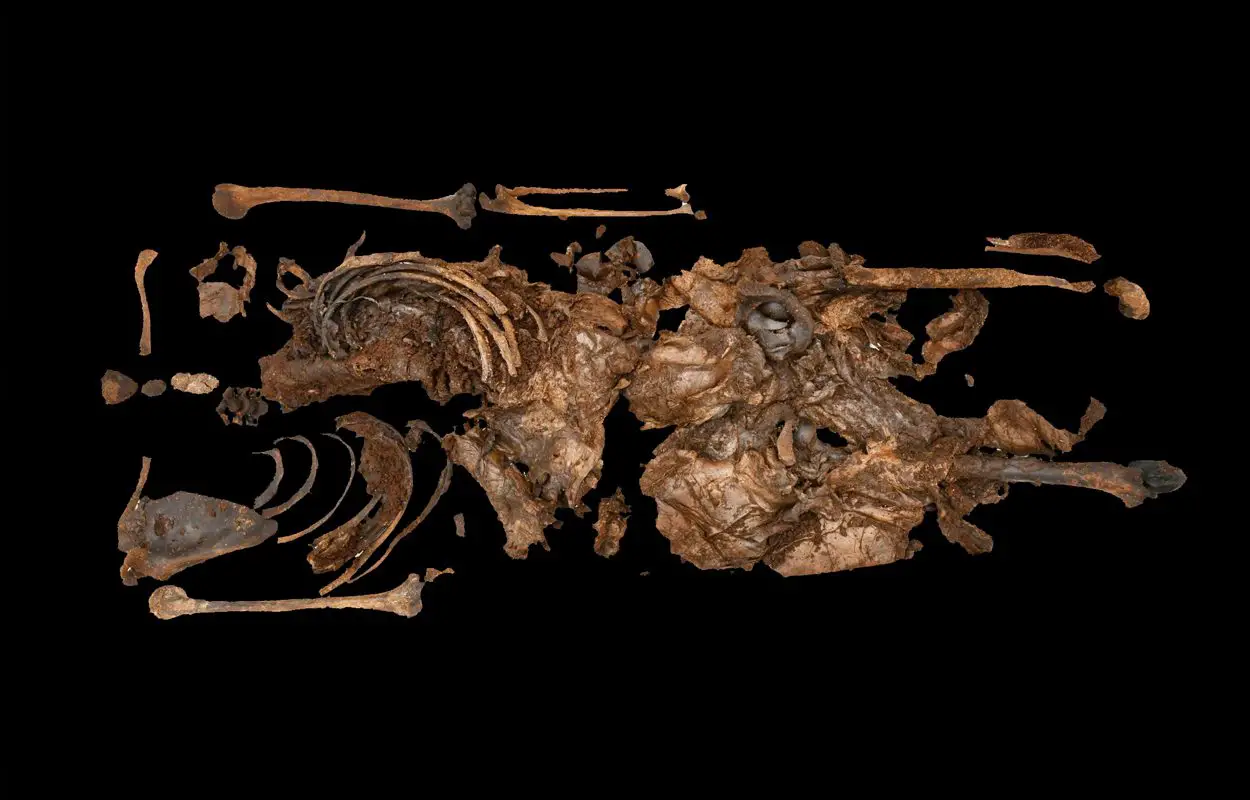
Archaeologists from the Police Service of Northern Ireland have uncovered a 2,000 to 2,500-year-old bog body in Northern Ireland.
