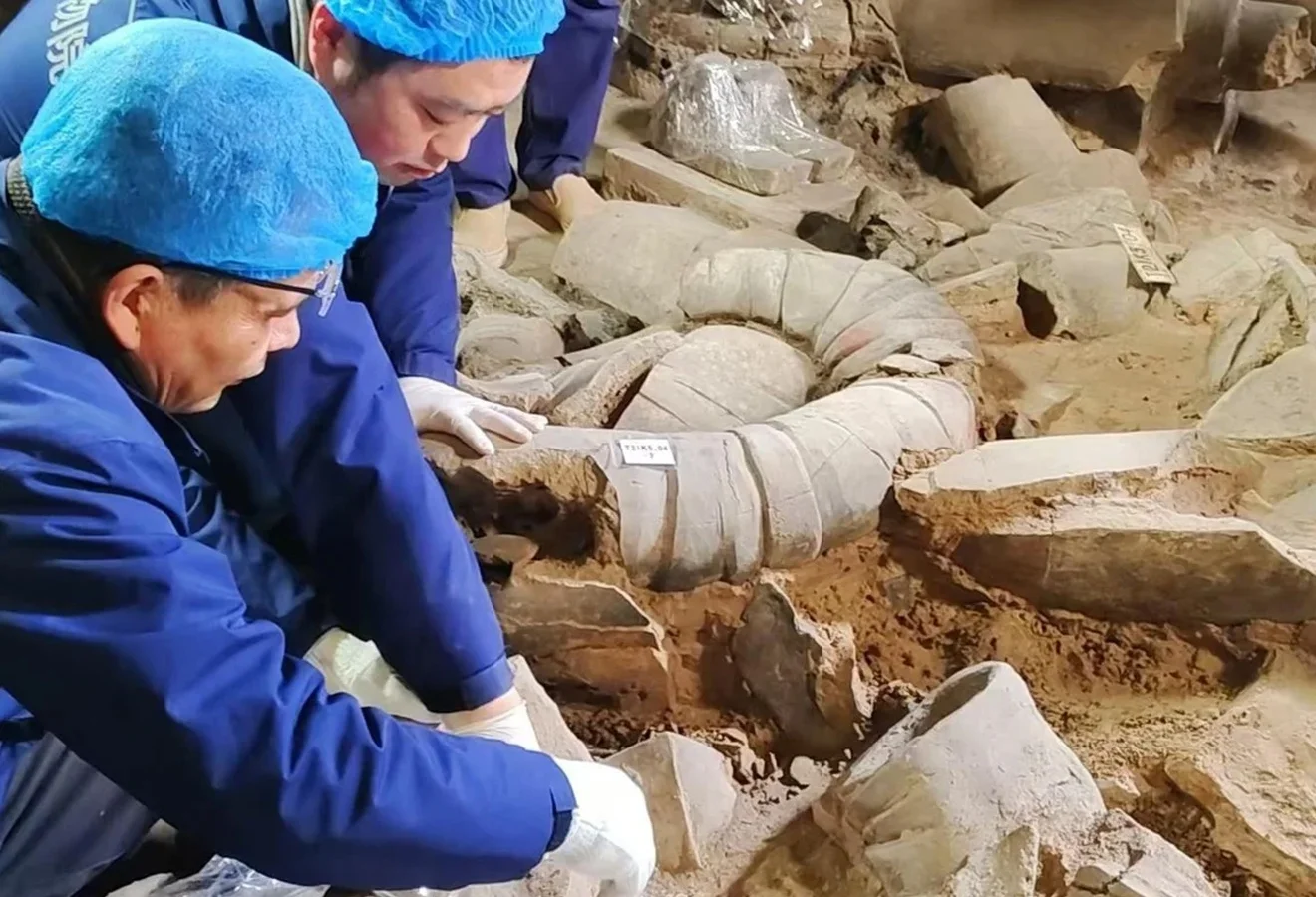
Archaeologists excavating the mausoleum of Qin Shi Huang have uncovered a terracotta warrior depicting a high-ranking commander.
