Dolphins are the most diverse family of living marine mammals and include species such as the bottlenose dolphin and the killer whale.
However, their early evolution and fossil record has been steeped in mystery due to lack of good specimens. A new paper published in latest issue of theJournal of Vertebrate Paleontology re-describes the oldest species of dolphin with a new name: Eodelphis kabatensis. Although the partial skull was previously described in the 1970s the scientific community largely overlooked it. The new re-description has important implications for the evolutionary history of dolphins.
The skull of Eodelphis kabatensis was originally collected from a small tributary of the Oshirarika River in Hakkaido, Japan from an outcrop of the Mashike Formation. Researchers working on the specimen have narrowed its age to the late Miocene (13.0-8.5 million years ago), making it the earliest true dolphin species described. “The early evolution of true dolphins is still covered in mystery. Eodelphis kabatensis informs us about the morphology of early dolphins”, said lead author Mizuki Murakami.
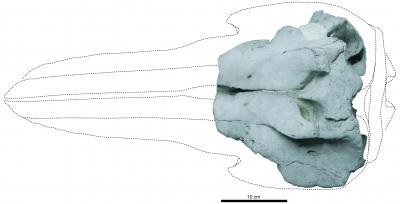
Eodelphis is an important link in the evolutionary history of dolphins. Prior to this study, there was inconsistency between the fossil record of the dolphins and molecular-based studies. The oldest true dolphin fossils found were less than 6 million years old, while molecular studies suggested they originated and started to diversity between 9-12 million years ago. “Eodelphis kabatensis, being discovered from sediments that were deposited 8-13 million years ago, has largely resolved this discrepancy and provides the best glimpse yet of what the skull of the first dolphins may have looked like”, said Jonathan Geisler, a marine mammal paleontologist at the New York Institute of Technology College of Osteopathic Medicine.
In addition to its importance as the earliest true dolphin, this new study also incorporates the most comprehensive analysis of the relationships within the Delphinoidea, the group that encompasses toothed whales.
By including Eodelphis in the analysis, the authors were able to get a much clearer picture of the evolution of the toothed whales. Furthermore, the presence of Eodelphis in the Pacific Ocean during the late Miocene has implications for the geographic history of dolphins. While more specimens need to be discovered, this study suggests that dolphins might have had their origins in the Pacific.
Header Image : WikiPedia
Contributing Source : Society of Vertebrate Paleontology




