A study, published in the journal Science Direct, has revealed the discovery of two infant burials beneath a prehistoric “dragon stone” in Armenia.
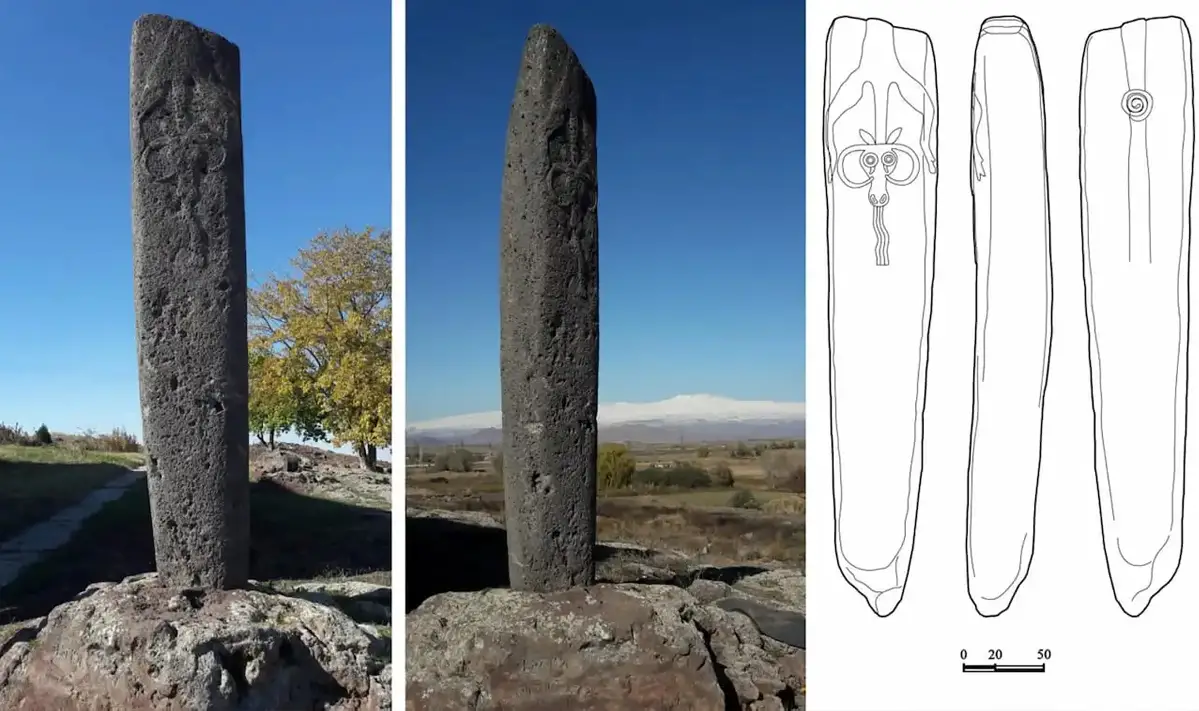
“Dragon stones”, also known as vishapakar, are basalt monoliths found in the Armenian Highlands. The stones are decorated with carved animal imagery such as fish heads or serpents, supposedly depicting the image of vishaps, a water dragon of Armenian folklore.
Nearly all the monoliths are found near mountain springs or canals, suggesting a ritual association with water.
Archaeologists have been excavating a “dragon stone” decorated with the image of a sacrificed bovid at the village of Lchashen on the north-western edge of the high-altitude Sevan Lake. A liquid flowing from the mouth of the bovid may represent water, blood, or a synecdoche of both.
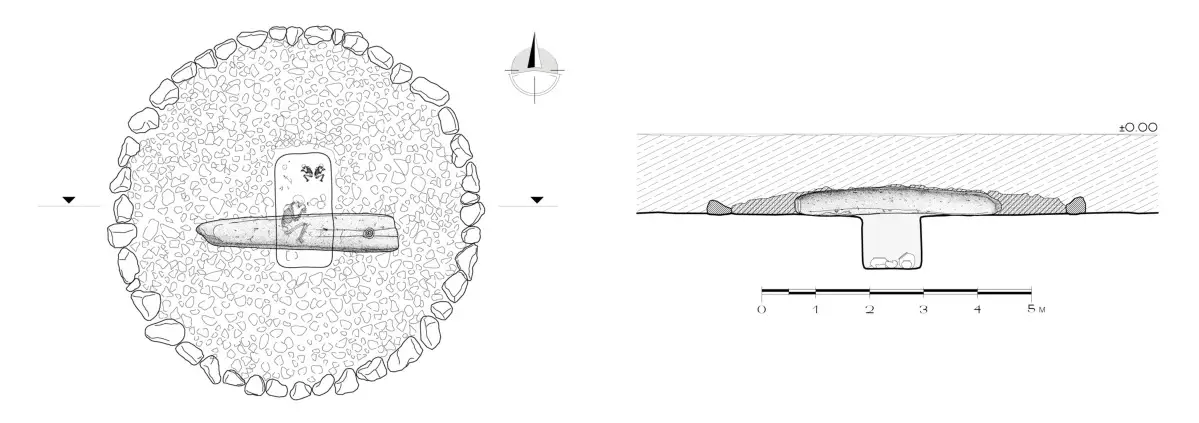
Excavations have revealed a burial pit beneath the stone which dates from the 16th century BC. Within the pit are two infant burials, in which a study of their DNA has showed them to be second-degree related females with identical mitochondrial sequences, indicating that the infants are closely related.
The pit also contained archaeological material, such as painted pottery, a bronze hair pin, a carnelian bead, a bone needle, a fragment of obsidian, as well as human bones of an adult.
According to the study authors, “In Late Bronze Age Armenia in general and at Lchashen in particular, burials of children are rare, and the burial of two newborns combined with a monumental stela is unique.”
“In the South Caucasus, stelae are sometimes used to mark graves. However, out of 454 Bronze Age graves excavated at Lchashen, not one was marked by any kind of stelae. Only this grave was marked with a dragon stone.”
Header Image Credit : A. Hakhverdyan
Sources : Burial of two closely related infants under a “dragon stone” from prehistoric Armenia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jasrep.2024.104601





