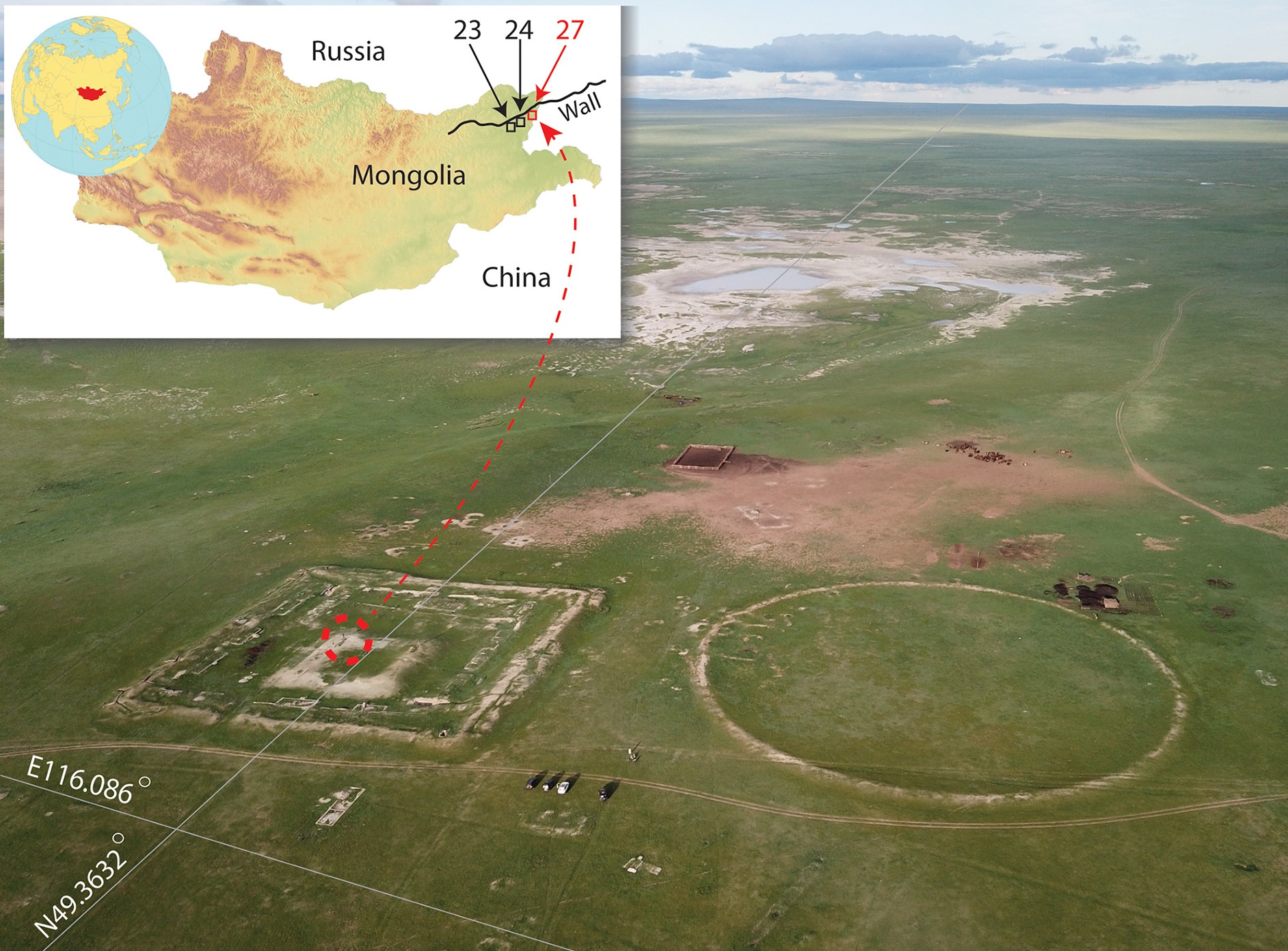
A Multi-institutional team of archaeologists have uncovered an elite burial belonging to a Khar Nuur steppe nomad from the pre-Mongol period in Dornod Province, Mongolia.
The excavation involved researchers from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, the National University of Mongolia, and Yale University, as part of the Mongol-Israeli-American Archaeological Project.
According to a press statement, the discovery provides new insights into the period following the collapse of the Kitan Empire around AD 1125, to the rise of the Mongol Empire under Chinggis Khan in AD 1206 – a period marked by post-imperial destabilisation and intense political competition.
The Khar Nuur burial, as it is now known, was found within the enclosure wall of a Kitan-era frontier fortress. It contains the skeletal remains of an elite individual that postdates the fortress, suggesting that the Khar Nuur steppe nomads likely saw the fortress as a symbol of prestige and power for the deceased.
“The Khar Nuur burial represents a unique window into the complex social and political landscape of 12th century Mongolia,” said Prof. Shelach-Lavi. “It demonstrates how local elites may have used symbolic connections to past empires to legitimise their own power and status, even as they navigated a rapidly changing political environment.”
These theories, though not mutually exclusive, together provide a comprehensive explanation for the social and political dynamics unfolding on the eastern steppe during the post-Kitan era.
As imperial authority weakened and steppe groups struggled for dominance, the Khar Nuur burial emerged as a powerful symbol of identity, memory, and power in a period of significant transition.
As further analysis of the burial and its contents continues, researchers anticipate gaining even more insights into this pivotal period in Mongolian and world history.
Header Image Credit : Dan Golan
Sources : An elite grave of the pre-Mongol period, from Dornod Province, Mongolia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ara.2024.100537