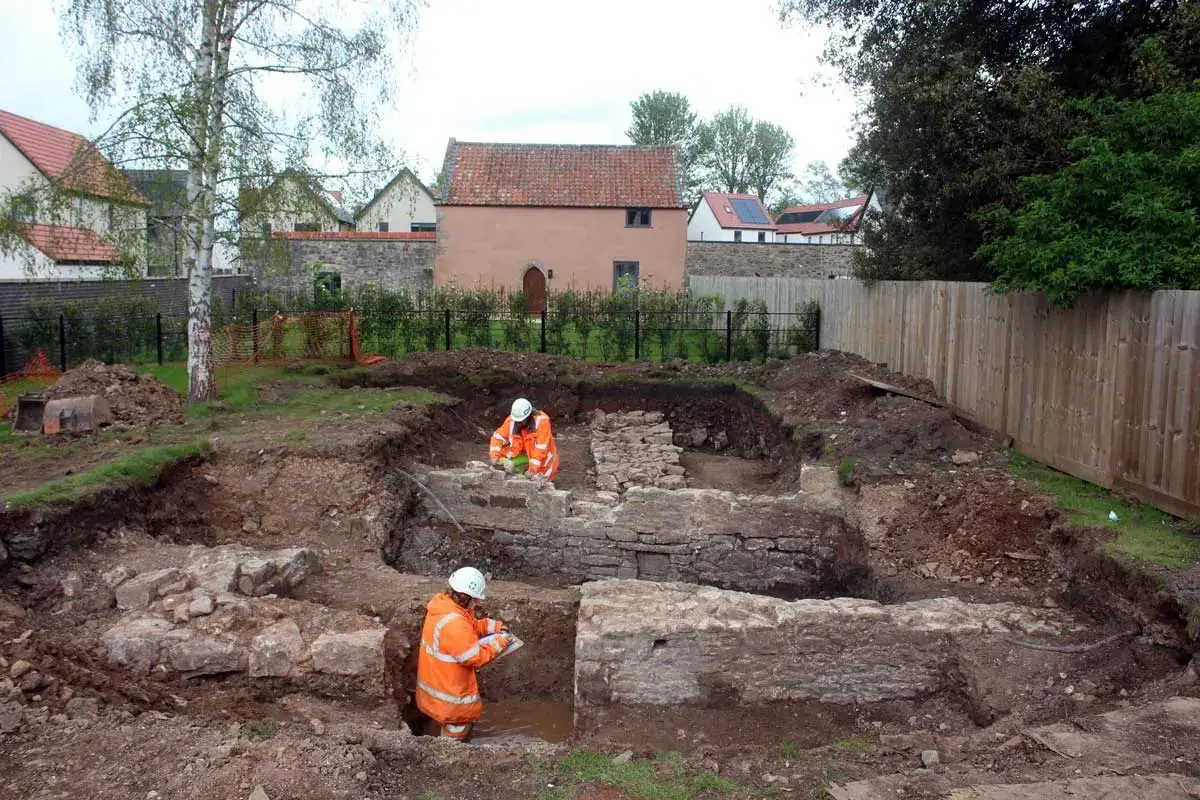
Archaeologists from Cotswold Archaeology are conducting a project to rediscover the medieval manor of Court De Wyck.
The researchers are excavating on the outskirts of the village of Claverham in North Somerset, England. During the medieval period, a settlement recorded in the Domesday Survey of AD 1086 consisted of two hamlets: Claverham and Week.
The latter was primarily centred around the manor of Court De Wyck, named after the De Wyck family, which was founded in the 12th century by the Bishop of Bath and Wells.
According to several historical accounts, remnants of the manor persisted in some form until 1815, when it was ultimately demolished due to a fire leaving only a chapel and the tithe barn and stables.
