Embalming practices, once considered exotic rituals mainly linked to ancient Egypt or South American cultures, have now been confirmed in Europe at recent discoveries at Château des Milandes in Castelnaud-la-Chapelle, Dordogne, France.
These findings indicate that such techniques were employed among European aristocracy during the 16th and 17th centuries.
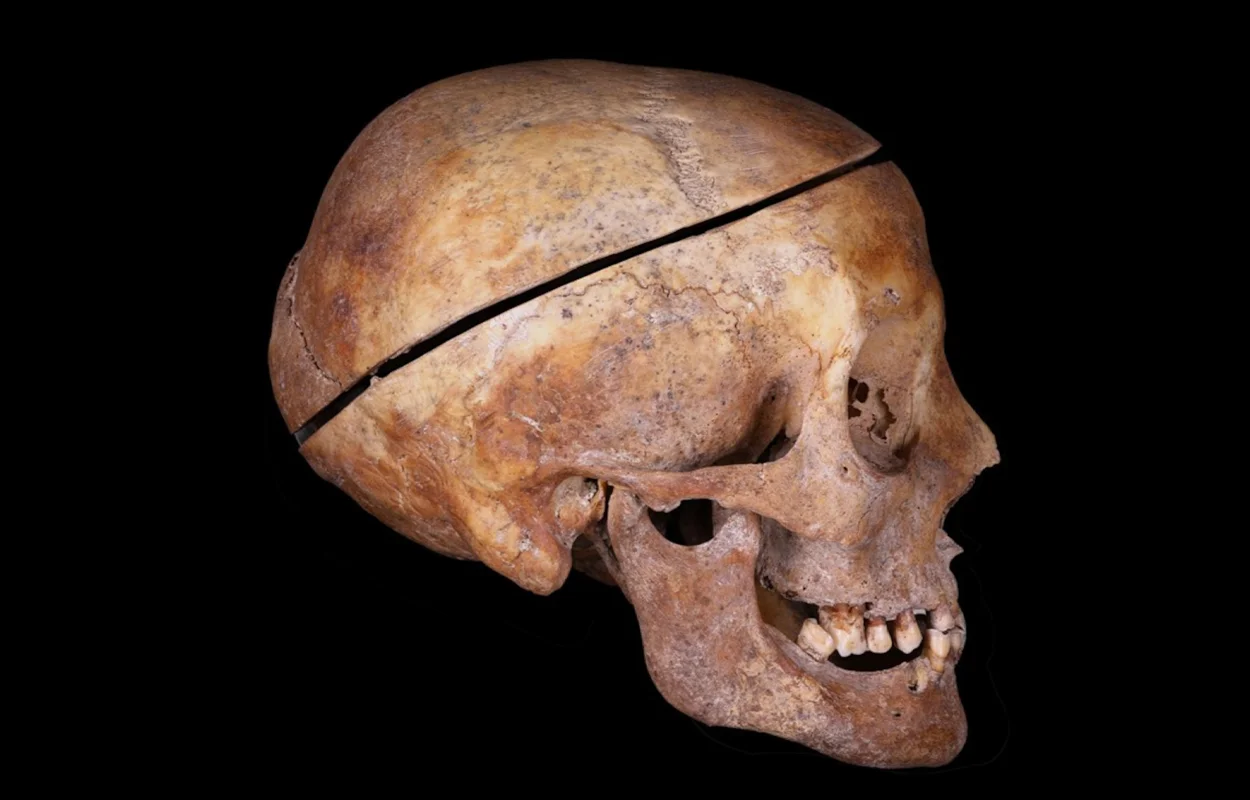
The remains of seven adults and five children from the noble Caumont family were all found embalmed in a crypt, along with a separately buried woman.
According to archaeologists from the Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW), the discovery will provide significant insights into the first historical embalming methods in Europe.
Caroline Partiot from ÖAW, said “Our examinations of a complete individual and the almost 2,000 fragments show a careful and highly standardised technical treatment of the deceased, which is similar for adults and children. This shows a know-how that has been passed down for over two centuries.”
Researchers examined the skeletal remains to reconstruct the embalming methods, noting precise cut marks that indicate complete skinning, including the arms, legs, fingertips, and toes.
These techniques closely align with methods described by the renowned French surgeon Pierre Dionis in 1708, which were used in an 18th-century autopsy in Marseille.
The embalming practices uncovered at Château des Milandes reveals a deeply rooted tradition within the Caumont family, highlighting their elevated social status. The primary purpose of embalming was likely not long-term preservation but rather the ability to display the body during elaborate funeral ceremonies. “The application to family members, regardless of age and gender at death, also reflects the acquisition of this status by birth,” emphasises Partiot.
Header Image Credit : M. Bessou/CNRS UMR
Sources : ÖAW