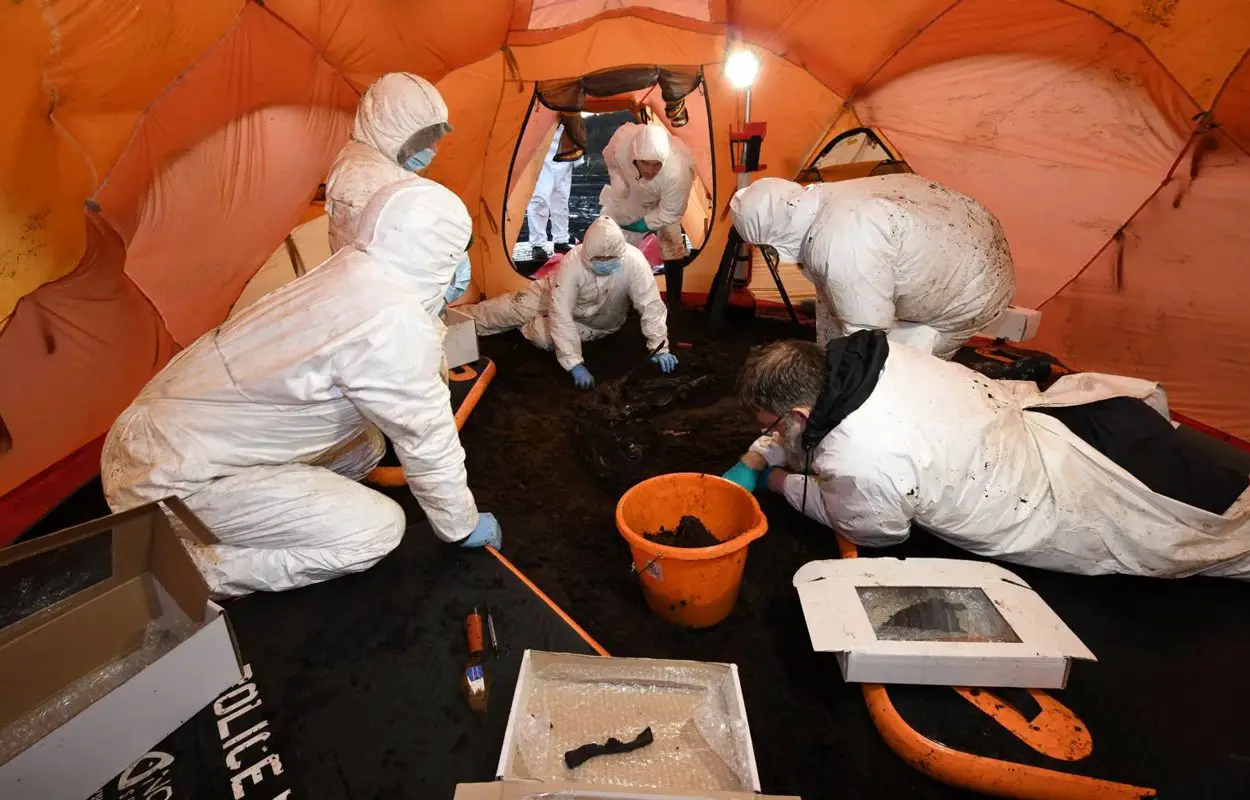
Authorities were alerted to human remains on the surface of peatland in Bellaghy, resulting in the Archaeological Unit within the Police Service of Northern Ireland’s Body Recovery Team being dispatched to conduct a forensic examination.
Detective Inspector Nikki Deehan said: “On initial examination, we couldn’t be sure if the remains were ancient or the result of a more recent death. Therefore, we proceeded to excavate the body with full forensic considerations in a sensitive and professional manner. This approach also ensures that any DNA evidence could be secured for any potential criminal investigation.”
A certified forensic anthropologist conducted a post-mortem examination, revealing that the individual was likely a male aged between 13 and 17 years old at the time of death. Although the cause of death remains unclear, the individual’s remains are remarkably well-preserved, with partial skin, fingernails of the left hand, toenails, and possibly a kidney still intact.

Radiocarbon dating conducted at the 14Chrono Centre, part of Queen’s University Belfast, has placed the year of death to around 500 BC during the early Iron Age.
Dr Alastair Ruffell of Queen’s University, Belfast said: “The remains were discovered at approximately one metre below the current land surface which matches the radiocarbon estimates. In addition, they were amongst a cluster of fossil tree remains suggesting that the body may have died or been buried in a copse or stand of trees, or washed in.”
John Joe O’Boyle, Chief Executive of Forest Service, said: “Forest Service recognises the significance of this very exciting find. This ancient bog body was discovered on land owned by the Department and we are now working with National Museums NI to transfer it to them so that they can continue with further examination and preservation of the remains.
Header Image Credit : Police Service of Northern Ireland