A study by researchers from the Collaborative Research Center (SFB) 1266 at the Christian-Albrechts-Universität zu Kiel (CAU), has revealed that Europe’s prehistoric mega-settlements relied on fertiliser and plant protein.
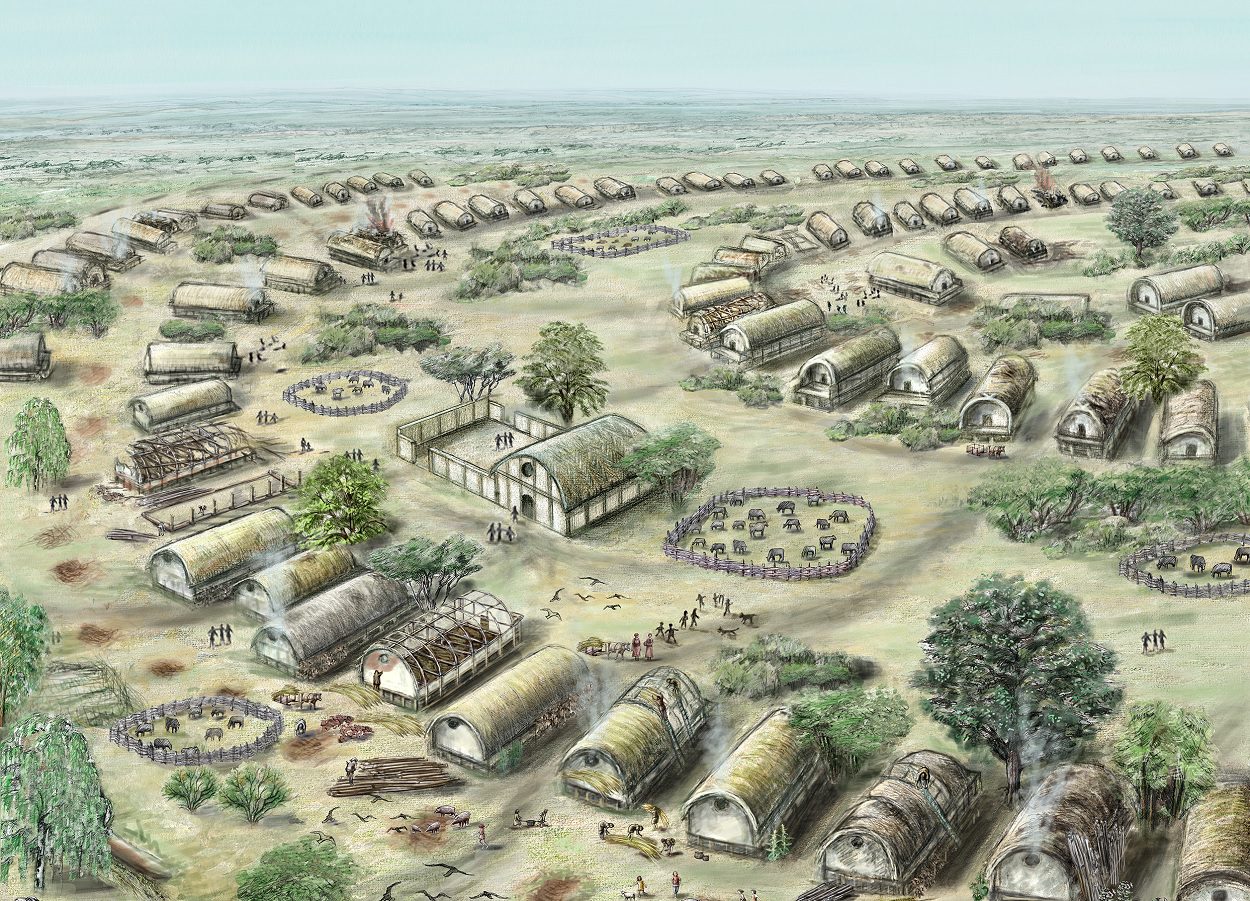
Mega-settlements of the Trypillia societies arose around 6,000 years ago in the territory of the Republic of Moldova and Ukraine. Starting around 4,150 BC, these societies constructed large planned settlements covering areas of up to 790 acres, which many researchers argue were the earliest cities in Europe.
It was previously assumed that these large communities relied on subsistence farming, however, according to Kiel paleoecologist Doctor Frank Schlütz: “The supply of the residents of the mega-settlements was based on extremely sophisticated food and pasture management.”
But how could such large groups of people ensure their nutrition with Neolithic technology? “In order to answer this question, we have determined the carbon and nitrogen isotope composition of hundreds of samples over the last 10 years,” says Johannes Müller.
The isotopes can be used to determine how domestic animals were raised, whether crops were grown with fertiliser, and the role plants and animals played in human nutrition.
“We came to the conclusion that a large proportion of the cattle and sheep were kept in fenced pastures. And the animal dung produced there was used by people to intensively fertilise peas,” says Frank Schlütz.
This is supported by studies by the University of Kiel, which determined that Trypillia farmers relied primarily on a diet of grain and peas, in what is now Ukraine and Moldova 7,000-years-ago.
Peas and grains provide nutritional value to the human diet, but are also a balance in essential amino acids. Furthermore, the resulting pea straw likely served as feed for the livestock grazing in the pastures.
According to the study: “Because of this close connection between crop production and livestock farming, the people of the mega-settlements were able to eat adequately and healthily. The labour-intensive and resource-consuming production of meat was largely eliminated.”
Header Image Credit : Susanne Beyer, University of Kiel