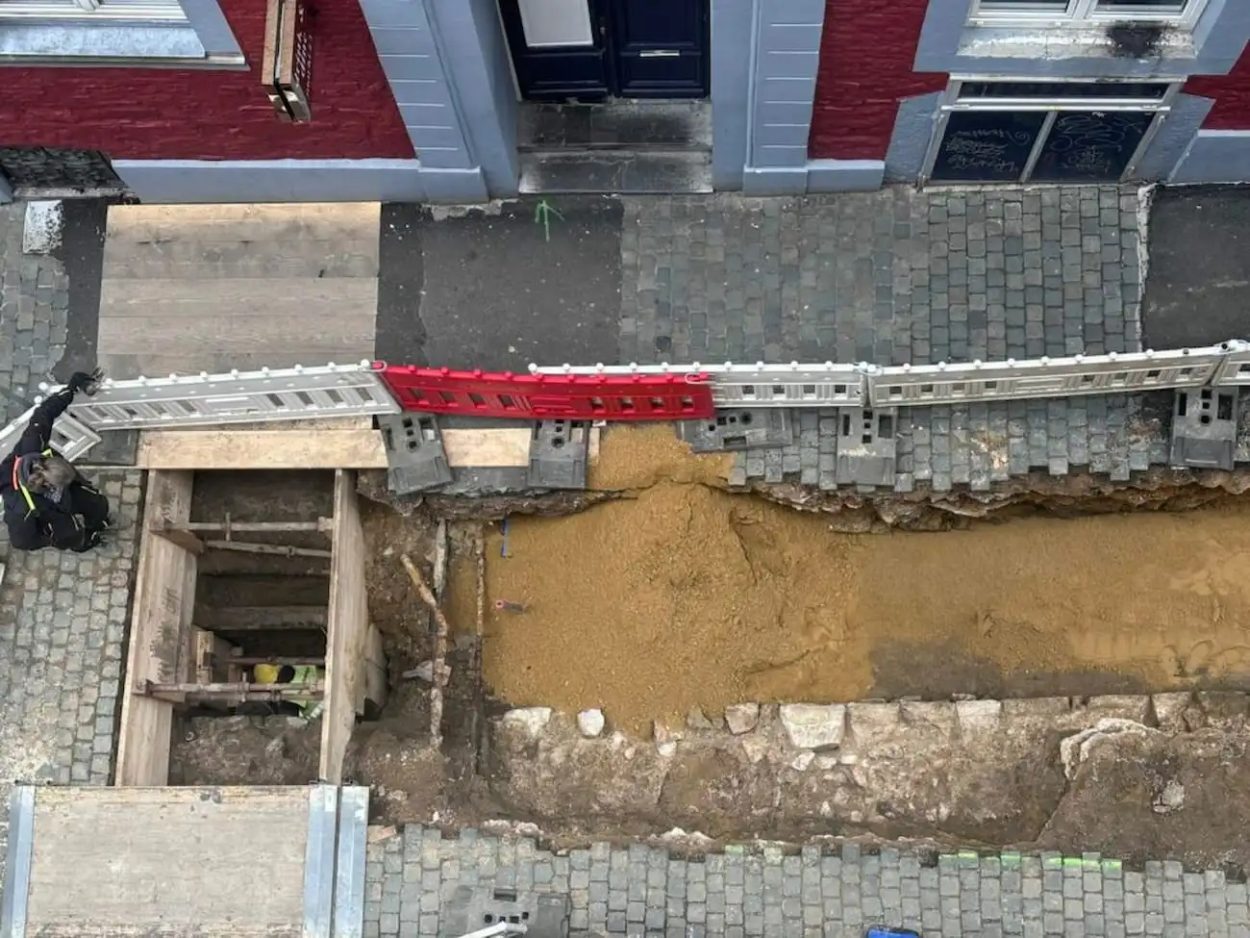
Archaeologists from ArcheoConsult have found traces of a Roman fort during excavations in Aachen, Germany.
Aachen, known as Aquae Granni during the Roman period, was first settled by the Romans during the 1st century AD.
The town was named for the Aachen thermal springs, with “Aquae” referring to “water”, and “Granni” to “Grannus”, a pagan god of healing.
Archaeologists have always suspected that Aachen had a Roman fort, but this was only confirmed during excavations between 2011 and 2014.
