Historic England’s Scientific Dating team have been running a project on the dating of the Late Neolithic palisaded enclosures around West Kennet in Wiltshire.
By looking at the original excavation archive and by obtaining new radiocarbon dates from material including fragments of the palisade timbers hidden away in a British Museum store, the enclosures are now dated to the decades around 3300 cal BC, some 800 years earlier than previously suggested.
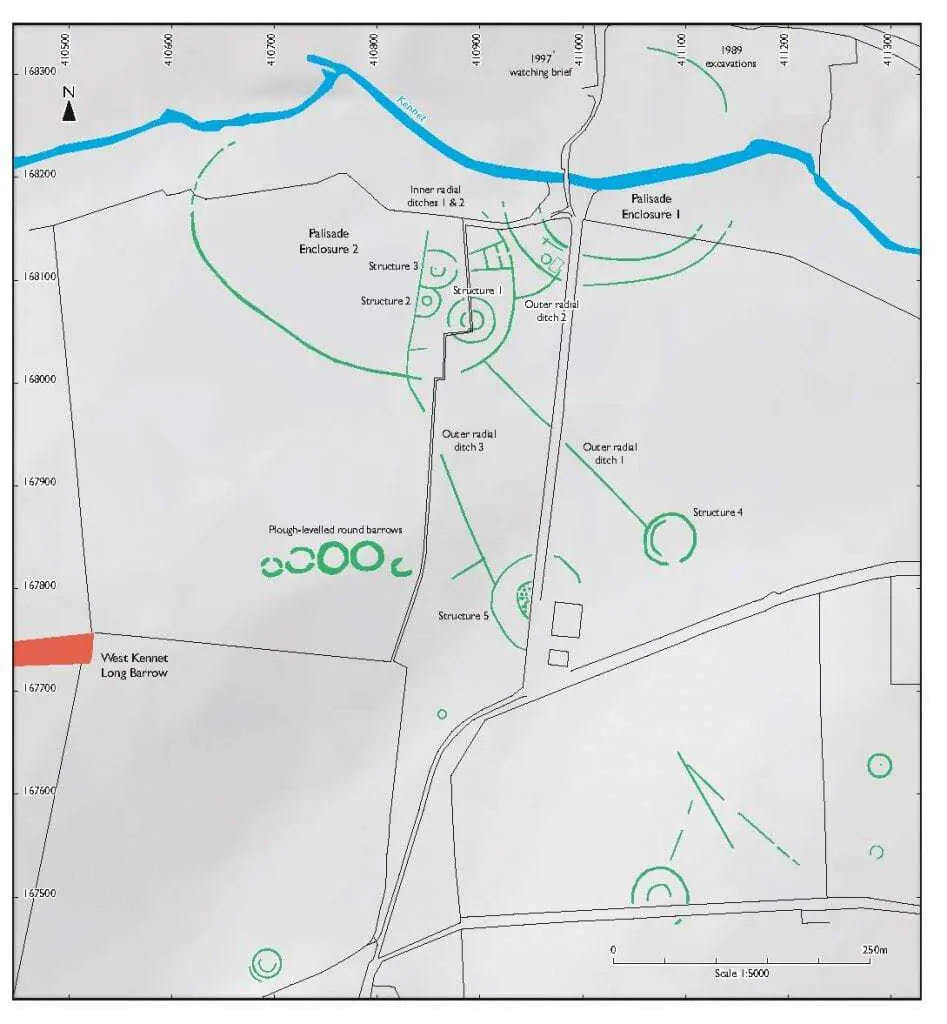
The enclosures might represent a new monument type – the round cursus.
The revised dating for the construction of the West Kennet palisade enclosures places them in an entirely different contemporary context and has demanded a new explanation for the large assemblages of Late Neolithic material recovered from the site.
Alex Bayliss, Head of Scientific Dating, and Peter Marshall, Scientific Dating Radiocarbon Specialist now think the previously-excavated Grooved Ware and associated finds were part of an extensive settlement that may have been the ‘worker’s camp’ for nearby Silbury Hill.
Professor Alex Bayliss, Historic England’s Head of Scientific Dating, said: “The West Kennet enclosures were two massive circles made up of thousands of timbers. This earlier date is an exciting finding as it seems likely they were constructed 800 years earlier than the nearby Avebury stones, rather than being contemporaneous. It puts the palisades in a completely different context.”
These findings are part of a Festschrift for Prof Alasdair Whittle from Cardiff University who was central to archaeological work on the site between 1987 and 1992. The site has been a scheduled monument since 1989.
The project was funded by Historic England




