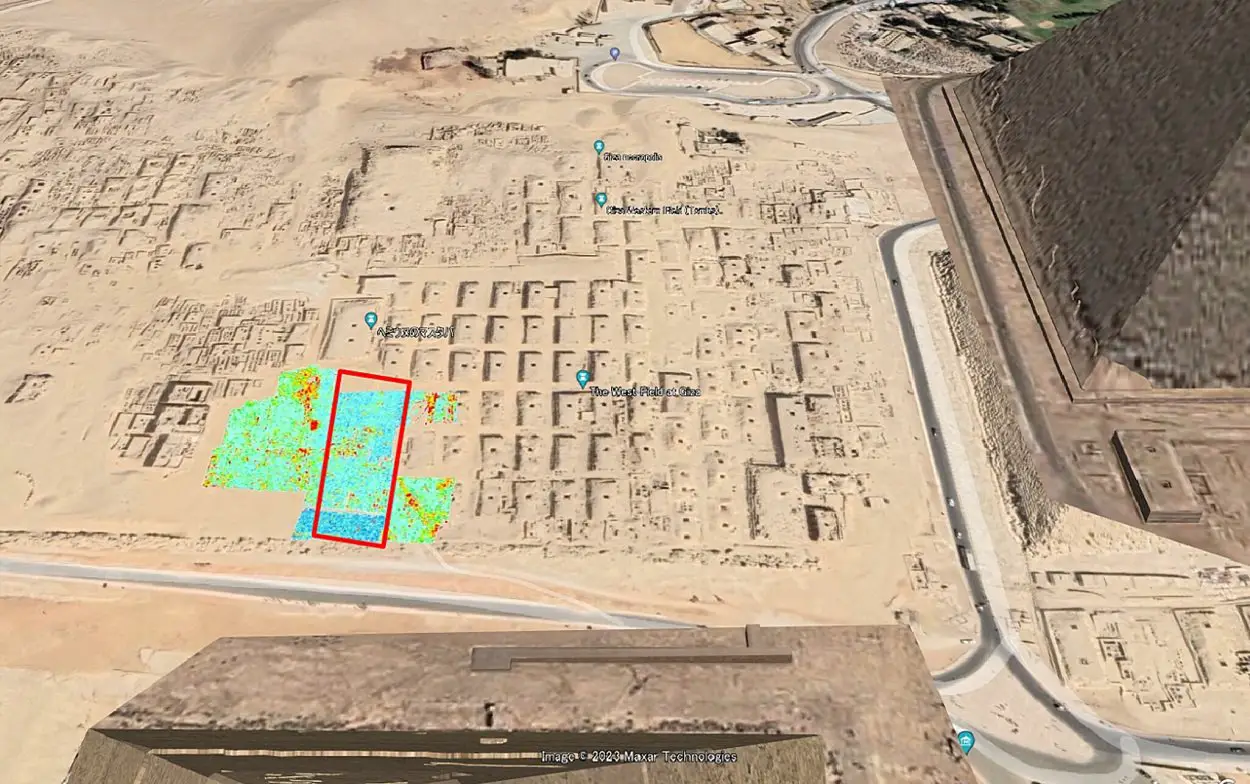
A geophysical study by archaeologists from the Higashi Nippon International University, Tohoku University, and the National Research Institute of Astronomy and Geophysics (NRIAG), have detected an L-shaped structure and several anomalies near the Giza Pyramids using geophysics.
Archaeologists detected the structure using a combination of ground-penetrating radar (GPR) and electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) during a survey of the Western Cemetery.
The Western Cemetery, also known as the Giza West Field, is located on the Giza Plateau to the west of the Great Pyramid of Giza. It is divided into smaller cemeteries, consisting of linear alignments of mastabas and subsurface structures.
Mastabas served as a burial structure for the royal family and high-class officers, characterised by its flat roof and rectangular design constructed using limestone or mudbricks. Central to its construction is a vertical shaft that links to an underground chamber.
According to the researchers, the L-shaped structure was located at a depth of 2 metres directly south from mastaba G4000. The structure appears to have been filled with sand and may have served as an entrance tunnel to a deeper structure.
This is supported by the detection of deeper anomalies beneath the L-shaped structure, concentrated at a depth of 3.5 to 5 metres, with two features persisting down to a depth of 11 metres.
According to a paper published in the journal Archaeological Prospection: “The data show clear anomalies that could be attributed to an archaeological potentiality (high-resistivity contour spots) at the surveyed region. The features have shown a further extension, up to 3–5 m more than the depth screened by the GPR survey. We conclude from these results that the structure causing the anomalies could be vertical walls of limestone or shafts leading to a tomb structure.”
“We believe that the continuity of the shallow structure and the deep large structure is important. From the survey results, we cannot determine the material causing the anomaly, but it may be a large subsurface archaeological structure,” said the study authors.
Header Image Credit : Archaeological Prospection
Sources : GPR and ERT Exploration in the Western Cemetery in Giza, Egypt. https://doi.org/10.1002/arp.1940