Archaeologists from the Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW), working in collaboration with the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA), have discovered a lost crusader altar in the Church of the Holy Sepulchre.
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, also known as the Church of the Resurrection, is the holiest site in the Christian world, located in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem.
According to tradition, the 4th century church was built on the site where Jesus was crucified, and is also the location of Jesus’ empty tomb, where he was buried and resurrected.
Archaeologists conducting a study of the church interior have made a sensational discovery within one of the rear corridors connecting to the middle chamber.
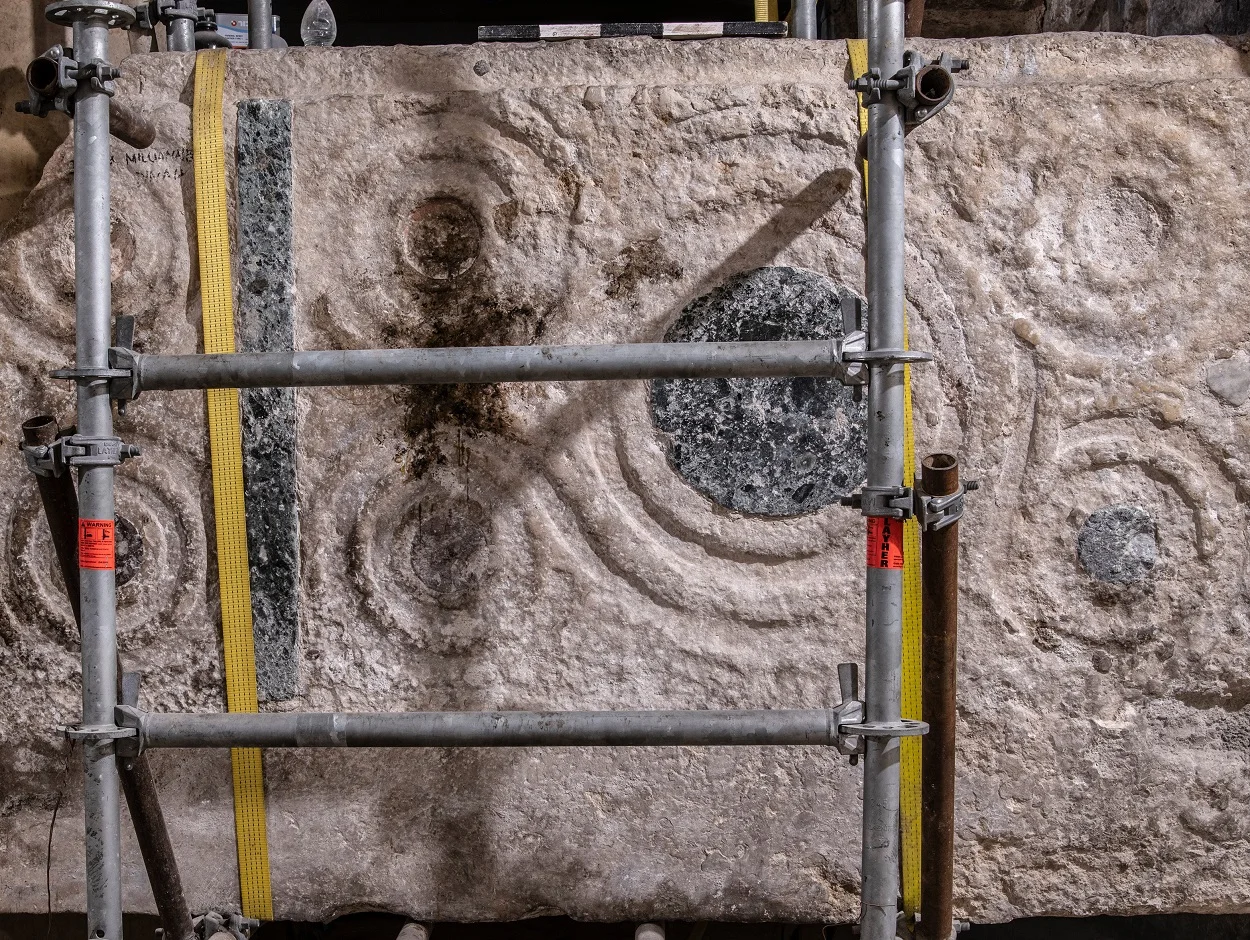
Leaning against a wall for decades was a neglected stone slab that tourists have been writing graffiti on. When the stone was turned, it was revealed to be a long-lost crusader altar from the medieval period, consecrated in 1149.
“We know of pilgrimage reports from the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries about a magnificent marble altar in Jerusalem,” says Ilya Berkovich, historian at the Institute for Research on the Habsburg Monarchy and the Balkans at the Austrian Academy of Sciences (ÖAW).
In 1808, a large fire destroyed much of the Romanesque part of the church, with the crusader altar thought to be lost in the destruction.
How the slab could remain hidden for so long is a mystery, but the discovery provides new information about a previously unknown connection between Rome and the Christian Kingdom of Jerusalem.
The altar is decorated with a unique technique known as “Cosmatesque” for producing marble decorations, mastered exclusively by guild masters in papal Rome.
According to a press statement by ÖAW “The technique was characterised by the fact that its masters could decorate large areas with small amounts of the precious marble, which in medieval Rome was mainly scraped from ancient buildings – by assembling small marble splinters with the greatest precision and attaching them to stone supports to create geometric patterns and dazzling ornaments.”
Archaeologists suggest that the altar must have been created with the Pope’s permission, who likely commissioned one of the Cosmatesque masters to honour the holiest church in Christendom.
Header Image Credit : Shai Halevi – Israel Antiquities Authority
Sources : Austrian Academy of Sciences