Further evidence of the fort has recently been uncovered during construction works for housing utility pipes, revealing traces of a seven metre stone wall from the fort’s exterior fortifications that date from around 2,000 years ago.
Dr. Donata Kyritz from ArcheoConsult, said: “In the longitudinal direction, the foundation could be traced a few metres towards the market. A final row of ashlar masonry was now visible here. However, the exact dimensions have not yet been recorded in either the longitudinal or transverse direction.”
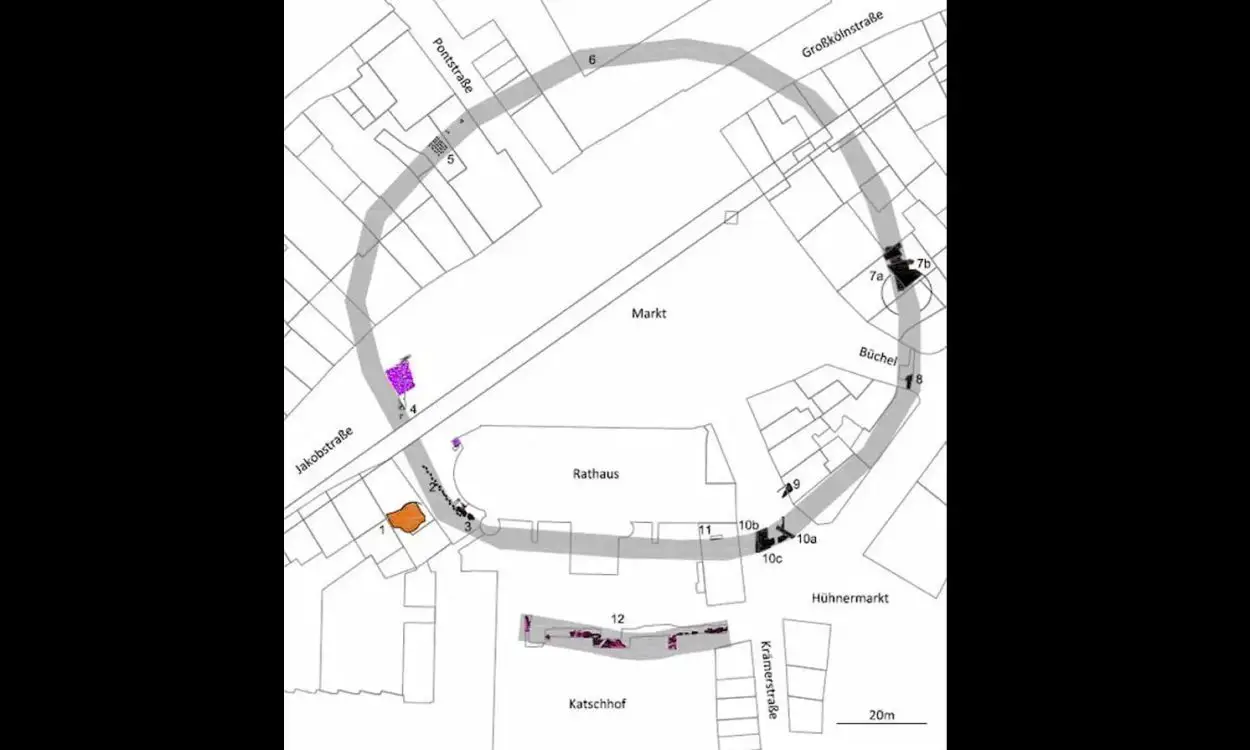
According to the researchers, Aachen was destroyed in the course of Frankish raids around AD 275 to 276, resulting in the construction of a castrum reinforced with a stone wall and circular towers on the area of present-day market mill.
The castrum’s fortifications were later used by Charlemagne, with the King’s Hall (the site of the present-day town hall) built on the forts southern flank. Historical text indicates that the fort’s walls remained until the 12th century, when they were demolished following the expansion of the medieval city of Aachen.
Speaking to HeritageDaily, a representative of ArcheoConsult, said: “Our aim is to preserve the archaeological find as best as possible. Intensive discussions are currently underway on this. After the archaeological finds have been assessed and documented, construction work at the site will continue as planned.”
Header Image Credit : Stadt Aachen / Stefan Herrmann
Sources : Aachen.de





