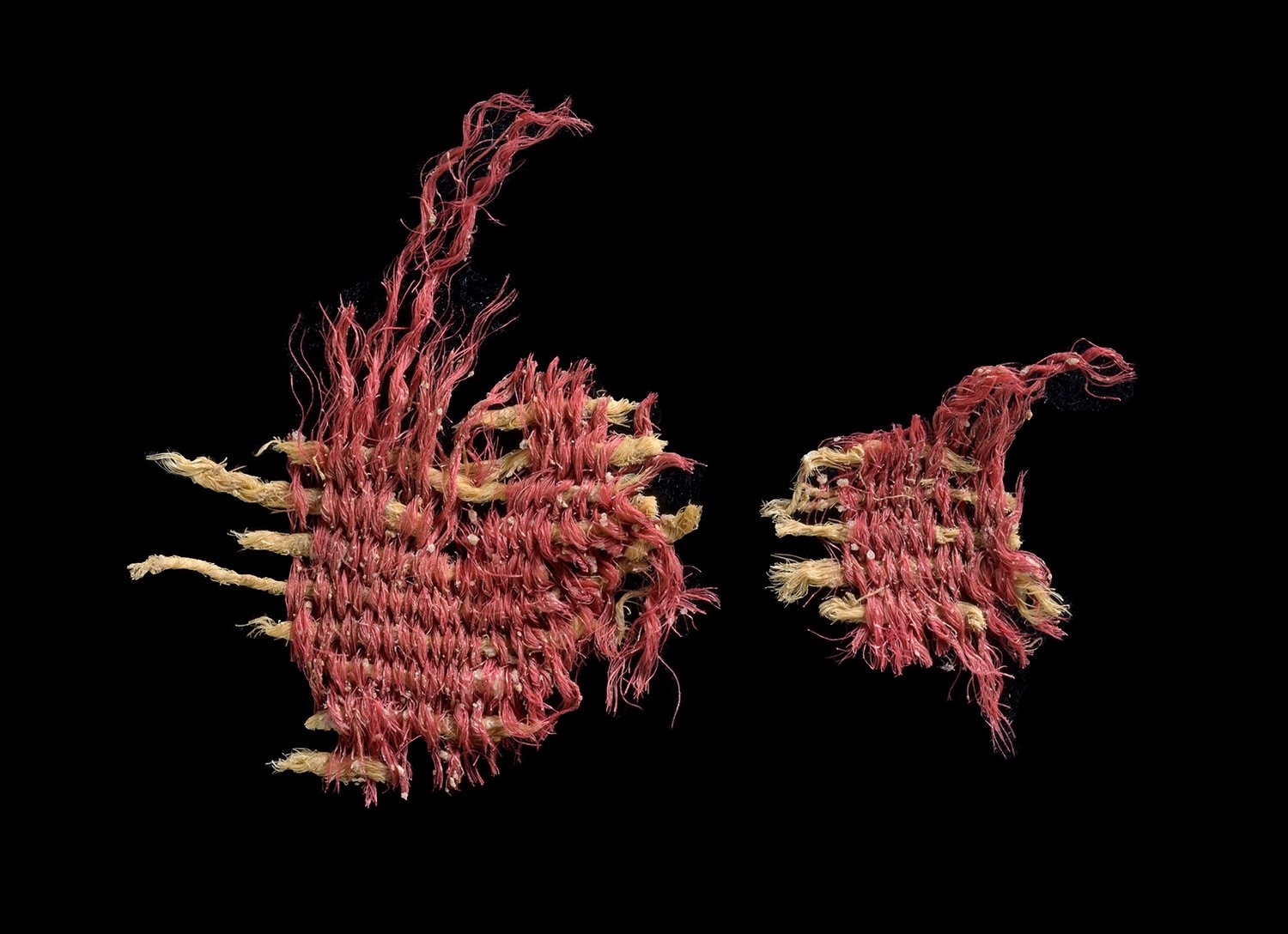
Archaeologists from the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA), Bar-Ilan University, and the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, have discovered the earliest known example in Israel of red-dyed textiles made using insects.
The textile fragment was found in a cave in the Judean Desert, which was dyed using Kermes oak (Quercus coccifera) insects, known from biblical text as the “Tola‛at Hashani” (scarlet worm).
Scale insects can be used to make red kermes dyes in crimson and scarlet, which are derived from the dried bodies of the females.
Since antiquity, the Ancient Egyptians, Mesopotamians, Indians, Greeks, Romans, and Iranians, have been known to use the insects to produce red dye, however, the discovery in the Judean Desert is the earliest known example in Israel as described in the Hebrew Bible.
The Bible describes the “scarlet worm” 25 times, often alongside blue (Tekhelet) and purple (Argaman), in the context of luxurious clothing, in the use of Tabernacle textiles, and in other cultic contexts.
The textile, dated to the Middle Bronze Age (1767-1954 BC), is less than 2 cm in size, and was discovered in the “Cave of Skulls” during excavations as part of project to save archaeological remains from looting.
A closer analysis found that the woolen weft threads were dyed using Kermes vermilio scale insects, which lives on the kermes oak tree (Quercus coccifera), a species not indigenous to Israel.
“The important find bridges the gap between written sources and the archaeological discoveries, providing evidence that the ancient textile dyeing industry was — already at this stage, sufficiently established for dyeing using animals,” said Dr. Sukenik from the Israel Antiquities Authority.
“The rare textile is a testament to broad international commercial networks functioning already at this time and indicates the presence of an elite society,” added Dr Sukenik.
Header Image Credit : IAA
Sources : IAA