As Curiosity rover marches across Mars, the red planet’s watery past comes into clearer focus.
In early 2017 scientists announced the discovery of possible desiccation cracks in Gale Crater, which was filled by lakes 3.5 billion years ago. Now, a new study has confirmed that these features are indeed desiccation cracks, and reveals fresh details about Mars’ ancient climate.
“We are now confident that these are mudcracks,” explains lead author Nathaniel Stein, a geologist at the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena. Since desiccation mudcracks form only where wet sediment is exposed to air, their position closer to the center of the ancient lake bed rather than the edge also suggests that lake levels rose and fell dramatically over time.
“The mudcracks show that the lakes in Gale Crater had gone through the same type of cycles that we see on Earth,” says Stein.

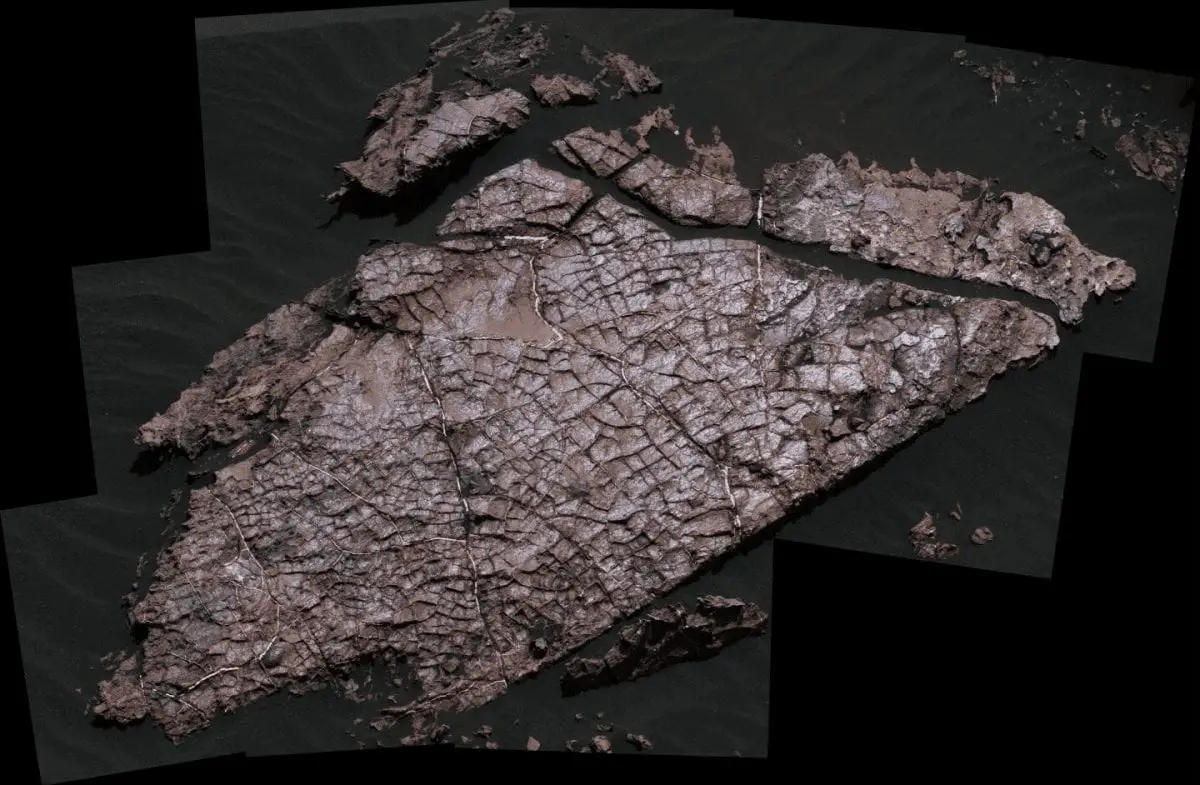
The researchers focused on a coffee table-sized slab of rock nicknamed “Old Soaker.” Old Soaker is crisscrossed with polygons identical in appearance to desiccation features on Earth. The team took a close physical and chemical look at those polygons using Curiosity’s Mastcam, Mars Hand Lens Imager, ChemCam Laser Induced Breakdown Spectrometer (LIBS), and Alpha-Particle X-Ray Spectrometer (APXS).
That close look proved that the polygons — confined to a single layer of rock and with sediment filling the cracks between them — formed from exposure to air, rather than other mechanisms such as thermal or hydraulic fracturing. And although scientists have known almost since the moment Curiosity landed in 2012 that Gale Crater once contained lakes, explains Stein, “the mudcracks are exciting because they add context to our understanding of this ancient lacustrine system.”
“We are capturing a moment in time,” he adds. “This research is just a chapter in a story that Curiosity has been building since the beginning of its mission.”
Header Image: Curiosity Mastcam image of the Old Soaker rock slab taken on Sol 1555. Image courtesy NASA.