Archaeologists have unearthed a statuette of Isis during excavations at Pagus Belsinonensis, an ancient Roman settlement in modern-day Mallén, Spain.
Pagus Belsinonensis was founded on the El Convento hill, near the Huecha River. In Roman times, it served as a key stopover for travelers along the route connecting Tarraco (Tarragona) to Asturica Augusta (Astorga).
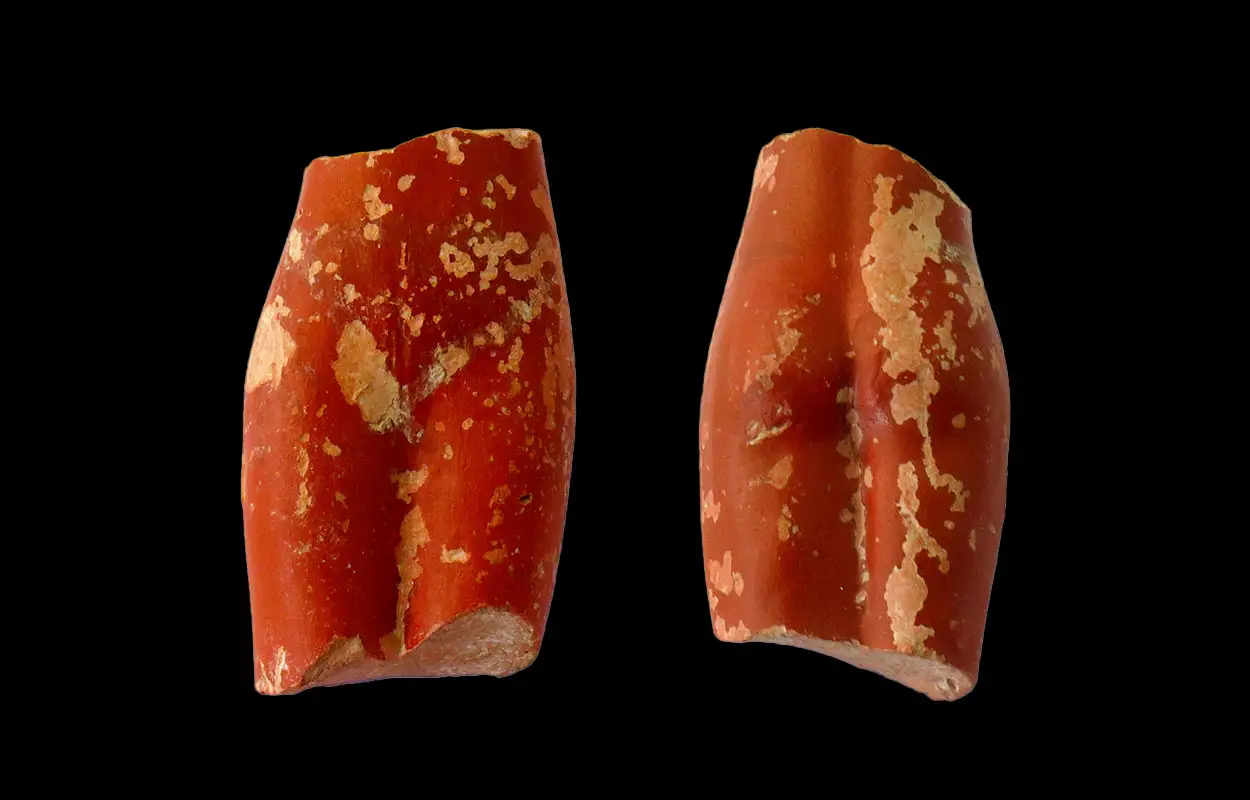
Excavations by the Belsinon Project have unearthed a statuette of the ancient Egyptian goddess Isis. Revered as a goddess of protection, magic, and motherhood, Isis was also associated with healing, fertility, and the divine role of the pharaoh’s mother.
By the 1st century BC, the cult of Isis had become part of the Roman pantheon and was honored through distinctive festivals such as the Navigium Isidis. It spread across the Roman world and remained widely practiced until Christianity emerged as the dominant religion in the empire.
The discovery of the statuette at Pagus Belsinonensis suggests that the cult of Isis reached the region by the late 1st or early 2nd century AD.
According to a study published in the latest issue of SAGVNTVM, the statuette is crafted from terra sigillata hispánica, a fine red-slipped Roman pottery that originates from the workshops of Tritium Magallum (modern-day Tricio, La Rioja).
These types of statuettes were placed in a prominent place of worship in Roman households known as the lararium. A lararium was a shrine or sacred altar where offerings were made for protection to the household god or goddess.
“In order to determine which divinity the Mallén statuette represented, it was essential to examine it under a microscope,” says archaeologist Ángel Santos.
“The piece has white paint that represents the divinity’s attire. Thanks to the detailed examination of the piece, it was possible to determine that the characteristic Isis knot with three hanging strands at the waist of the statuette was preserved,” added Santos.
According to the study authers, the statuette provides new insights into Eastern religious influences and the presence of Egyptian cults in domestic spaces during Roman-era Hispania.
Header Image Credit : Belsinon Project
Sources : Belsinon Project