Archaeologists from the University of Bologna have developed a system of AI algorithms that can identify previously undiscovered archaeological sites in the southern Mesopotamian plain.
Deep learning has found multiple uses in every field of application. In the context of archaeology, it can help in classifying objects and text, finding similarities, building 3D models, and the detection of sites.
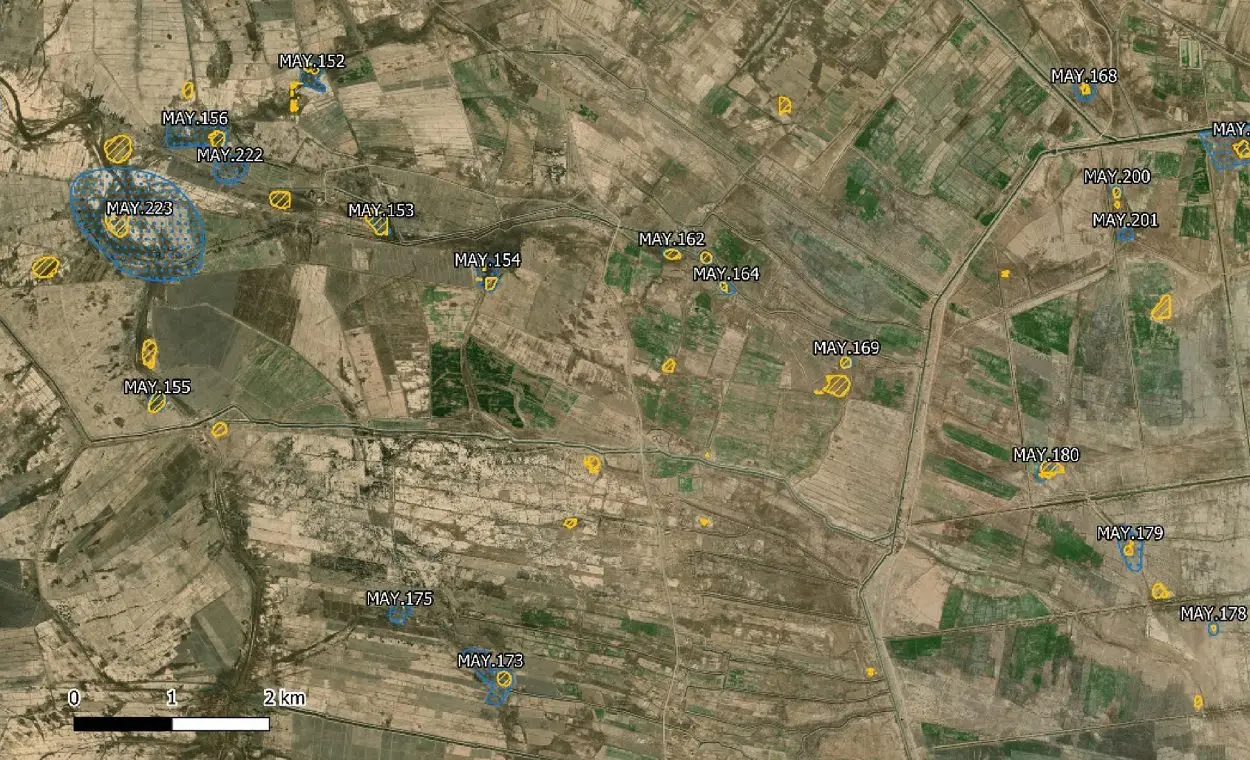
The team conducted a test in the Maysan Province of Iraq, where the AI algorithm correctly identified sites of interest with an accuracy of 80%.
The results of the study, published in the journal Scientific Reports, emphasises the issue of thousands of satellite photos in archives that would require a large amount of resources to analyse, however, using an automatic AI system, this would massively reduce the time and resources needed.
According to the study authors: “This procedure falls into the domain of Remote Sensing (RS) which indicates the act of detecting and/or monitoring a point of interest from a distance. In the world of archaeology, this operation has become invaluable with the availability of more and better imagery from satellites that can be combined with older sources of information.”
The researchers utilised a dataset consisting of vector shapes representing the archaeologically recorded sites within the southern Mesopotamian floodplain. Through training, they developed a system capable of identifying and delineating sites using pretrained models for semantic segmentation, fine-tuned on satellite imagery, and masks of the site shapes.
The study authors said: “The potential applications of this method are far reaching and do not only concern its speed: it should rather be seen as a necessary complement to traditional expert-based photointerpretation, adding to the latter in many cases site features which may go overlooked but are likely to be significant.”
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-36015-5
Header Image Credit : University of Bologna