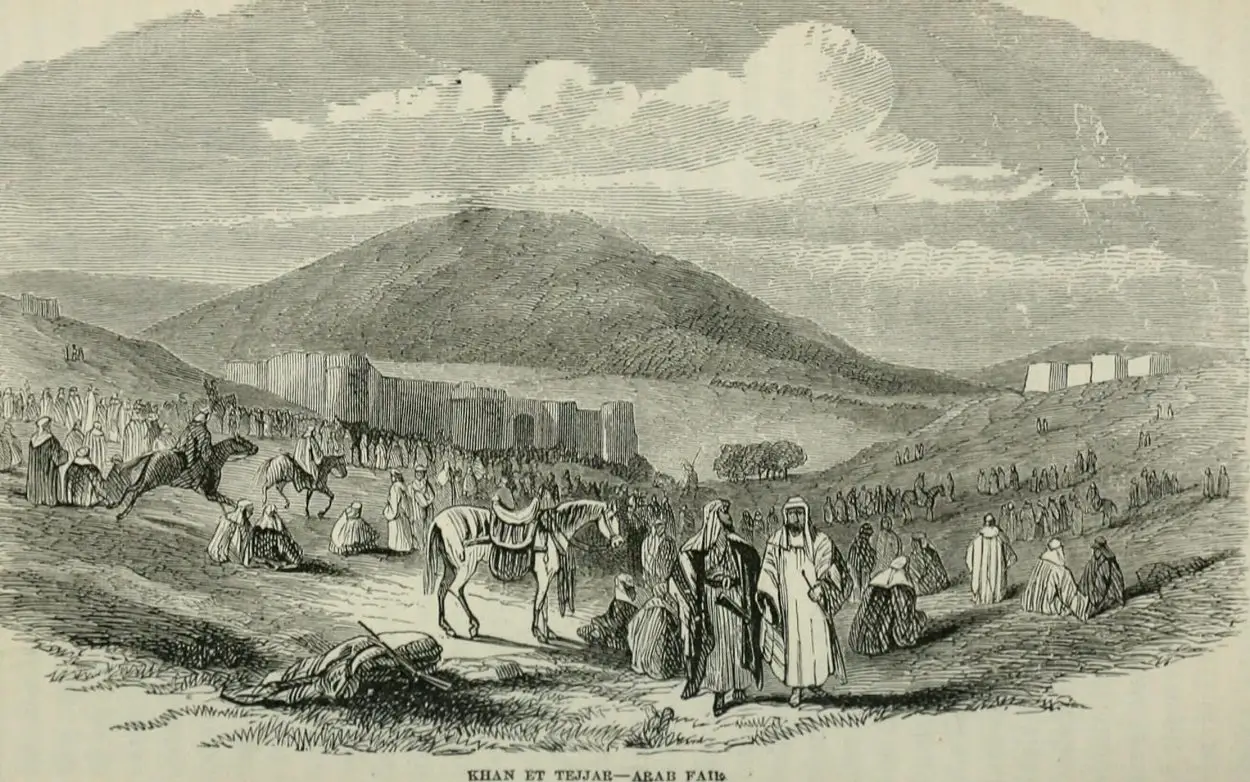
During excavations near Beit Keshet in Lower Galilee, Israel, archaeologists from the Israel Antiquities Authority (IAA) have uncovered traces of a market within the historic Khan al-Tujjar caravanserais.
Khan al-Tujjar, meaning “merchants caravanserais”, was a resting and meeting place for merchants travelling on the trading routes between Damascus and Cairo, and between Transjordan and Acre.
Typically, a caravanserais functioned as a hostel and market, supporting the flow of commerce, information, and people as they journeyed across the network of trade routes covering Asia, North Africa and Southeast Europe, most notably the Silk Road.
The caravanserais at Khan al-Tujjar was founded during the late 16th century by Grand Vizier Sinan Pasha, an Albanian-born statesman who served five times as Grand Vizier until his death.
Describing Khan al-Tujjar, the Ottoman traveller, Dervish Mehmed Zillî, said: “It is a square, perfect fortress, built of masonry in the midst of a large, verdant meadow. It has a circumference of six hundred paces. The garrison consists of a warden and 150 men. It has a ‘double’ iron gate facing north.”
Located within Khan al-Tujjar was the Mosque of Sinan Pasha, an ornately decorated structure decorated with light blue glass enamel and rock crystal. Towering above the mosque was three minarets and seven tall domes.
Recent excavations have uncovered a compacted layer of soil containing numerous finds from the Mamluk and Ottoman periods (15th–18th centuries). According to IAA archaeologists, the finds provide a rare glimpse into the merchant market that functioned for centuries in the area between an adjacent fort and the khan.
The team found traces of animal bones belonging to dogs, horses, camels, sheep and cattle, indicative of the livestock industry and animal trading which is corroborated in a mid-19th century account by W. M. Thomson, an American Protestant missionary who worked in Ottoman Syria.
In addition, a large number of ceramic smoking pipes were found, which historical sources recount on how merchants would sit at shop entrances drinking coffee and smoking pipes.
Edna Amos-Dalali, the excavation director on behalf of the Israel Antiquities Authority, said: “The excavation also uncovered a variety of pottery vessels, some made locally, and others imported from regions such as Syria, Turkey, Italy, and China, alongside finds such as rings and jewellery. These finds provide material evidence of the large market that operated at the site.”
Header Image Credit : Internet Archive Book
Sources : IAA