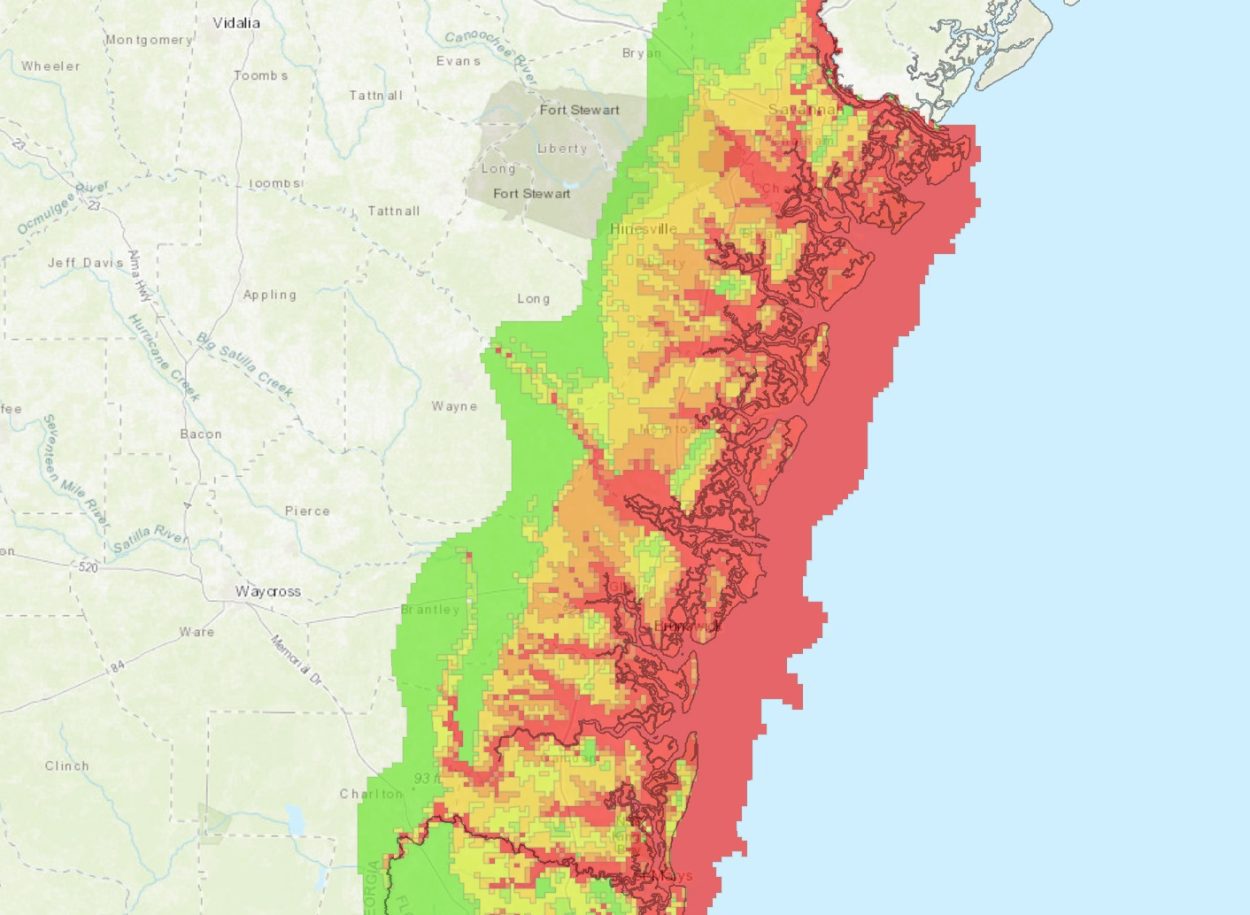
Thousands of Native American and colonial sites in Georgia are under threat from increasing storm surges caused by climate change, according to a new study published in the journal PLOS One.
The study has identified 4,200 sites at risk of flooding or inundation from Category 5 hurricanes at present sea level. However, this number will increase to around 5,000 sites by the year 2100, with over 2,000 additional sites threatened by weak tropical storms.
Sites mainly consist of Native American settlements and colonial sites, such as the Fort Frederica National Monument, the Fort King George State Historic Site, Horton House, and the Queen Anne–style ruins of Dungeness.
Victor D. Thompson said: “The Georgia coast’s cultural heritage spans millennia, from the earliest Native American villages of Ancestral Muskogean people to its colonial missions and later plantations. These cultural sites are increasingly being impacted by storms and sea level change which threaten the material link to the broader histories of Native peoples, the enslaved, and their place in American history.”
Locations were identified by using models that focus on projected sea level rises, such as the Lake and Overland Surges from Hurricanes (SLOSH) model developed by the National Weather Service.
According to the researchers, the number of sites are more than ten times the estimates from previous models.
Matthew D. Howland adds: “This study shows that the archaeological resources of the Georgia coast are at great risk of damage from potential storm surge at any time. Up until now, archaeologists have generally underestimated the threat to coastal cultural heritage since they have been thinking of long term averages of sea level rise rather than the kind of dramatic disaster events that can happen in Georgia and the Atlantic Coast, like Hurricane Michael in 2018.
Header Image Credit : Georgia Storm Surge Projections
Sources : PLOS ONE – Howland MD, Thompson VD (2024) Modeling the potential impact of storm surge and sea level rise on coastal archaeological heritage: A case study from Georgia. PLoS ONE 19(2): e0297178. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0297178