To produce the deepest image of the Universe from space a group of researchers from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC) led by Alejandro S.
Borlaff used original images from the Hubble Space Telescope (HST taken over a region in the sky called the Hubble Ultra-Deep Field (HUDF).
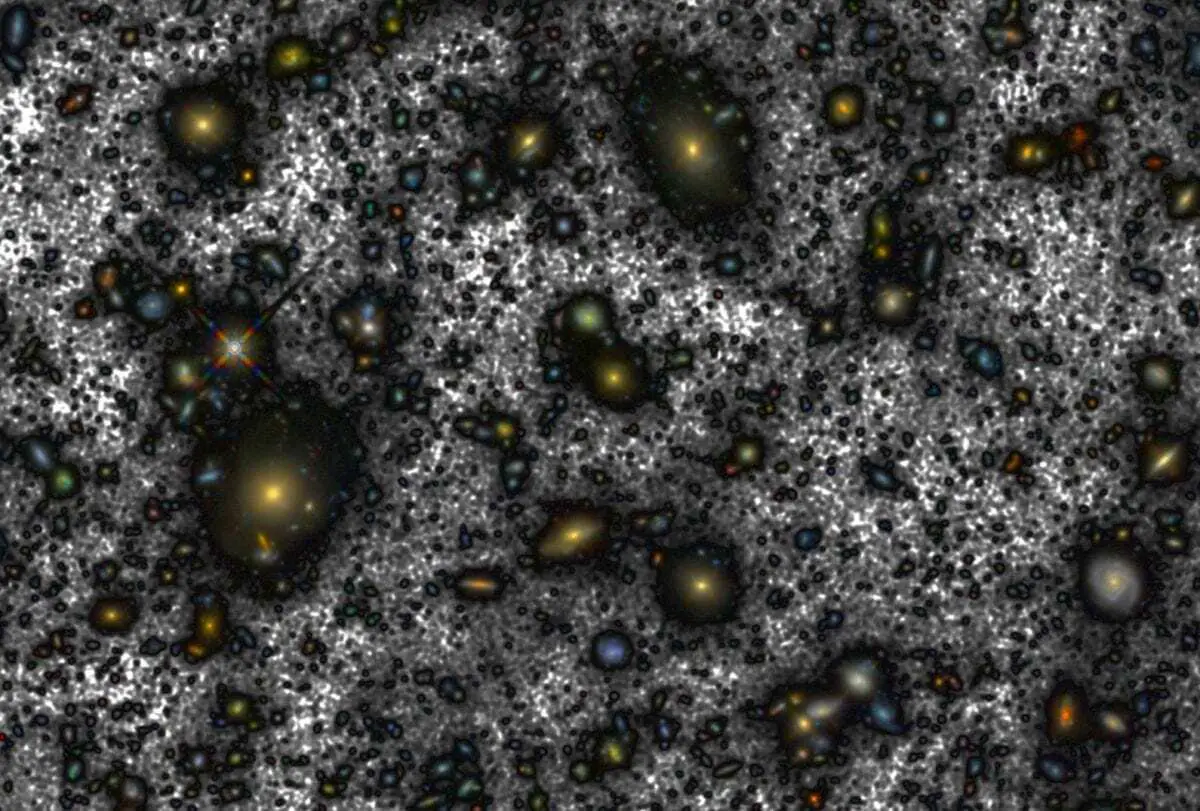
After improving the process of combining several images the group was able to recover a large quantity of light from the outer zones of the largest galaxies in the HUDF. Recovering this light, emitted by the stars in these outer zones, was equivalent to recovering the light from a complete galaxy (“smeared out” over the whole field) and for some galaxies this missing light shows that they have diameters almost twice as big as previously measured.
The HUDF is the result of combining hundreds of images taken with the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3) of the HST during over 230 hours of observation which, in 2012, yielded the deepest image of the Universe taken until then. But the method of combining the individual images was not ideally suited to detect faint extended objects. To do this, Borlaff explains “What we have done is to go back to the archive of the original images, directly as observed by the HST, and improve the process of combination, aiming at the best image quality not only for the more distant smaller galaxies but also for the extended regions of the largest galaxies.
The WFC3 with which the data were taken was installed by astronauts in May 2009, when the Hubble had already been in space for 19 years. This was a major challenge for the researchers because the complete instrument (telescope+ camera) could not be tested on the ground, which made calibration more difficult. To overcome the problems they analysed several thousand images of different regions on the sky, with the aim of improving the calibration of the telescope on orbit.
The image of the universe which is now the deepest “has been possible thanks to a striking improvement in the techniques of image processing which has been achieved in recent years, a field in which the group working in the IAC is at the forefront”, says Borlaff.
INSTITUTO DE ASTROFÍSICA DE CANARIAS (IAC)
Header Image – The new version of Hubble’s deep image. In dark grey you can see the new light that has been found around the galaxies in this field. That light corresponds to the brightness of more than one hundred billion suns. Credit : A. S. Borlaff et al.