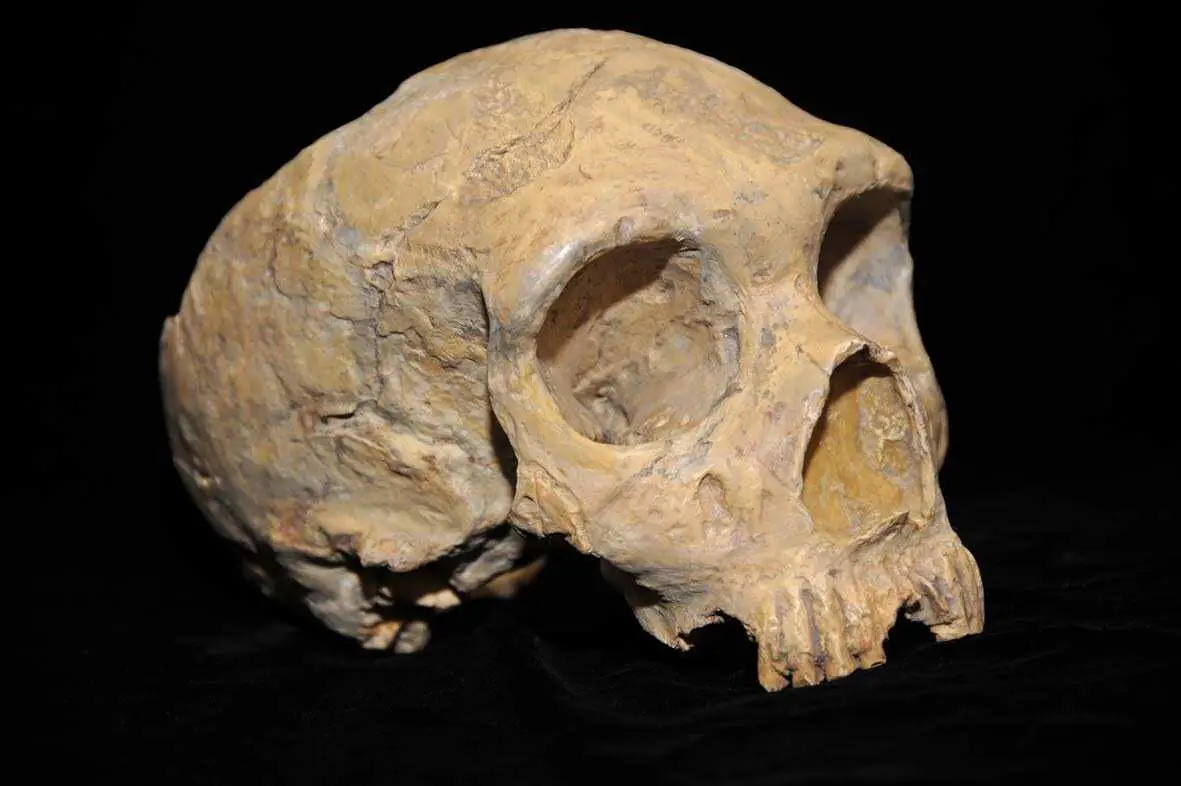
The study of neanderthals’ tartar reveals the widespread consumption of plants as a subsistence strategy.
The Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) inhabitedEurope and parts of Western Asiabetween 230,000 and 28,000 years ago, coinciding during the final millennia with Homo Sapiens, and died out for reasons that are still being disputed; what actually became of the Neanderthals has fascinated and continues to fascinate researchers across the world.
The most popular idea is that the disappearance of the Neanderthals was caused by the greater competition of the ancestors of modern humans, Homo Sapiens, who appeared more or less at the same time as the Neanderthals disappeared from Europe, and one of the explanations as to how that happened could be their diet. The Neanderthals are thought to have had more limited diets, while our ancestors had more flexible, adaptive diets that included seafood and a variety of plants.
Yet even though archaeological science has advanced considerably over the last few decades and has come up with new theories about the diets of the Neanderthals, today we still only have a patchy image of their dietary ecology given that we lack full, environmentally representative information about how they used plants and other foods.
This new piece of research into the fragments of dental calculus or tartar shows that the use of plants was a widespread, deeply-rooted subsistence strategy of the Neanderthals.
Yet when modelling the various diets of more current gatherers from the Tropics right up to the Arctic, it has not been possible to find traces of dietary variation in terms of time and space in the consumption of plant food. This could mean that the consumption of plants by the Neanderthals was widespread, but limited to a specific type of plant or vegetable, unlike the way in which modern humans ate.
According to Domingo C. Salazar, “rather than being a sign of primitiveness, this way of eating reflects a strategy that was simply followed over thousands of years because of its effectiveness”.
University of the Basque Country
Header Image Credit : CC License – AquilaGib