Researchers from the University of Granada (UGR) have found that Argaric societies of the Bronze Age (2200–1550 BC) exploited copper mining resources in the Granada province as early as 4,000 years ago.
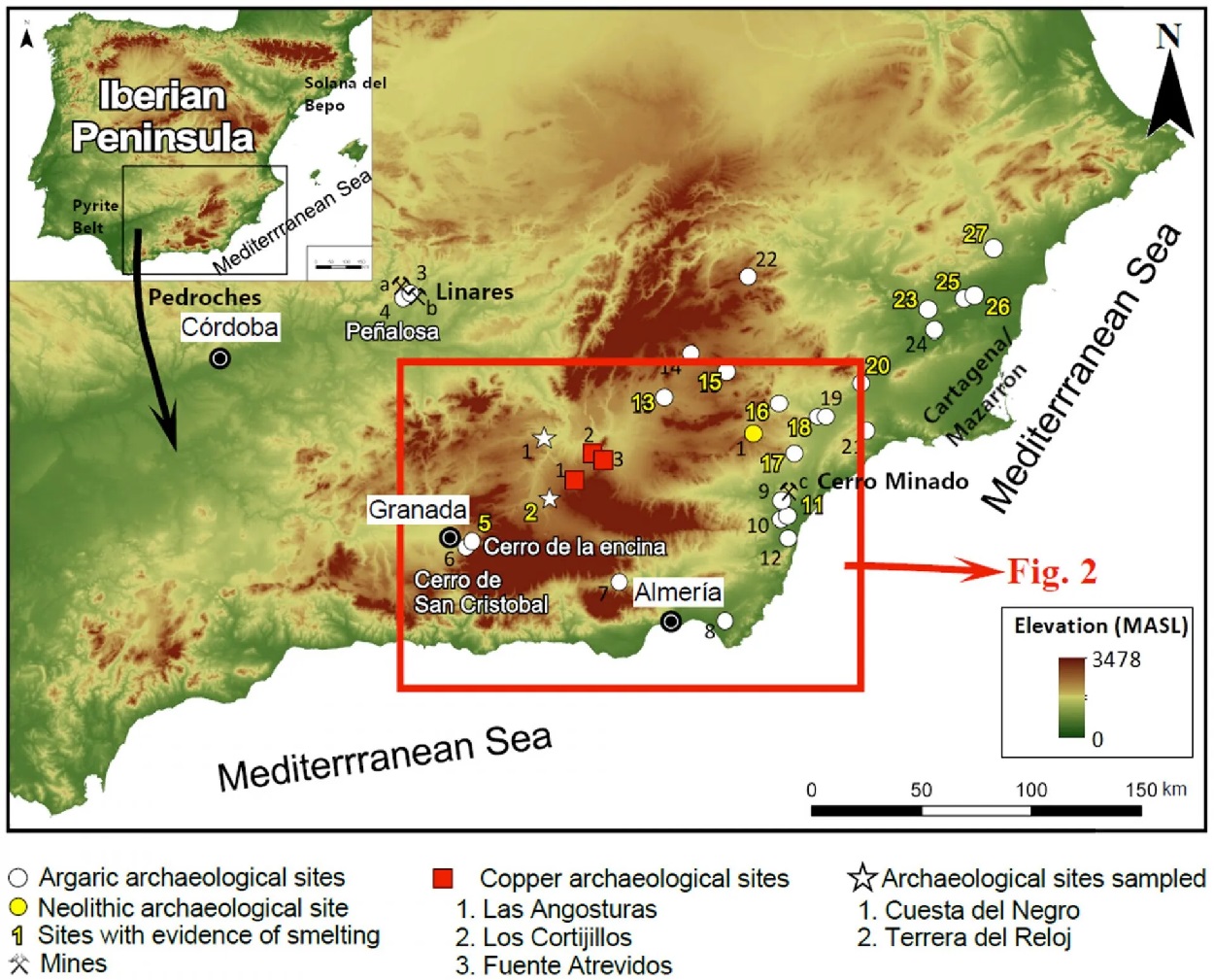
The results of the study, published in the journal Geoarchaeology, analysed archaeological samples from the Guadix-Baza basin in the Betic Mountain Range in southern Spain.