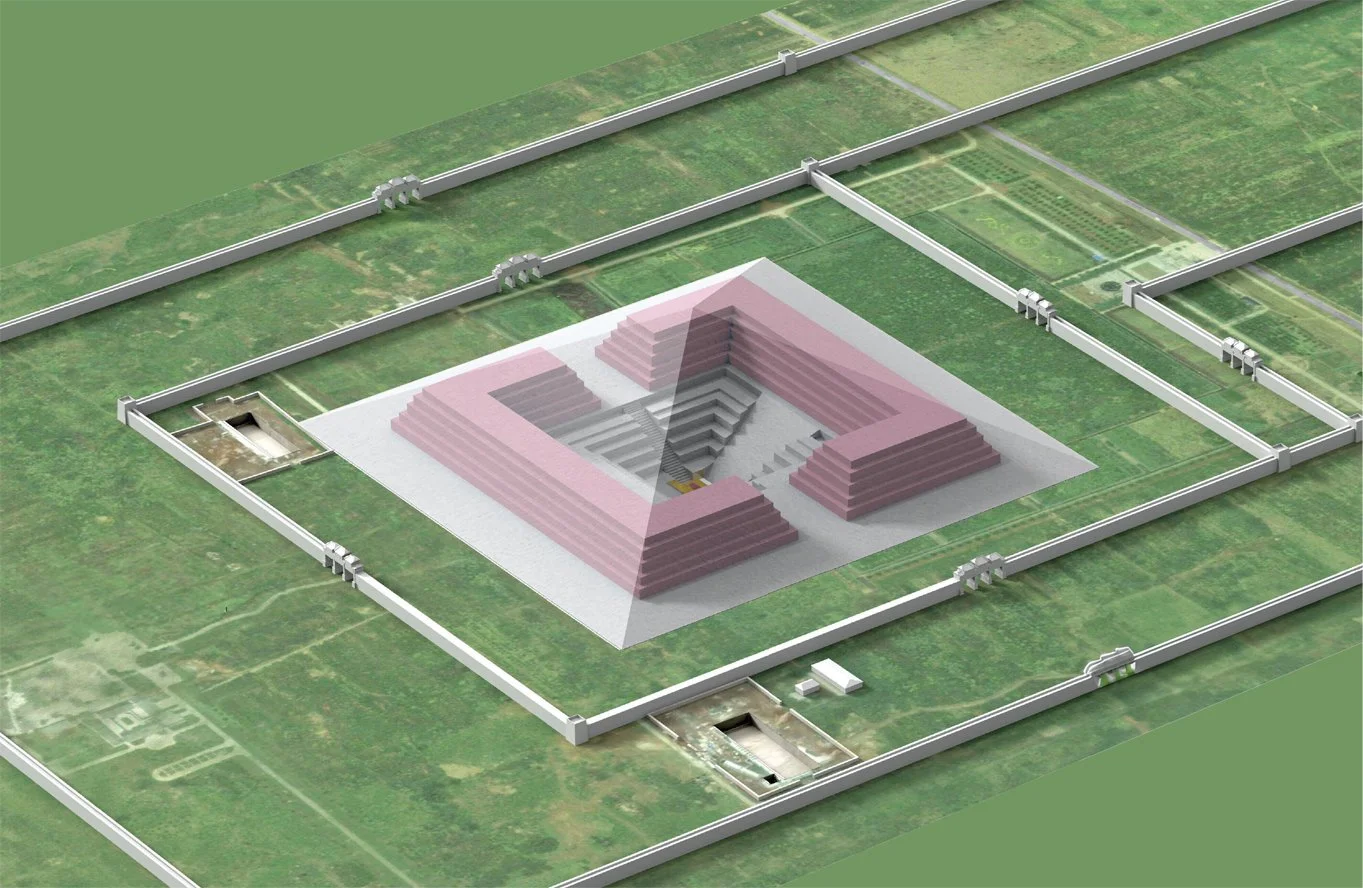
The Mausoleum of the First Emperor is the burial complex and mausoleum of Qin Shi Huang, the architect of China’s unification and founder of the Qin Dynasty.
Situated in Xi’an’s Lintong District, the mausoleum was built over a span of 38 years by a workforce of 700,000 labourers, as recorded in historical texts. The main burial chamber is located beneath a 76-metre-tall hillock (mound) shaped like a truncated pyramid.
What is known about the tomb interior comes from the “Records of the Grand Historian” by Sima Qian, who describes a vast chamber containing palaces and scenic towers, a coffin cast from bronze, and rare artefacts from across China.
Previous excavations around the complex have discovered thousands of warriors, horses, officials, acrobats, strongmen, musicians made from terracotta, and around 100 wooden battle chariots.
Archaeologists excavating Pit No. 2 (thought to contain a military guard) have recently uncovered a terracotta warrior depicting a high-ranking commander. According to experts, this marks the first discovery of a commander since the pit was first opened for excavations in 1994.
