A skeletal analysis has revealed that a period of violence followed the collapse of the Chavín culture in Peru.
The Chavín culture was a pre-Columbian people that emerged in the Andean highlands of Peru around 900 BC. The Chavín were the main culture of the Early Horizon period and had an advanced understanding of metallurgy, ceramic production, irrigation, and an intensified religious cult.
Its center was Chavín de Huantar, a monumental ceremonial site in northern Peru in the Marañon River basin.
Just before the collapse of the culture around 500 and 400 BC, the Chavín people went through a turbulent period caused by political disintegration and inter-group violence, possibly caused by a transition from a theocracy to secular government. After the collapse, it is likely that surviving communities competed for the scant resources in the Supe Valley region.
A new study, published in the journal Latin American Antiquity, has analysed the skeletal remains of 67 individuals from a burial site in the Supe Valley region near Caral. The burials date from between 500-400 BC and show injury patterns characteristic of repeated events of interpersonal violence in 80% of the individuals.
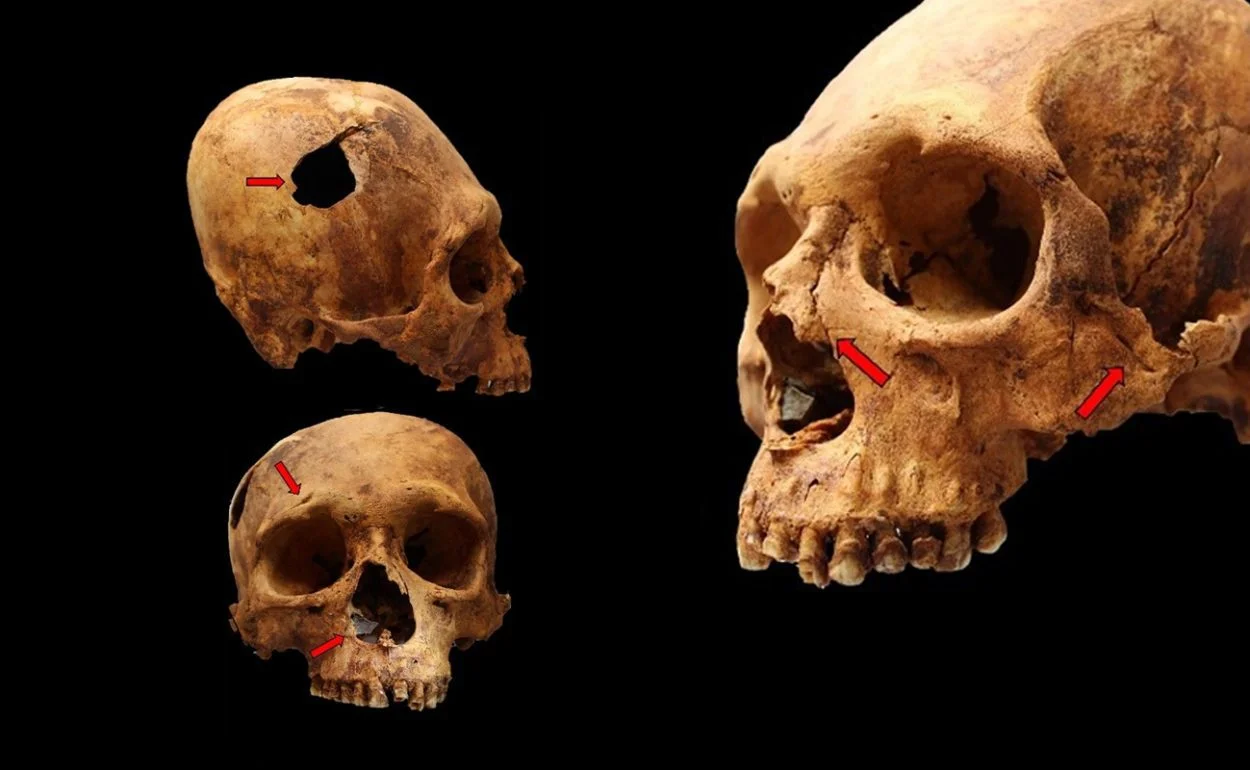
Perimortem injuries to the skull, face and chest observed in several individuals are compatible with lethal, probably intercommunity, violence, whose victims included children. “Our hypothesis is that a group of strangers came to the community and committed the murders. After the aggressors left, the murder victims were buried by their own people with the usual funeral rites, as suggested by the burial patterns,” said Pezo-Lanfranco Autonomous University of Barcelona (UAB).
Although perimortem trauma was the most frequent type of injury among the adult skeletons studied, as well as some of the child remains, many examples of antemortem trauma were also found, and several individuals displayed both, suggesting the occurrence of at least two violent events during their lives.
“The markers point to exposure to repetitive and lethal violence during the course of their lives,” Pezo-Lanfranco said. The most frequent injuries were depressed fractures of the cranial vault, other maxillofacial fractures, thoracic fractures (mainly in ribs and scapulae), and “defensive” fractures of the ulna (forearm, indicating an attempt to parry a blow).
Out of the 67 individuals examined, 64 were interred in a fetal position: 12 lying on their back (dorsal decubitus), four on their stomach (ventral decubitus), seven on their left side (left lateral decubitus), and 41 on their right side (right lateral decubitus). The fetal position was as a common burial practice across various prehistoric and ancient societies globally. Its symbolism, often linked with the womb, leads some scholars to suggest an anticipation of rebirth following death.
Header Image Credit : Luis Pezo-Lanfranco
Sources : São Paulo State Research Support Foundation – Pezo-Lanfranco L, Romero MIB, Filippini J, et al. Bioarchaeological Evidence of Violence between the Middle and Late Formative (500–400 BC) in the Peruvian North-Central Coast. Latin American Antiquity. Published online 2024:1-17. doi:10.1017/laq.2023.38