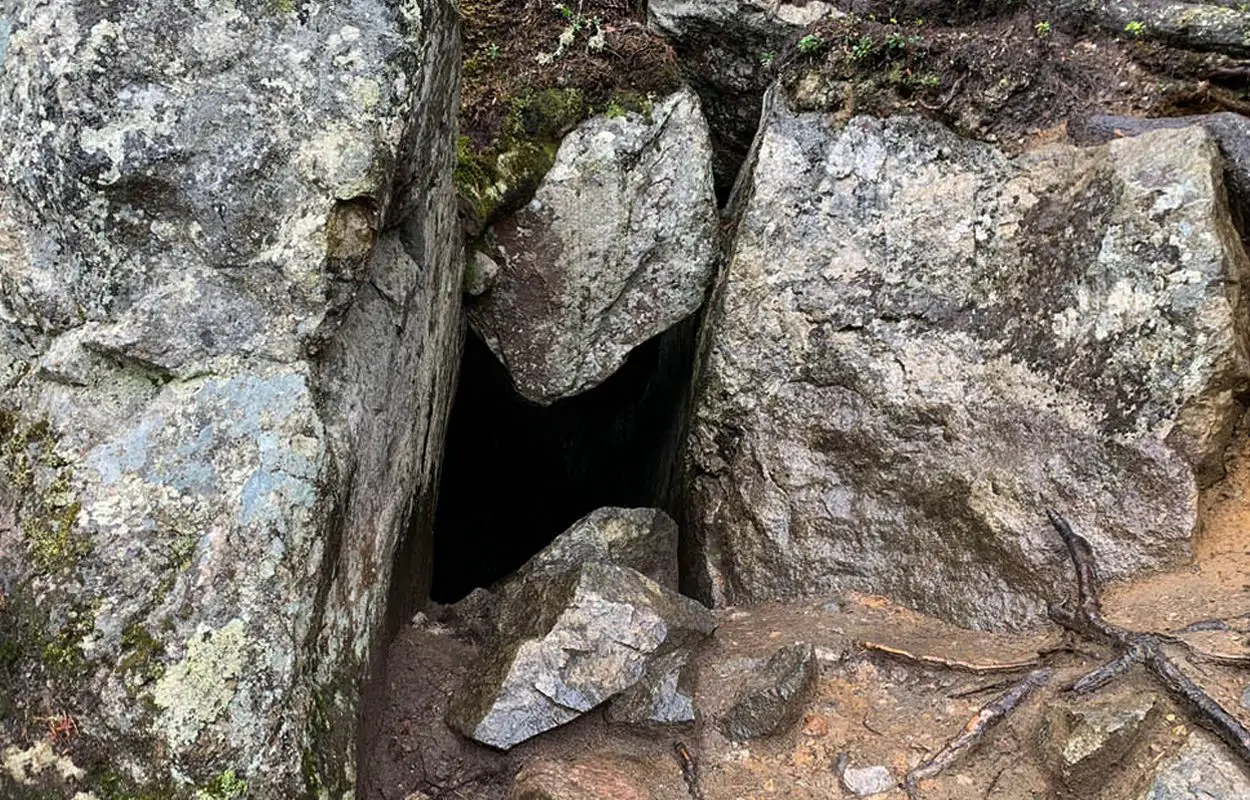
Archaeologists from the University of Eastern Finland suggest that the purported “witchcraft” associated with the Devil’s Church can be attributed to acoustic resonance.
The Devil’s Church, also known as Pirunkirkko, is a 34-metre-long crevice cave located in the Koli National Park, Finland. In the vicinity are several other caves referring to the devil, such as Pirunluola (“Devil’s Cave”), Pirunvaara (“Devil’s Mountain”), and Pirunkallio (“Devil’s Rock”).
For centuries, the Koli mountain range has been revered as a realm inhabited by spiritual entities. The peaks, named Ukko-Koli and Akka-Koli, pay homage to the pre-Christian thunder god and his consort, reflecting their significance in local mythology.
Archival sources from the Finnish Literature Society (SKS) tell of “mountain elves,” “invisible fairies,” and “great lords” that move in the area:
“The inhabitants of the mountain only play and yell there, and walk through the woods, and dance and play and drive with the bells along the mountain ravines. There’s a kind of crack where they play and walk. It is said that an iron road passes via the crack through the mountain of Koli, all the way from Taipale.”