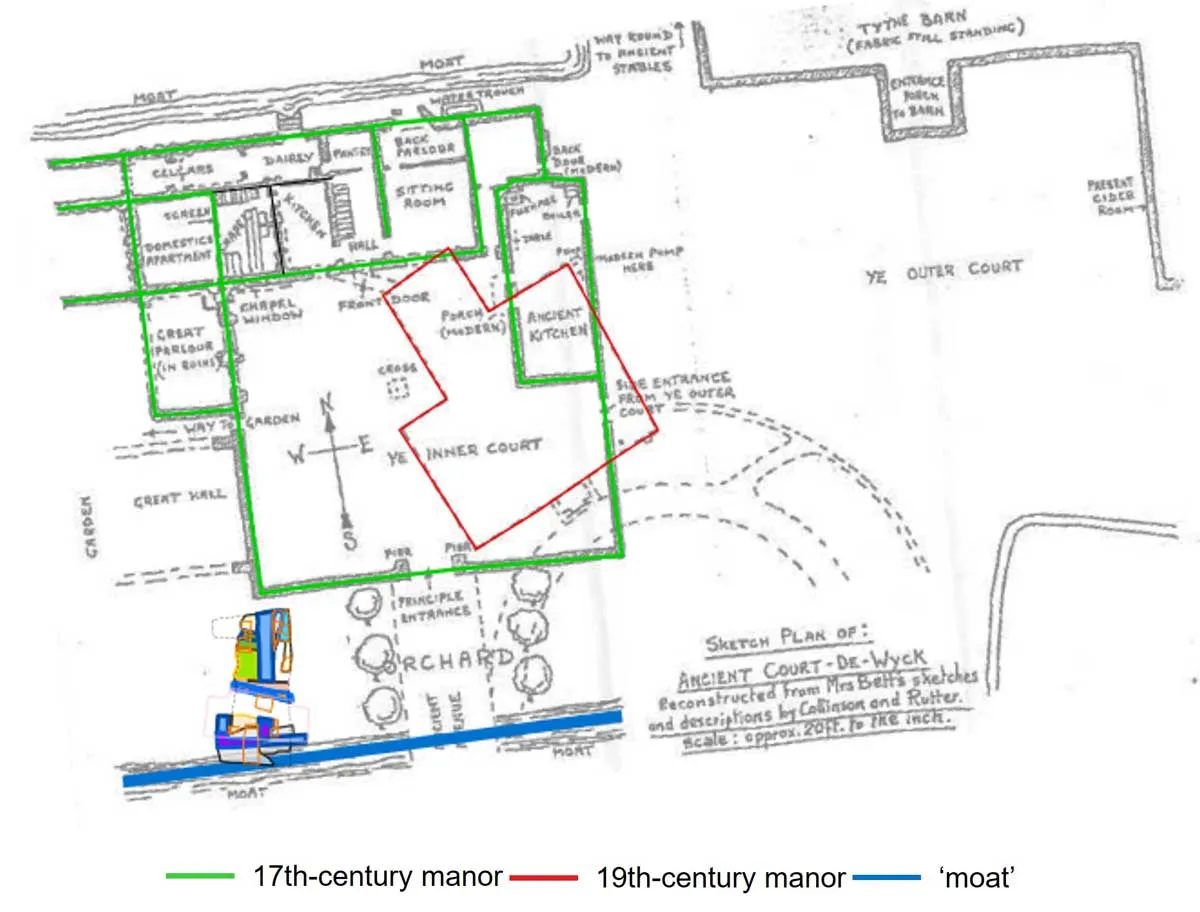
Little contemporary evidence survives regarding the layout of the manor, however, the researchers have been able to use a hand-drawn sketch plan by a Mrs Betts from the 19th century to aid in their excavations.
According to an announcement by Cotswold Archaeology: “The plan shows a range of buildings, including the chapel, positioned along the north, east, and west sides of a large courtyard, with an entrance to the south, and the chapel and other rooms to the north. From this plan, which turned out to be impressively accurate, we were able to use the location of the extant chapel to orient ourselves on the ground.”
During their excavations, the archaeologists uncovered a north/south orientated stone wall on the same alignment as the courtyard wall of the manorial complex (as shown on the 19th century drawing plan), and potentially representing the remains of one of the western walls of the manor or its chapel.
To the south, the researchers discovered the remnants of a significant east-west stone wall, which stood at nearly 2 meters in height. This wall seems to indicate a later development of what was originally thought to be a “moat.” In reality, this “moat” is more likely a substantial boundary ditch and could have served as a precursor to the boundary wall identified in the southern section of the excavation site.
In the northern part of the excavation area below the north/south wall are the foundations of an even earlier building, evidenced by ceramics that indicate a potential date from the 13th–14th century.
Excavations also found two perpendicular Roman ditches with Southeast Dorset and Southwest Black Burnished Ware ceramics, a fragment of boxed flue tile which was an essential part of the heating system of Roman buildings.
Header Image Credit : Cotswold Archaeology







