Archaeologists from the University of Southampton have revealed for the first time the plan of a network of buildings in a once thriving medieval city at the historic site of Old Sarum, near Salisbury.
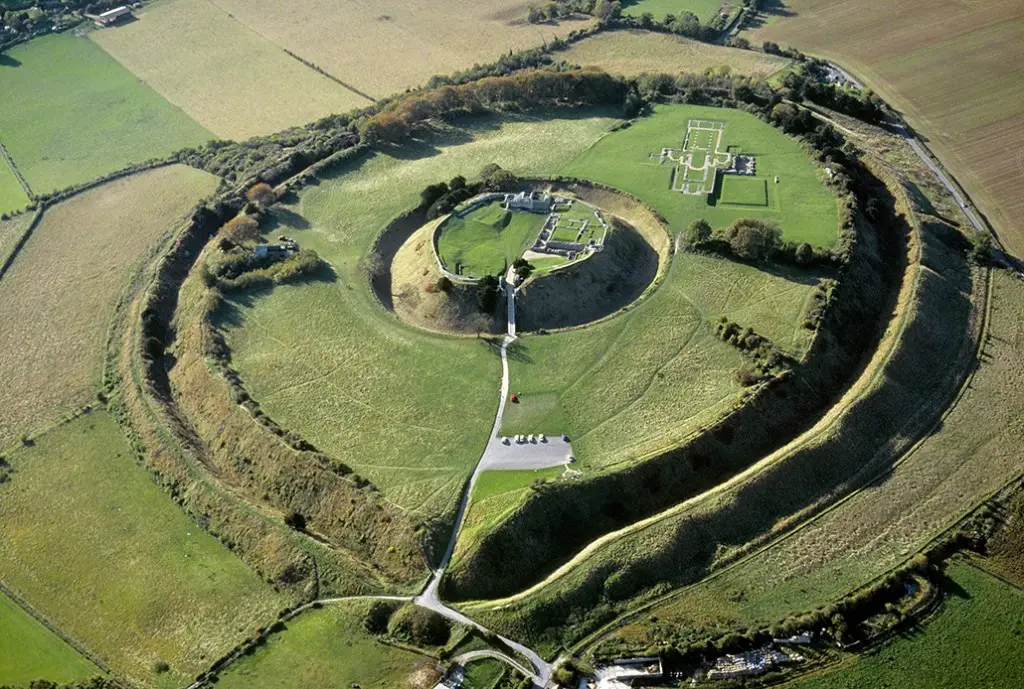

A research team of students and academics carried out a geophysical survey of the ancient monument, scanning ground at the site with state-of-the-art equipment to map the remains of buried structures. They concentrated their survey around the inner and outer baileys of what was once a fortification, with its origins in the Iron Age and the Roman conquest.
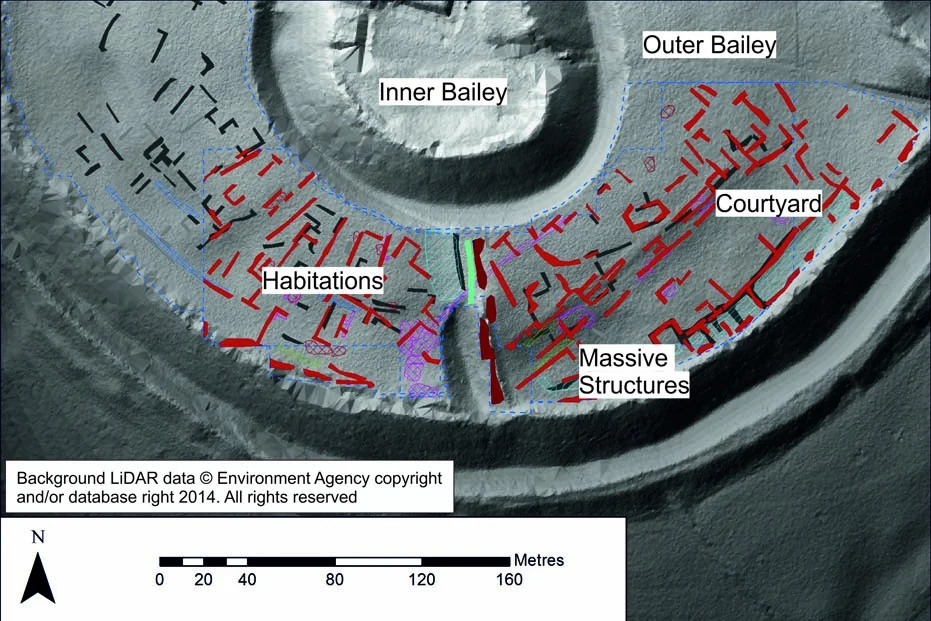
Their investigations reveal the layout of a settlement including structures from the late 11th century, contemporary with the construction of a cathedral and castle. The city was inhabited for over 300 years, but declined in the 13th century with the rise of New Sarum (Salisbury).
