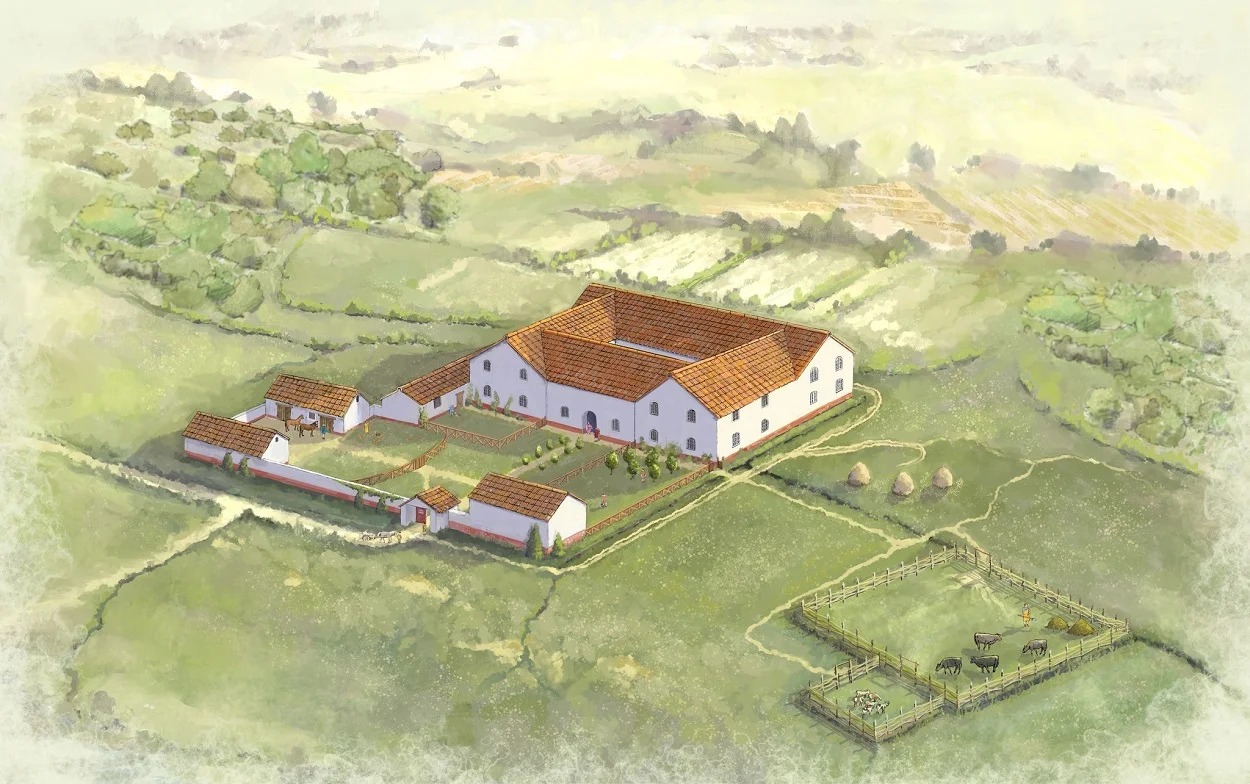
Archaeologists conducting a geophysical survey for the National Trust have discovered two Roman villas near the ancient city of Wroxeter (Viriconium Cornoviorum), England.
Wroxeter was a major Roman centre, first established as a frontier post for Thracian Auxilia during campaigns by Publius Ostorius Scapula in Britannia.
At its peak, the city covered an area of 173 acres and had a population of more than 15,000 inhabitants. Previous excavations have revealed the remains of various public buildings, such as thermae, temples, a basilica, and a colonnaded forum.
The National Trust recently commissioned “Magnitude Surveys” to conduct a geophysical study encompassing over 2,471 acres at the Attingham Estate in Shropshire. Geophysics is a non-invasive method that can reveal subsurface features and anomalies for archaeological inspection.

The survey discovered the traces of two previously unknown Roman villas and a Roman roadside cemetery on a road leading from Wroxeter.
According to the researchers: “The two rural villas, (the equivalent of a large country estate) show evidence of at least two construction or occupation phases, along with floor plans with internal room divisions and associated outbuildings.”
Villas of this type normally have a hypocaust system (underfloor heating), and were decorated with painted plaster and mosaic floors. Only six other Roman villas are currently known in Shropshire.
They survey also identified evidence for several Roman roads to the west of Wroxeter, eight ditched enclosures from the Iron Age, and known archaeological remains from the Anglo Saxon period.
National Trust Archaeologist Janine Young said: “This new geophysical survey has really transformed our knowledge by establishing a comprehensive ‘map’ of what is below our feet, providing us with a fascinating picture of the estate’s hidden past, revealing previously unknown sites of importance.”
Header Image Credit : Jennie Anderson
Sources : National Trust Archaeology