A LiDAR study of Guiengola, a 15th-century Zapotec site in southern Oaxaca, Mexico, has revealed a vast fortified city.
Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR), is a method of remote sensing using light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure ranges (variable distances) to the Earth. The differences in the laser return times and wavelengths can be used to compile a 3-D digital map of the landscape.
According to Colonial documents, Guiengola (meaning “large stone”) was a military fortress for the Zapotec, an indigenous pre-Columbian civilisation that emerged in the Y-shaped Central Valleys of Oaxaca around 700 BC.
In the 15th century AD, the Aztecs invaded the valleys to expand their control and impose tribute, with the last decisive battle against the Zapotecs taking place at Guiengola between 1497 and 1502.
After Francisco de Orozco’s arrival to the valleys in 1521, the Zapotecs submitted to Hernán Cortés, resulting in the destruction of their cities and the forced labour and cultural assimilation of their people.

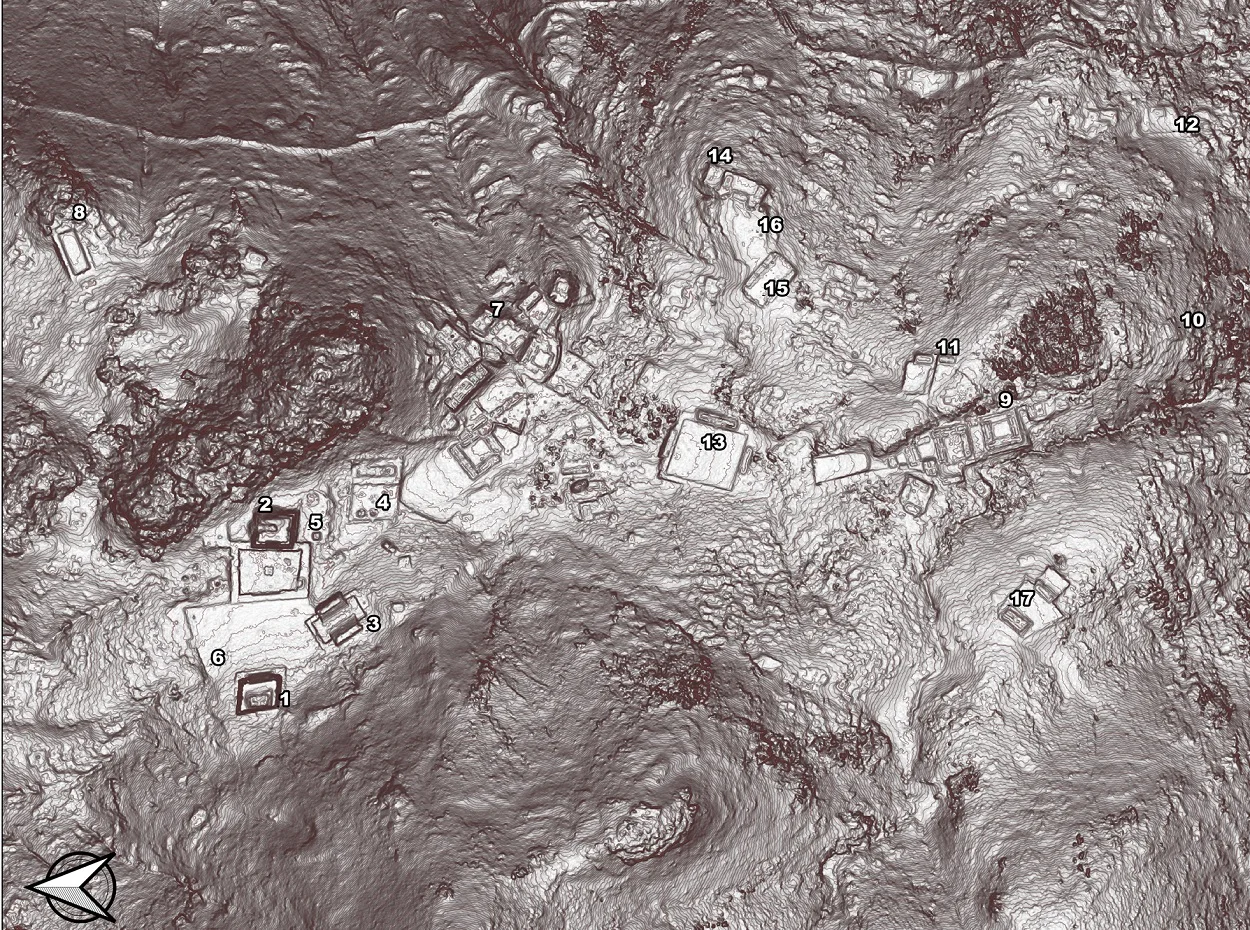
In a recent LiDAR study by McGill University, archaeologists have revealed that Guiengola was actually a vast fortified city covering over 360 hectares and containing over 1,100 buildings. The study also found four kilometres of defensive walls, an extensive road network, and an urban layout with temples, ballcourts, and distinct neighbourhoods for elites and commoners.
According to Pedro Guillermo Ramón Celis, a Banting postdoctoral researcher in McGill’s Department of Anthropology and the author of a recent article in Ancient Mesoamerica: “Although you could reach the site using a footpath, it was covered by a canopy of trees. Until very recently, there would have been no way for anyone to discover the full extent of the site without spending years on the ground walking and searching. We were able to do it within two hours by using remote sensing equipment and scanning from a plane.”
“Because the city is only between 500 and 600 years old, it is amazingly well preserved, so you can walk there in the jungle, and you find that houses are still standing… you can see the doors… the hallways… the fences that split it from other houses. So, it is easy to identify a residential lot. It’s like a city frozen in time, before any of the deep cultural transformations brought by the Spanish arrival had taken place,” added Celis.
Header Image Credit : Pedro Guillermo Ramón Celi
Sources : McGill University – https://doi.org/10.1017/S0956536124000166