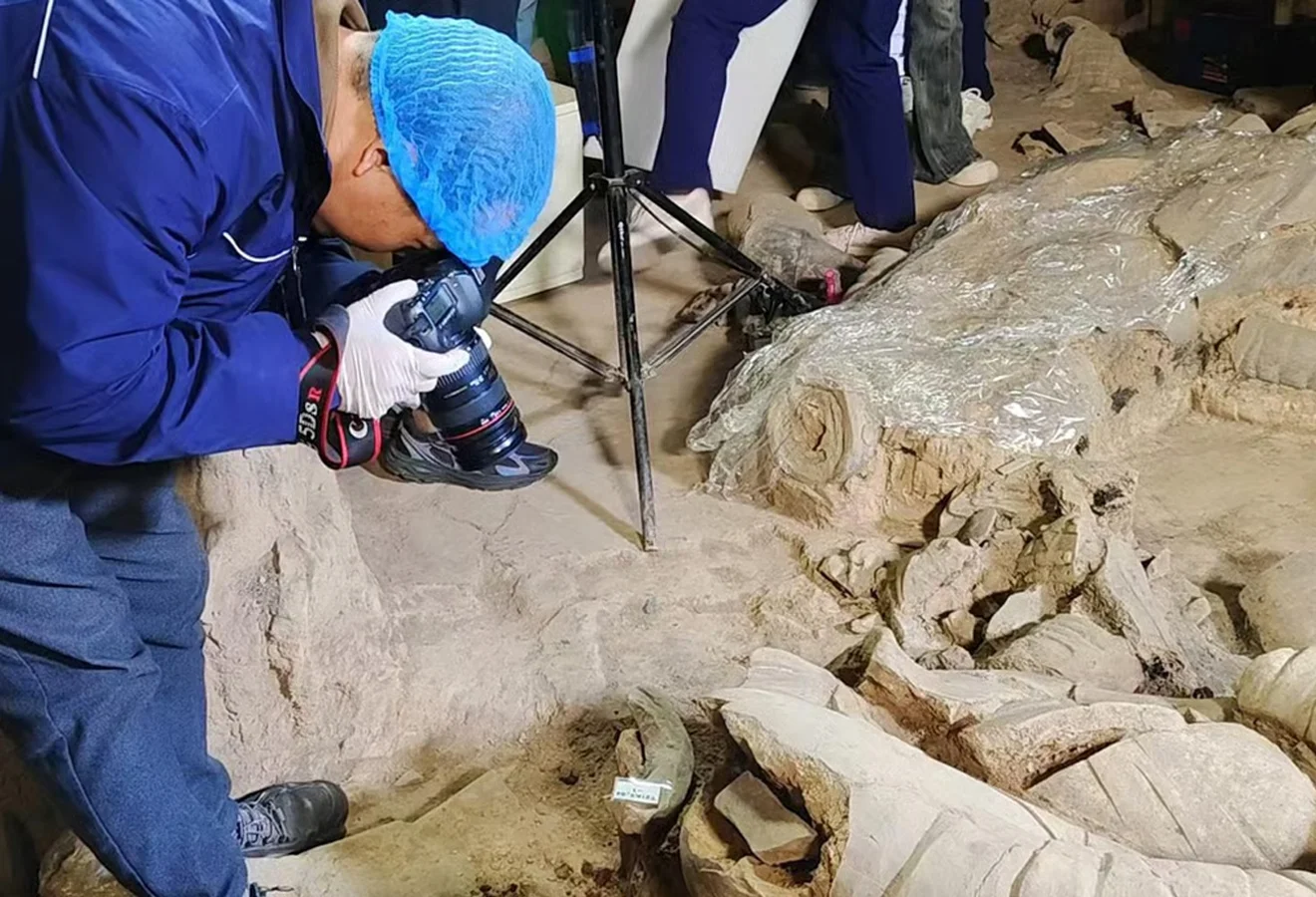

Archaeologists also found two high-level officer figurines, and five figurines dressed in contemporary armour accompanying the terracotta commander.
To date, only 10 high-level officer figurines have been discovered among the Terracotta Warriors, making this find a significant contribution to the study of Qin Dynasty military organisation and systems.
This year marks the 50th anniversary of the archaeological excavation of the Qin Terracotta Warriors.
Header Image Credit : CCTV
Sources : South China Morning Post





