Archaeologists from the National Institute of Anthropology and History (INAH) have announced the recovery of the Codices of San Andrés Tetepilco.
The three codices date from the late 16th to early 17th century and are believed to be a continuation of the Boturini Codex.
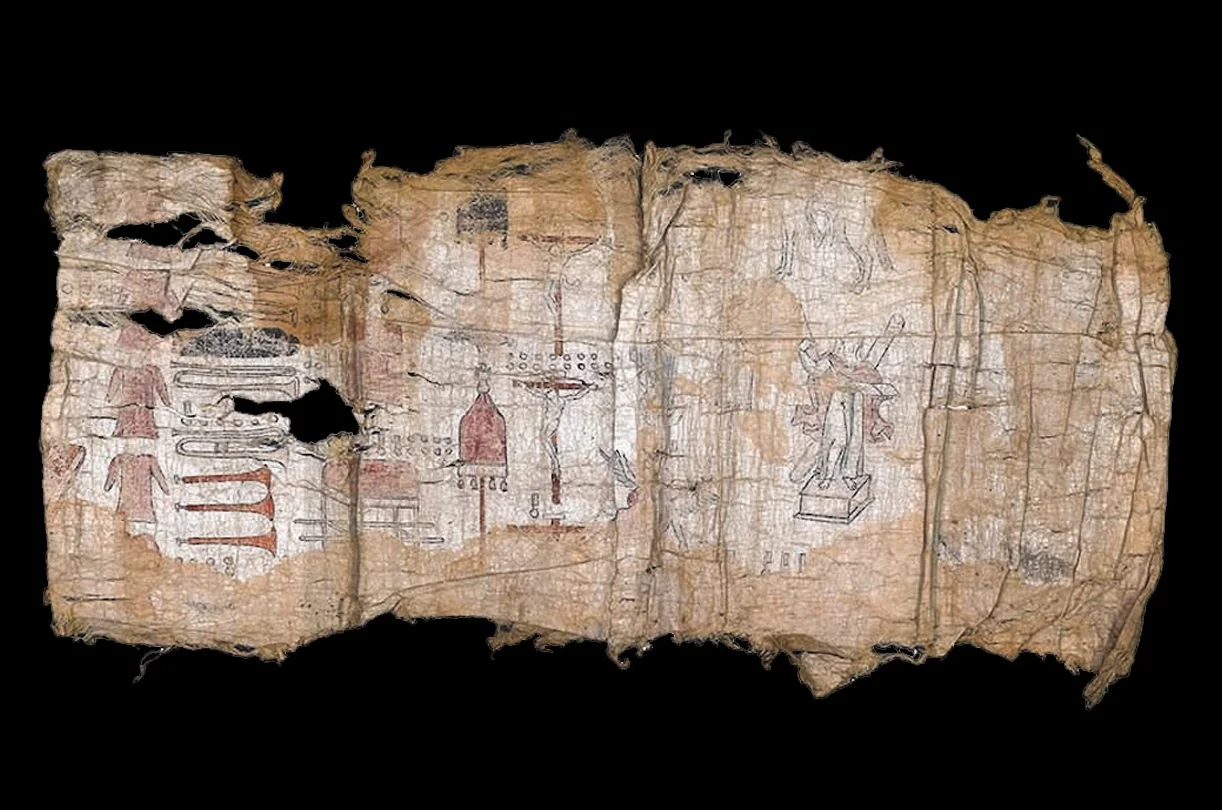
The codices depicts a transition from pre-Hispanic Mexica to the arrival of the Spanish, the latter represented with the image of Hernán Cortés who appears dressed like a Roman centurion. Another scene corresponds to the reign of Izcóatl, the fourth king of Tenochtitlan, and the founder of the Aztec Empire.
According to a press statement, the collection was in private ownership and has been acquired for the National Library of Anthropology and History (BNAH).
Following confirmation of authenticity by experts, INAH, in collaboration with various companies and philanthropists raised 9.5 million pesos (237,115.00 Pound sterling) for the purchase.
A closer examination has revealed that the codices were made on amate, a type of bark paper, with an applied layer of gesso and cochineal extract. Inks used to paint the various scenes come from plants, charcoal, indigo, and different shades of ochre.

Speaking to HeritageDaily, a representative of INAH said: “It wasn’t until two years ago that BNAH authorities were able to see them directly and manage a study to confirm their authenticity, which has involved the analysis of their composition by experts from the UNAM Physics Institute and the Coordination National Conservation of Cultural Heritage of the INAH.”
“Thanks to the transfer of ownership, the people of Mexico now hold the Codices of San Andrés Tetepilco which are part of the so-called mixed codices, as they contain paintings from indigenous tradition and texts in Nahuatl or Spanish, written with the European alphabet,” added INAH.
Header Image Credit : INAH
Sources : INAH





