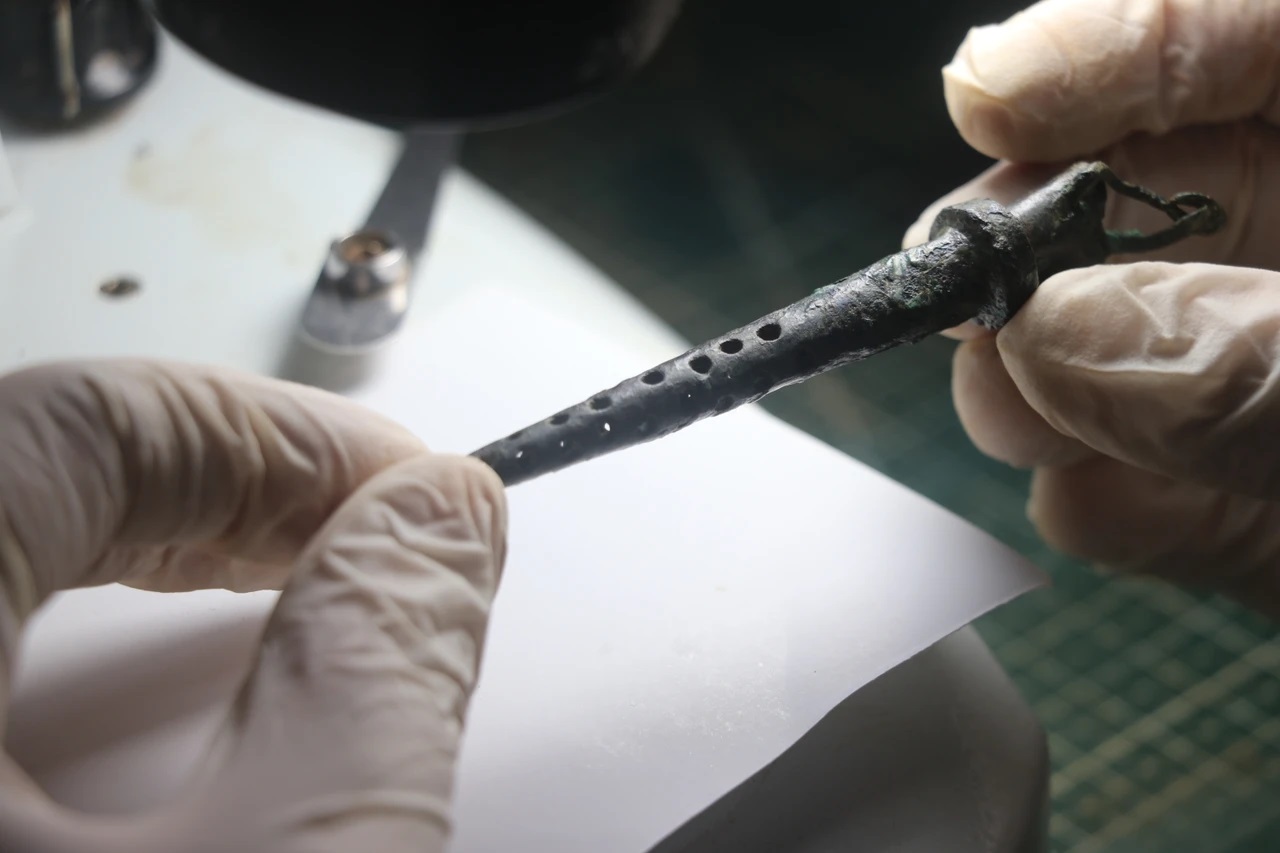
Archaeologists excavating in Hadrianopolis, located in Turkey’s Karabük province, have discovered a 5th century AD bronze object believed to have been used as a beverage filter.
Hadrianopolis is an ancient city named after the Roman emperor Hadrian. The site was inhabited during the Late Chalcolithic, Roman, and Early Byzantine periods, until it was suddenly abandoned and left to ruin.
Ongoing excavations by archaeologists have uncovered numerous public buildings, including bath houses, a theatre, villas, and churches decorated with ornate mosaics featuring images of the Gihon, Pishon, Tigris, and Euphrates rivers, which are referenced in the Bible. Additionally, various animals are depicted in the mosaics, leading to comparisons between Hadrianopolis and the ancient city of Zeugma.
According to a previous statement by Ersin Çelikbaş from Karabük University’s archaeology department: “It is a very important ancient city and a ‘mosaic haven,’ because Hadrianapolis is known mostly for its mosaics. We can say that it is the most important city in the western Black Sea region.”
Archaeologists have recently uncovered a 9.2 cm-long conical bronze object with a carrying ring, offering new insights into ancient drinking practices. Experts studying the object suggest that it was designed to filter drinks, where small holes in the filter allowed liquids to pass through while trapping unwanted solids.
“This bronze filter was used repeatedly in ancient times. It was cleaned and preserved after each use,” Çelikbaş explained – evidenced by the carrying ring that suggests it was a reusable item rather than a disposable one.
“The filter was placed on the end of straws made of reed, allowing drinks to be consumed more easily. Today, we use plastic straws, but the people of Hadrianopolis did this process in a much healthier way, with herbal materials and bronze filters,” added Çelikbaş.
Header Image Credit : AA
Sources : Karabük University