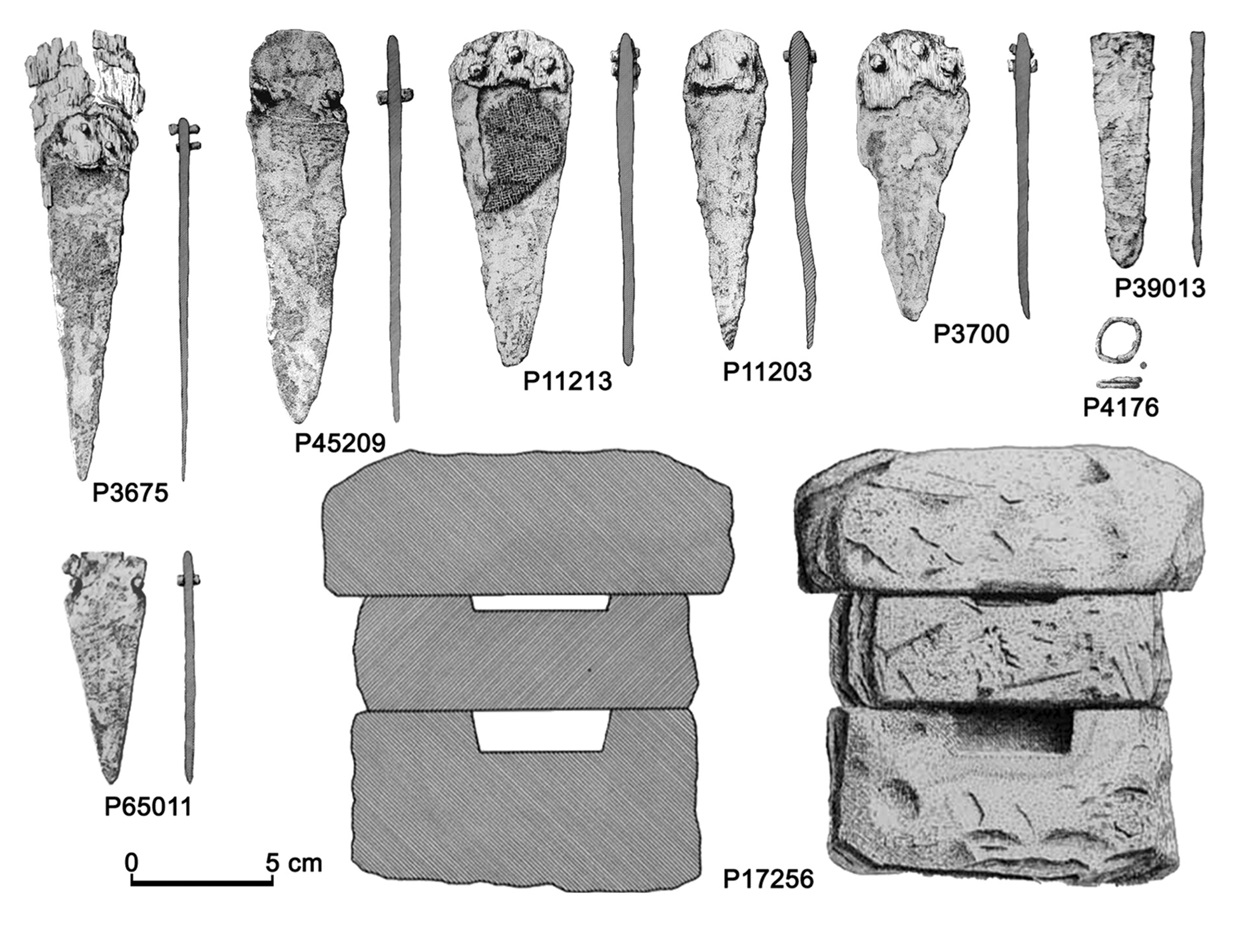
The samples included objects such as daggers, arrowheads, punches, chisels, and axes, as well as items made from copper, arsenical copper, and bronze.
Through the analysis of lead isotopes and trace elements, the study revealed that Argaric societies sourced copper from multiple locations, including sites beyond their cultural sphere. According to the study authors, this demonstrates a diversified supply network rather than reliance on a single source.
Mercedes Murillo Barroso, professor of the Department of Prehistory and Archaeology at the University of Granada and principal investigator of the study, said: “these findings have great implications for our conception of society.”
The findings demonstrate that copper extraction in Granada was as significant for Argaric societies as the previously acknowledged Linares-La Carolina area, historically regarded as the primary metal supply source of the Bronze Age.
According to Aaron Lackinger, a co-author and researcher in the Department of Prehistory and Archaeology at UGR, the intensity of mining in Granada even surpassed that of the Almería-Cartagena region.
“Advances in laboratory techniques and interdisciplinary work in which archaeologists and geologists collaborate are allowing for a better understanding of resource exploitation and exchange networks in Prehistory,” added Barroso.
Header Image Credit : UGR
Sources : University of Granada