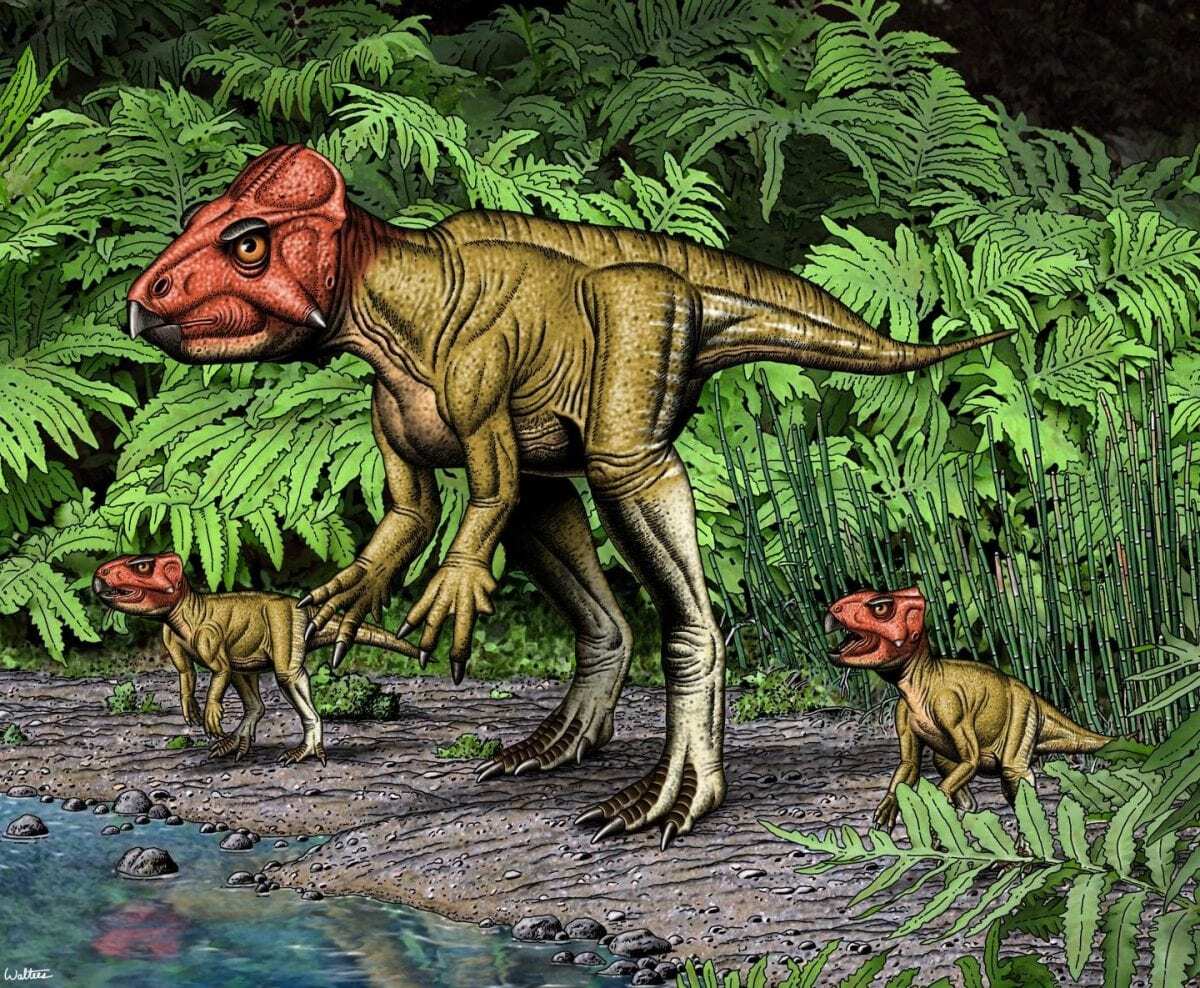
Their analysis places Auroraceratops, which lived roughly 115 million years ago, as an early member of the group Ceratopsia, or horned dinosaurs, the same group to which Triceratops belongs. In contrast to Triceratops, Auroraceratops is small, approximately 49 inches (1.25 meters) in length and 17 inches (44 cm) tall, weighing on average 34 pounds (15.5 kilograms). While Auroraceratops has a short frill and beak that characterize it as a horned dinosaur, it lacks the “true” horns and extensive cranial ornamentation of Triceratops.
“When I first saw this animal back in 2004, I knew instantly it was a new kind that had never been seen before and was very excited about it,” says paleontologist Peter Dodson, senior author on the work and a professor with appointments in Penn’s School of Veterinary Medicine and School of Arts and Sciences. “This monograph on Auroraceratops is long-awaited.”
In 2005, Dodson and his former students Hai-Lu You and Matthew Lamanna named Auroraceratops (in Latin, “dawn’s horned face”) in honor of Dodson’s wife, Dawn Dodson. You, along with fellow Chinese scientist Da-Qing Li–both authors on the current work–and collaborators followed up on the discovery, identifying more than 80 additional examples of the species, from near-hatchlings to adults.
Eric Morschhauser, lead author who is now on the faculty at Indiana University of Pennsylvania, completed his Ph.D. under Dodson at Penn, focused on characterizing Auroraceratops using this robust dataset.
Auroraceratops represents the only horned dinosaur in the group Neoceratopsia (the lineage leading to and including the large bodied ceratopsians such as Triceratops) from the Early Cretaceous with a complete skeleton. This exclusiveness is significant, the researchers say, because horned dinosaurs transitioned from being bipedal, like their ancestors, to being the large rhinoceros-like quadrupedal animals most people think of as horned dinosaurs during the later parts of the Cretaceous.
“Before this study,” says Morschhauser, “we had to rely on Psittacosaurus, a more distantly related and unusual ceratopsian, for our picture of what the last bipedal ceratopsian looked like.”
Auroraceratops preserves multiple features of the skeleton, like a curved femur and long, thin claws, that are unambiguously associated with walking bipedally in some dinosaurs.
“It can now provide us with a better picture of the starting point for the changes between bipedal and quadrupedal ceratopsians,” adds Morschhauser.
Peter Dodson is a professor of anatomy in the University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary Medicine’s Department of Biomedical Sciences and a professor of paleontology in the School of Arts and Sciences’ Department of Earth and Environmental Science.
Header Image – This is an artist’s rendering of Auroraceratops shows its bipedal posture as well as the beak and frill that characterize it as a member of the horned dinosaurs. Paleontologists from Penn led a team in characterizing this species, discovered in China. Credit : Robert Walters