A square monument complex comprising of 14 pillars inscribed with Turkic runic inscriptions has been discovered on the steppe at the archaeological site of Dongoin shiree in eastern Mongolia.
The discovery was made during a joint excavation by Osaka University and the Institute of History and Archaeology of the Mongolian Academy of Sciences on a three-year research project.
It was previously believed that inscriptions were only on the steppes in the western region of Ulan Bator, however the discovery has now shed light on relationships and the tribal balances of power in eastern Mongolia in the Middle Ages.
The monument itself is of a square configuration comprising of 14 stone pillars, surrounding a sarcophagus within the centre of a raised mound.
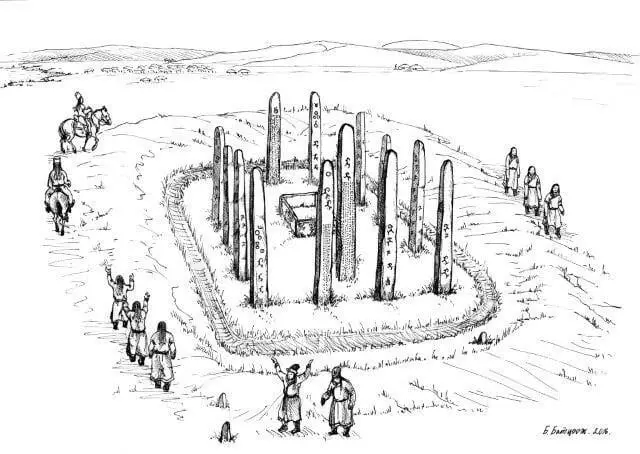
Each inscription contains the tamga of the ancient Turkic tribes. (A tamga is an abstract seal or stamp used by Eurasian nomadic peoples).
Using radiocarbon dating of pieces of calcined coal, sheepskin, and horse bone excavated from the sarcophagus, it was estimated that the burial complex was built in the 8th century, during the late Second Ancient Turkic Qaghanate.
Professor Takashi OSAWA has been deciphering the runic text and discovered that the burial was for a Yabgu, a title of office in the early Turkic states, roughly equivalent to viceroy.
It was also found that the Yabgu became a Tölis-Shad (Royalty of the East), a commander in chief and highest administrative officer, in eastern Mongolia during the reign of Tengri Qaghan (734-741 AD).
These findings show that the site of Dongoin shiree steppe was a tribal centre of the eastern Turkic Qaghanate and reveals the power relationships of rulers in the east as well as the political and military relationships with Mongolian tribes of the region.
Header Image Credit : Osaka University and Institute of History and Archaeology, Mongolian Academy of Science





