A 9,000 year-old case of human decapitation has been found in the rock shelter of Lapa do Santo in Brazil, according to a study by André Strauss from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Germany and colleagues.
An archaeological site called Lapa do Santo, located in east-central Brazil, contains evidence of human occupation dating back to ~12,000 years ago. In 2007, researchers found fragments of a buried body, Burial 26, including a cranium, jaw, the first six cervical vertebrae, and two severed hands at the site.
They dated the remains back to ~9,000 years ago using accelerator mass spectrometry. The researchers found amputated hands laid over the face of the skull arranged opposite each other and observed v-shaped cut marks on the jaw and sixth cervical vertebra.
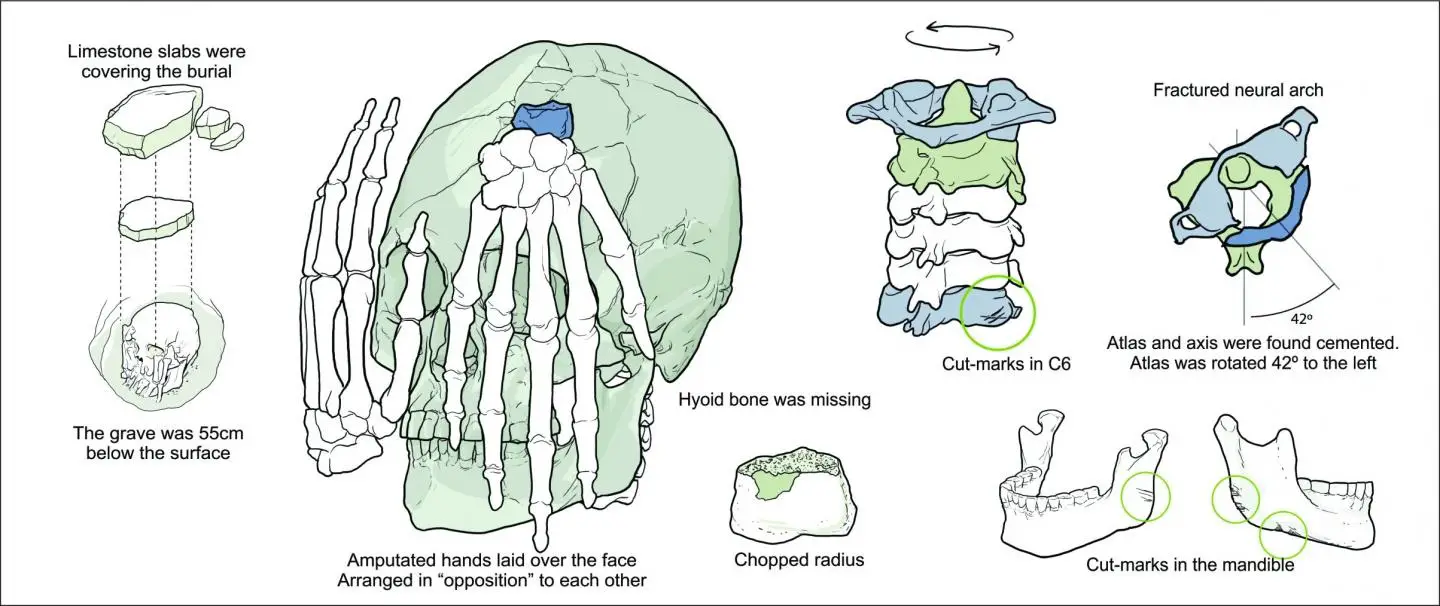
Based on strontium analysis comparing Burial 26’s isotopic signature to other specimens from Lapa do Santo, the researchers suggest Burial 26 was likely a local member of the group. Additionally, the presentation of the remains, lead the authors to think that this was likely a ritualized decapitation instead of trophy-taking.
If this is the case, these remains may demonstrate sophisticated mortuary rituals among hunter-gatherers in the Americas during this time period.
The authors think this may be the oldest case of decapitation found in the New Word, leading to a re-evaluation of the previous interpretations of this practice, particularly with regards to its origins and geographic dispersion.
Find out more : http://dx.






