Detectorists from the GRYF – Biskupieckie Stowarzyszenie Detektorystyczne have uncovered a two-handed medieval sword during a licensed rally near the village of Wielka Tymawa in Poland’s Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship.
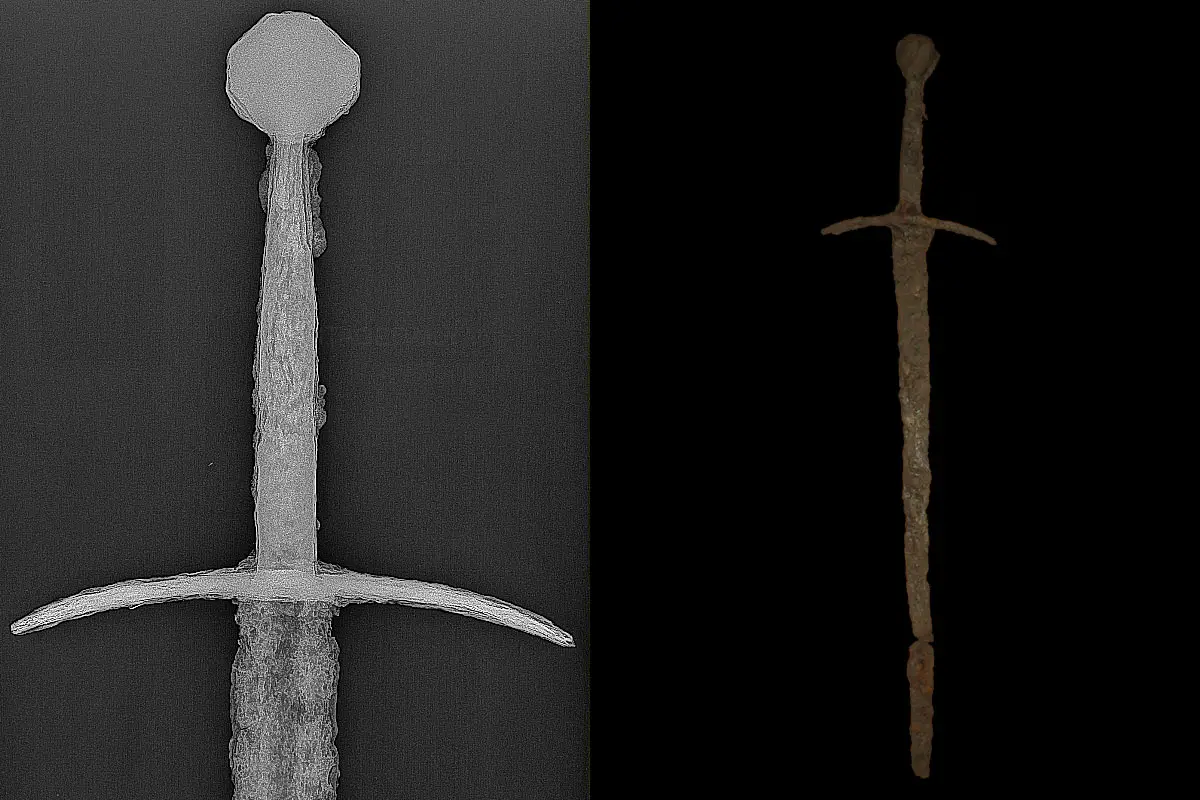
The sword was discovered in a weapons deposit alongside two axe heads dating back to the 14th-15th century AD. Experts from the Ostróda Museum note that the sword is exceptionally well preserved, with its hilt, pommel, and guard fully intact.
Measuring just under one metre in length from the tip of the blade to the pommel, the sword closely resembles Hand-and-a-Half Swords used throughout Western Europe in the Late Middle Ages. The steeply pointed blade, indicates that it was primarily intended for thrusting and piercing armour.
Łukasz Szczepański, an archaeologist from the Ostróda museum, said: “Undoubtedly, this deposit is related to the Osa backwaters. Today, this river is regulated, but in the past it had the wild character of a meandering riverbed. Perhaps there was a bridge crossing there, where these objects were lost by the owners.”
The provincial conservator of monuments has transferred the deposit to the Ostróda Museum, where museum staff have already begun X-raying the discovery. Following conservation works to stabilise the artefacts, they are expected to be featured in a permanent exhibition later this year.
“These discoveries are a valuable addition to our collection, especially since this is the first two-handed sword we’ve acquired. Our museum focuses on preserving medieval history and is housed in a former Teutonic castle,” he noted.
Header Image Credit : GRYF
Sources : GRYF – Biskupieckie Stowarzyszenie Detektorystyczn