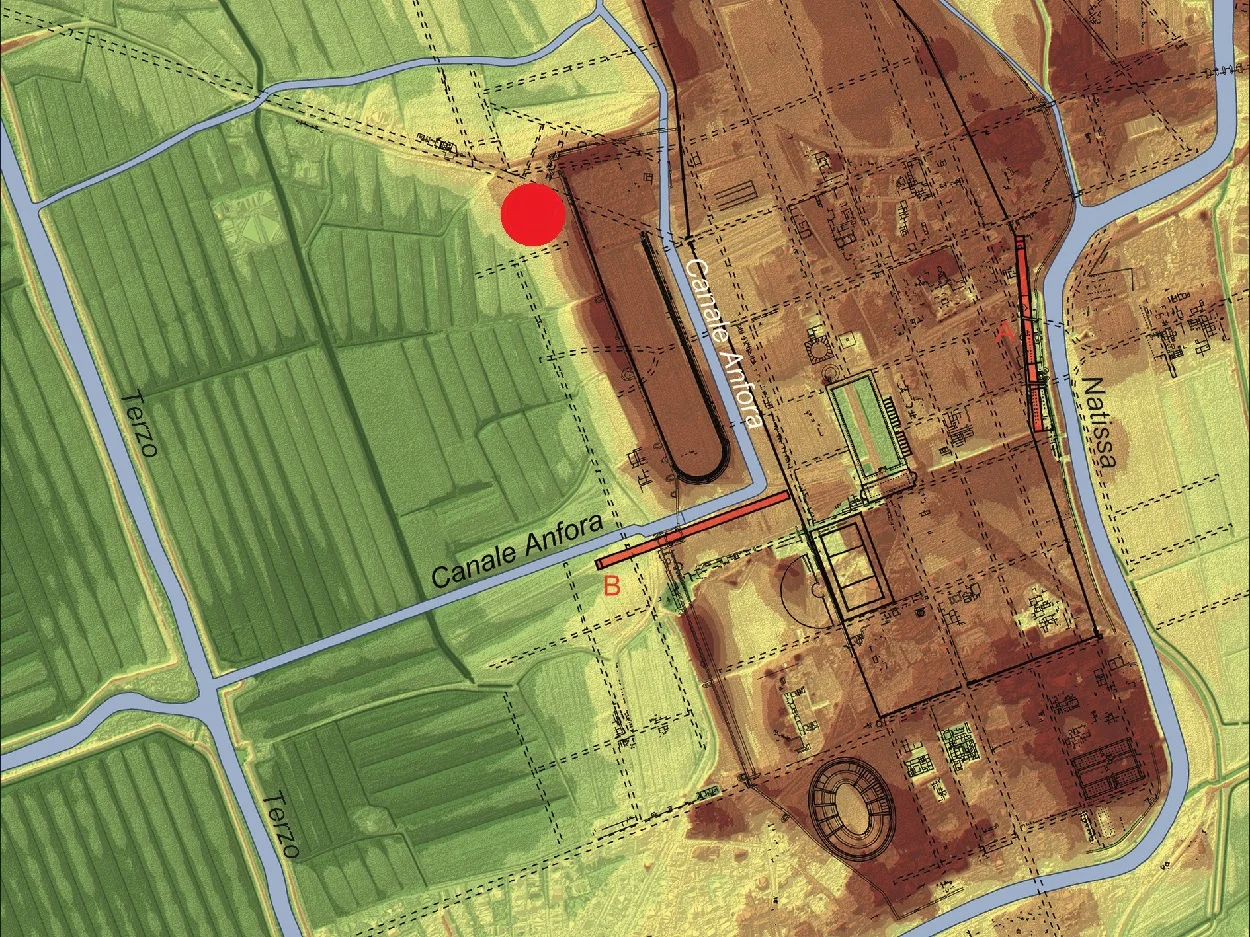
Archaeologists from the Austrian Archaeological Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW) have uncovered an early Christian basilica in the Roman city of Aquileia.
Aquileia, located in the Comune di Aquileia in the Italian province of Udine was founded in 181 BC as a Roman military colony and frontier fortress at the north-east corner of transpadane Italy.
Following ongoing raids by Attila and his Huns in the 5th century AD, the city was destroyed and its inhabitants fled en masse to the lagoons, where they laid the foundations of the cities of Venice and nearby Grado.
Centuries of sieges, earthquakes, floods, and the robbing of stone from the ancient structures have left no Roman-era buildings standing above ground. Despite this, the site is considered the largest unexcavated Roman city in Italy and holds a place on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
Recent excavations by archaeologists from ÖAW have uncovered a previously unknown Byzantine-style Christian basilica, the first large-scale building to be discovered in Aquileia after decades of intensive archaeological research.
According to the researchers, the basilica shows parallels with examples from the Eastern Roman Empire and was expanded into a large religious structure with three apses under Emperor Justinian I in the first half of the 6th century.
“Transept basilicas with apses can be found in the Eastern Roman Empire from Egypt through the Middle East, such as in Bethlehem, the Lycian coast, in southwestern Turkey and the Balkan region in Durrës, Albania, and now also in the Upper Adriatic,” explains Stefan Groh from ÖAW.
Archaeologists suggest that the basilica, which faces southeast towards Constantinople and Jerusalem is symbolic of the reconquest of Upper Italy by Justinian I who expelled the Arian Goths.
Header Image Credit : ÖAW
Sources : Austrian Archaeological Institute of the Austrian Academy of Sciences