A tiny Egyptian mummy long believed to be that of a hawk is actually a rare example of a near-to-term, severely malformed fetus, says an examination led by mummy expert Andrew Nelson of Western University in London, Canada.
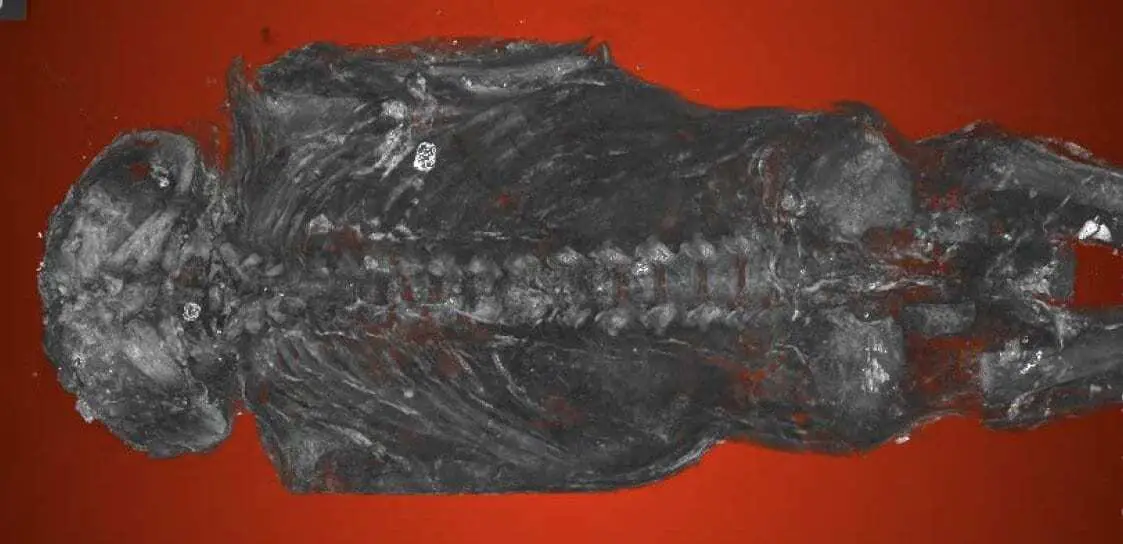
Detailed micro-CT scans have virtually unwrapped the mummy to reveal what would have been a family tragedy even two millennia ago: a male, stillborn at 23 to 28 weeks of gestation, and with a rare condition called anencephaly in which the brain and skull fail to develop properly
ts misidentification in the Maidstone Museum in the UK, as ‘EA 493 – Mummified Hawk Ptolemaic Period’, came to light in 2016 when the museum decided to CT-scan its resident female mummy and, incidentally, to scan ‘EA 493’ and other animal mummies at the same time. That’s when the smaller mummy surprised experts, who identified it as a human fetus.
But the CT scans lacked detail and Nelson worked with the Museum and Nikon Metrology (UK) to conduct a micro-CT scan: an extremely high-resolution scan that didn’t entail damaging the mummy in any way.
Nelson then assembled an interdisciplinary team to examine and interpret the images in what has become the highest-resolution scan ever conducted of a fetal mummy.
The images show well-formed toes and fingers but a skull with severe malformations, says Nelson, a bioarchaeologist and professor of anthropology at Western. “The whole top part of his skull isn’t formed. The arches of the vertebrae of his spine haven’t closed. His earbones are at the back of his head.”
There are no bones to shape the broad roof and sides of the skull, where the brain would ordinarily grow. “In this individual, this part of the vault never formed and there probably was no real brain,” Nelson says.

That makes it one of just two anencephalic mummies known to exist (the other was described in 1826), and by far the most-studied fetal mummy in history.
Nelson recently presented the team’s findings at the Extraordinary World Congress on Mummy Studies in the Canary Islands.
The research provides important clues to the maternal diet – anencephaly can result from lack of folic acid, found in green vegetables – and raises new questions about whether mummification in this case took place because fetuses were believed to have some power as talismans, Nelson says.
“It would have been a tragic moment for the family to lose their infant and to give birth to a very strange-looking fetus, not a normal-looking fetus at all. So this was a very special individual,” Nelson says.
A team of more than a dozen researchers – specialists in Egyptology, radiology, anatomy, neonatology and urology, from Western University to England to France to Cairo – lent their expertise to the project.
Header Image – Micro-CT scans determined a ‘hawk mummy’ at Maidstone Museum UK is in fact a stillborn male human with severe congenital abnormalities that include a malformed skull and vertebrae. An international team’s unprecedented analysis was led by bioarchaeologist and mummy expert Andrew Nelson of Western University, Canada. Credit : Maidstone Museum UK/Nikon Metrology UK