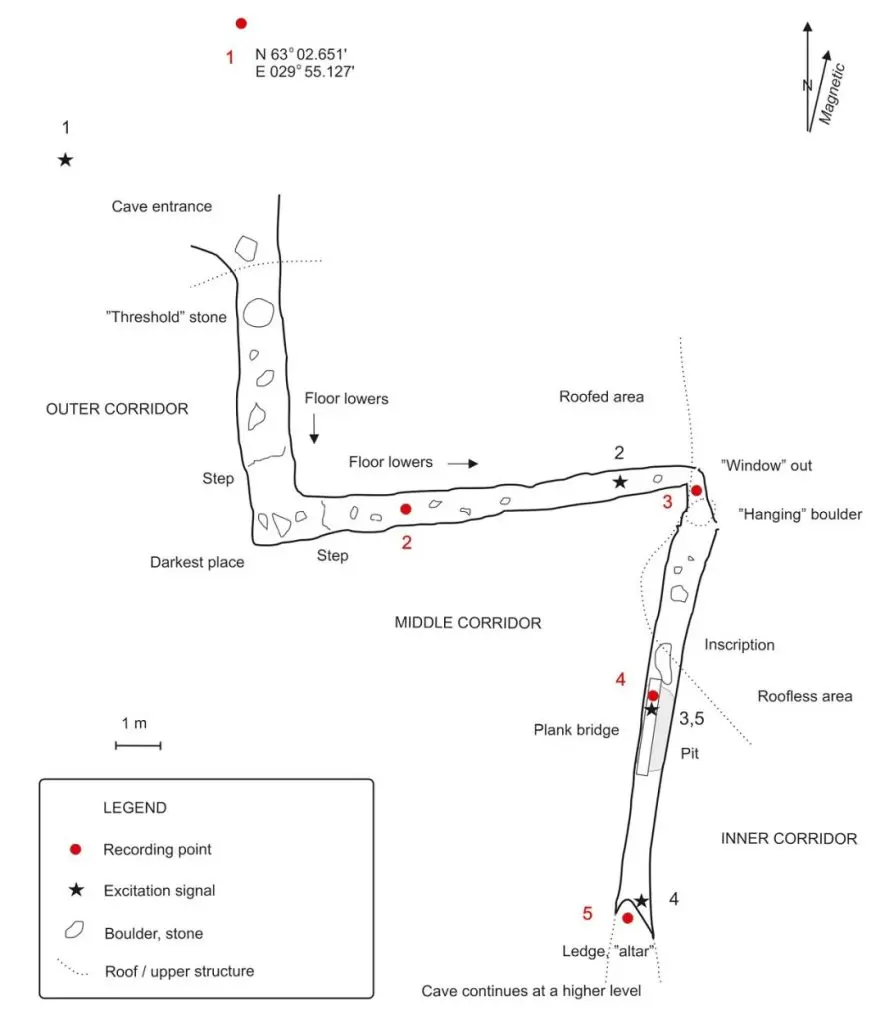
According to tradition, the Devil’s Church was a meeting place for shamans known as tietäjä, velho, or noita, who came from Finnish and Karelian agricultural communities to contact the spirit world, heal the sick, and bring balance to people and nature.
The most famous shaman was Kinolainen, also called Tossavainen, who would gather “patients” in the cave to commune with the Devil to find the causes and cures of their ailments.
Modern shamans still carry on the tradition to this day, and like their historical counterparts, they use the unique acoustic properties of the cave during incantation and singing rituals. The sages also shouted, raged, jumped, kicked, and trembled, as if fighting with or intimidating invisible forces.
In a paper published in the De Gruyter Open Access journal by Riitta Rainio from the University of Helsinki, and Elina Hytönen-Ng from the University of Eastern Finland, the researchers investigate whether the cave acoustics could have played a role in the ritualisation of the Devil’s Church and the power of its rituals.
The study used an impulse response recording and spectrum analysis, revealing a distinct resonance phenomenon that amplifies and lengthens sound at a specific frequency. According to Rainio: “Acoustic measurements conducted in the corridor-like cave show a strong resonance phenomenon.”
“The phenomenon is caused by a standing wave between the smooth parallel walls, generating a tone at the natural frequency of the cave, 231 Hz, that stays audible for around one second after sharp impulses, such as clapping, drumming or loud bangs. Tones vocalised in the cave near the 231 Hz frequency are amplified and lengthened by the cave,” added Rainio.
The researchers suggest that these specific acoustics and rituals are not individual actions but rather collective involvements with the physical surroundings and the natural environment. The reverberations enable a deep connection and interaction with a presence or entity beyond human, confirming their presence and indicating active involvement.
Header Image Credit : University of Eastern Finland





