A new study published in the Journal of Archaeological Science: Reports suggests beer brewing practices existed in the Eastern Mediterranean over five millennia before the earliest known evidence, discovered in northern China.
In an archaeological collaboration project between Stanford University in the United States, and University of Haifa, Israel, archaeologists analyzed three stone mortars from a 13,000-year old Natufian burial cave site in Israel. Their analysis confirmed that these mortars were used for brewing of wheat/barley, as well as for food storage.
“Alcohol making and food storage were among the major technological innovations that eventually led to the development of civilizations in the world, and archaeological science is a powerful means to help reveal their origins and decode their contents,” said Li Liu, PhD, Department of East Asian Languages and Cultures, Stanford University, USA. “We are excited to have the opportunity to present our findings, which shed new light on a deeper history of human society.”
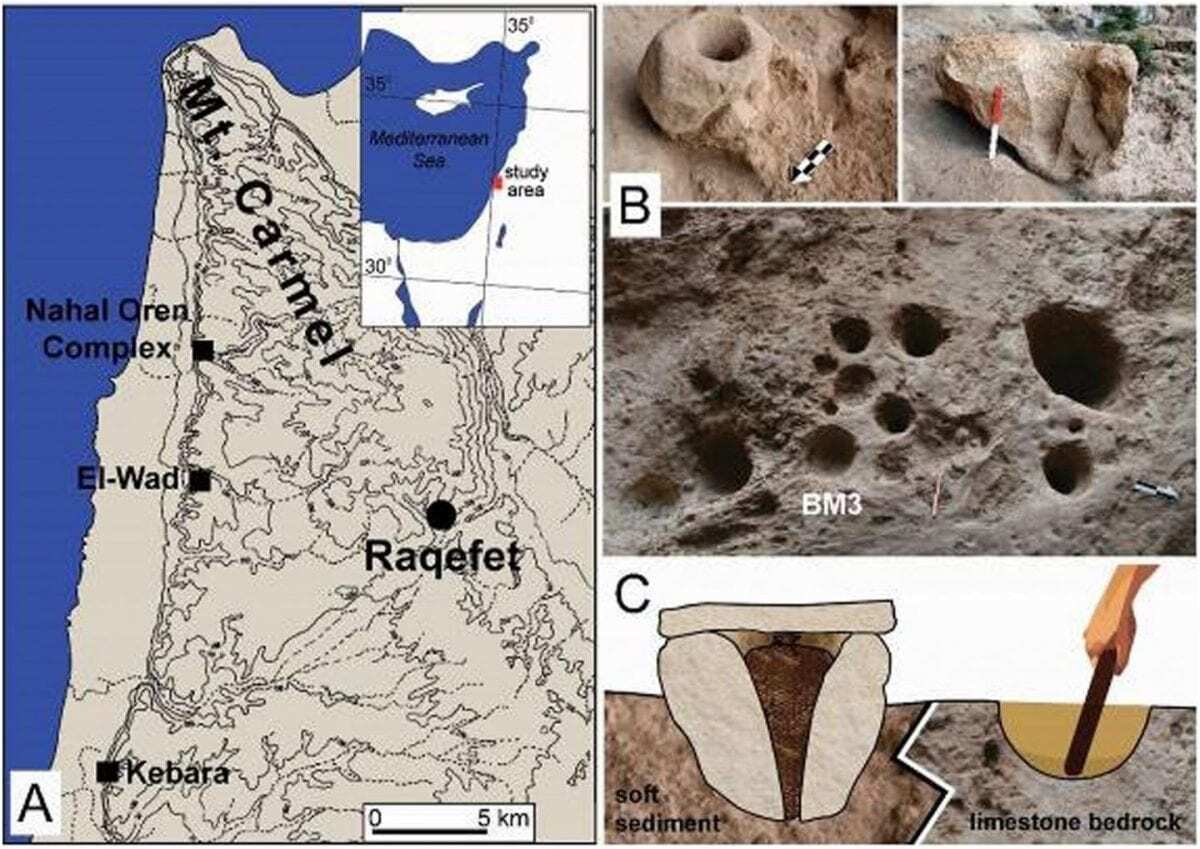
The earliest archaeological evidence for cereal-based beer brewing even before the advent of agriculture comes from the Natufians, semi-sedentary, foraging people, living in the Eastern Mediterranean between the Paleolithic and the Neolithic periods, following the last Ice Age. The Natufians at Raqefet Cave collected locally available plants, stored malted seeds, and made beer as a part of their rituals.
“The Natufian remains in Raqefet Cave never stop surprising us,” said Prof. Dani Nadel, Zinman Institute of Archaeology, University of Haifa, Israel, who was also an excavator of the site. “We exposed a Natufian burial area with about 30 individuals; a wealth of small finds such as flint tools, animal bones and ground stone implements, and about 100 stone mortars and cupmarks. Some of the skeletons are well-preserved and provided direct dates and even human DNA, and we have evidence for flower burials and wakes by the graves.
“And now, with the production of beer, the Raqefet Cave remains provide a very vivid and colorful picture of Natufian lifeways, their technological capabilities and inventions.”
After five seasons of excavations and a wide range of studies, the current study employed experimental archaeology, contextual examination, use-wear and residue analyses. The results indicate that the Natufians exploited at least seven plant types associated with the mortars, including wheat or barley, oat, legumes and bast fibers (including flax). They packed plant-foods in fiber-made containers and stored them in boulder mortars. They used bedrock mortars for pounding and cooking plant-foods, and for brewing wheat/barley-based beer, likely served in ritual feasts 13,000 years ago.
The use-wear patterns and microbotanical assemblage suggest that two of the three examined boulder mortars were used as storage containers for plant foods – including wheat/barley malts. Likely, they were covered with lids, probably made of stone slabs and other materials. The foods are likely to have been placed in baskets made of bast fibers for easy handing. The deep narrow shafts may have provided cool conditions suitable for storing food, especially for keeping cereal malts.
Combining use-wear and residue data, the third mortar studied was interpreted as a multi-functional vessel for food preparation, which included pounding plant foods and brewing wheat/barley-based beer, probably with legumes and other plants as additive ingredients.
The evidence of beer brewing at Raqefet Cave 13,000 years ago provides yet another example of the complex Natufian social and ritual realms. Beer brewing may have been, at least in part, an underlying motivation to cultivate cereals in the southern Levant, supporting the beer hypothesis proposed by archaeologists more than 60 years ago.
Header Image Credit : Bluemoose





