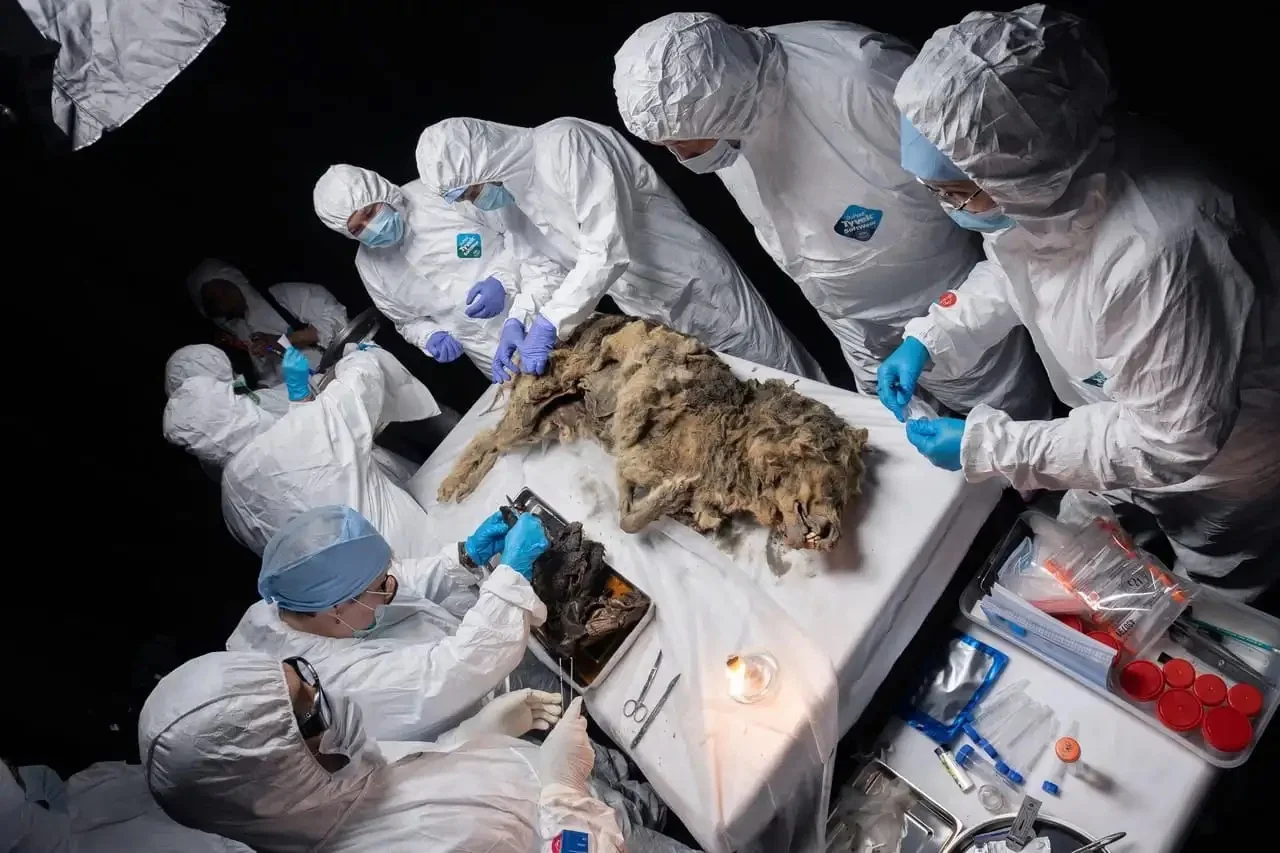
Scientists from the MKAmmosov North-Eastern Federal University have found the preserved remains of a Pleistocene wolf in the Republic of Sakha, Russia.
According to the researchers, the wolf lived more than 44,000 years ago during the Peistocene Epoch, a period that covers most of the latest period of repeated glaciation, up to and including the Younger Dryas cold spell.
The wolf was found in Russia’s Republic of Sakha, a region renowned for its palaeontological importance due to the frequent discoveries of prehistoric animals found preserved in ice or permafrost over the last several decades. Permafrost is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below 0°C for two years or more.
In 2015, two frozen cave lion cubs, estimated to be between 25,000 and 55,000 years old, were discovered close to the Uyandina River, and in 2019, the severed head of a large wolf from over 40,000 years ago was found close to the Tirekhtyakh River.
The latest discovery, also found near the Tirekhtyakh River, marks the first complete example of an adult predator preserved in such a state. Notably, the wolf’s stomach was found intact and uncontaminated, offering a rare and valuable glimpse into the dietary habits of wolves from that era.
“Under sterile conditions, we took samples of internal organs to study the animal’s diet, ancient viruses and microbiota, as well as samples to compare its genome with that of the modern wolf,” said the MKAmmosov North-Eastern Federal University. The researchers also took a premolar tooth to determine the biological age, revealing that the wolf was an adult male.
Professor Artemy Goncharov, head of the Functional Genomics and Proteomics Laboratory at the Institute of Experimental Medicine, said: ‘We see that live bacteria can survive in the finds of fossil animals for millennia, serving as witnesses to those ancient times.”
“It is possible that microorganisms will be found that can be applied in medicine and biotechnology as promising producers of biologically active substances.”
Header Image Credit : Michil YAKOVLEV
Sources : MKAmmosov North-Eastern Federal University