The project findings mainly concentrate on the medieval period and highlight:
• A series of massive structures along the southern edge of the outer bailey defensive wall, perhaps suggesting large buildings of a defensive nature.
• An open area of ground behind these large structures, perhaps for mustering resources or people, or as part of a circular route through the city.
• Residential areas in the south east and south west quadrants of the outer bailey alongside the inner bailey ditch.
• Evidence of deposits indicating industrial features, such as kilns or furnaces.
• Features suggesting quarrying at the site after the 1300s and following the city’s decline – indicating a later period of habitation at the site.
Archaeologist Kristian Strutt, Experimental Officer and Director of Archaeological Prospection Services at the University of Southampton, says: “Archaeologists and historians have known for centuries that there was a medieval city at Old Sarum, but until now there has been no proper plan of the site.
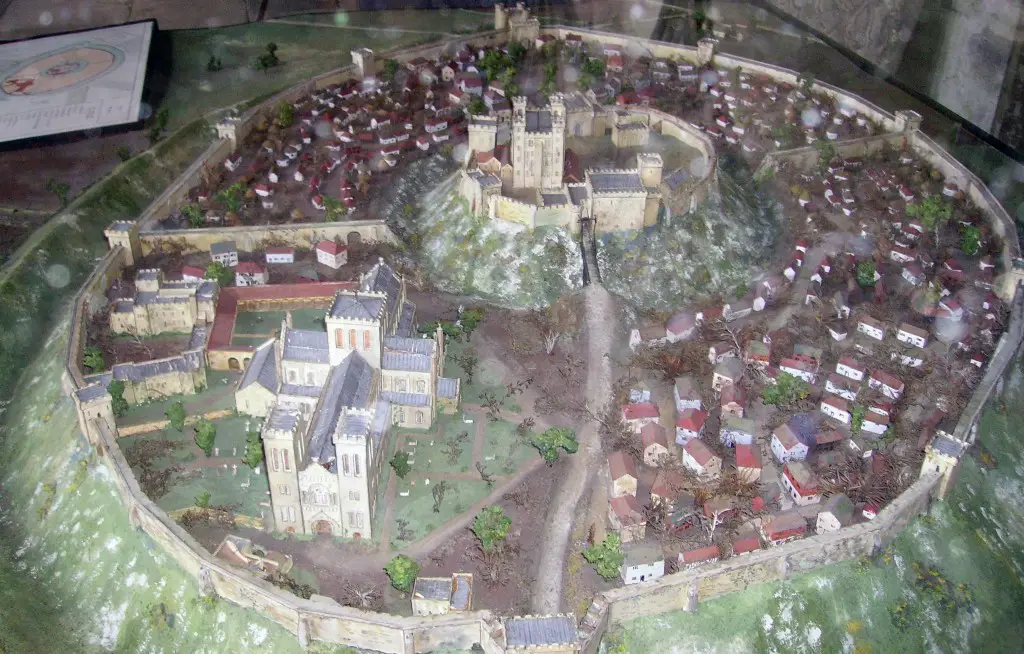

“Our survey shows where individual buildings are located and from this we can piece together a detailed picture of the urban plan within the city walls.”
The research was conducted as part of the Old Sarum and Stratford-Sub-Castle Archaeological Survey Project, directed by Kristian Strutt and fellow Southampton archaeologists Timothy Sly and Dominic Barker. Old Sarum is under the custodianship of English Heritage, who kindly granted permission for the investigation to take place.
Heather Sebire, Property Curator at English Heritage, comments: “Having the team of archaeologists on site over the summer gave our visitors a chance to find out more about how important historic landscapes are surveyed. The use of modern, non-invasive surveying is a great start to further research at Old Sarum.
“From this work we can surmise much about the site’s past and, whilst we can’t conclusively date the findings, it adds a new layer to Old Sarum’s story. We welcome the chance to find out more about our sites, and look forward to exploring ideas for further research in the future.”
The team used a variety of techniques to examine the outer and inner bailey of the site. These included the use of topographic survey methods and geophysical survey techniques – comprising of magnetometry, earth resistance, ground penetrating radar (GPR) and electric resistivity tomography (ERT) survey.
Kristian Strutt concludes: “Our research so far has shown how the entire outer bailey of the monument was heavily built up in the Middle Ages, representing a substantial urban centre. Results have given us compelling evidence as to the nature of some of the structures. It is clear, however, that there is more non-intrusive work that could be carried out to further expand our understanding of the site.”
The team hopes to return to complete the survey of the inner and outer baileys and survey the Romano-British settlement to the south of Old Sarum in Easter 2015. The project fieldwork in 2014 was used as a training season for undergraduate and postgraduate archaeology students at the University, continuing a long tradition of research-led teaching at some of the most impressive archaeological sites in the south of England. Previous fieldwork has been conducted by students at Portchester Castle, Netley Abbey and Bishop’s Waltham Palace in Hampshire, and at Bodiam Castle in East Sussex.






