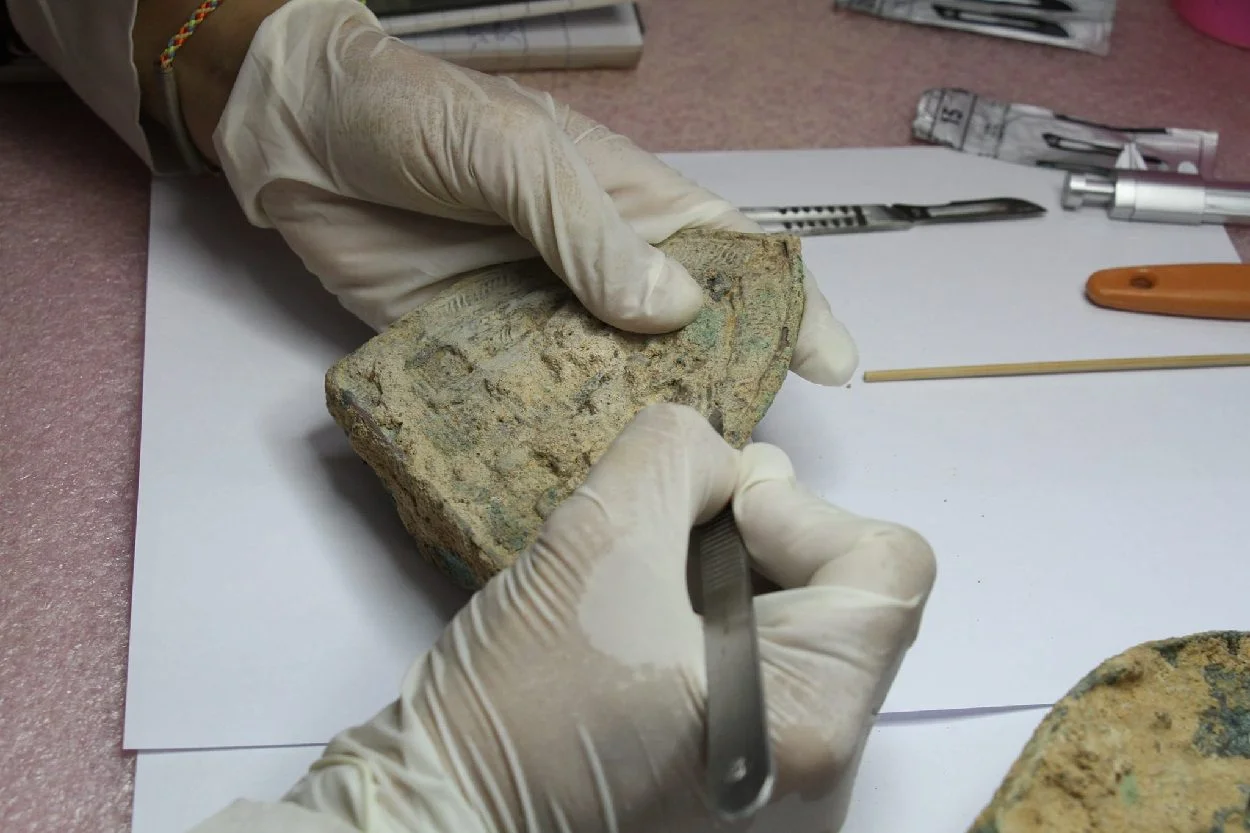
Archaeologists from the Apsara National Authority (ANA) have uncovered over 1,000 artefacts from the Angkor era during excavations at the Angkor Archaeological Park in Cambodia.
Stretching over some 400 square kilometres, the Angkor Archaeological Park contains the remains of several capitals of the Khmer Empire from the 9th to the 15th century AD, including the Temple of Angkor Wat, Angkor Thom, and the Bayon Temple with its ornate sculptural decorations.
The Khmer Empire, also known as the Angkorian Empire, is believed to have emerged in AD 802 when King Jayavarman II declared himself chakravartin (“universal ruler”, a title equivalent to “emperor”) in the Phnom Kulen mountains.
At its peak, the Khmer Empire ruled over and/or vassalized at times, most of mainland Southeast Asia and parts of Southern China, stretching from the tip of the Indochinese Peninsula northward to the modern Yunnan province of China, and from Vietnam westward to Myanmar.
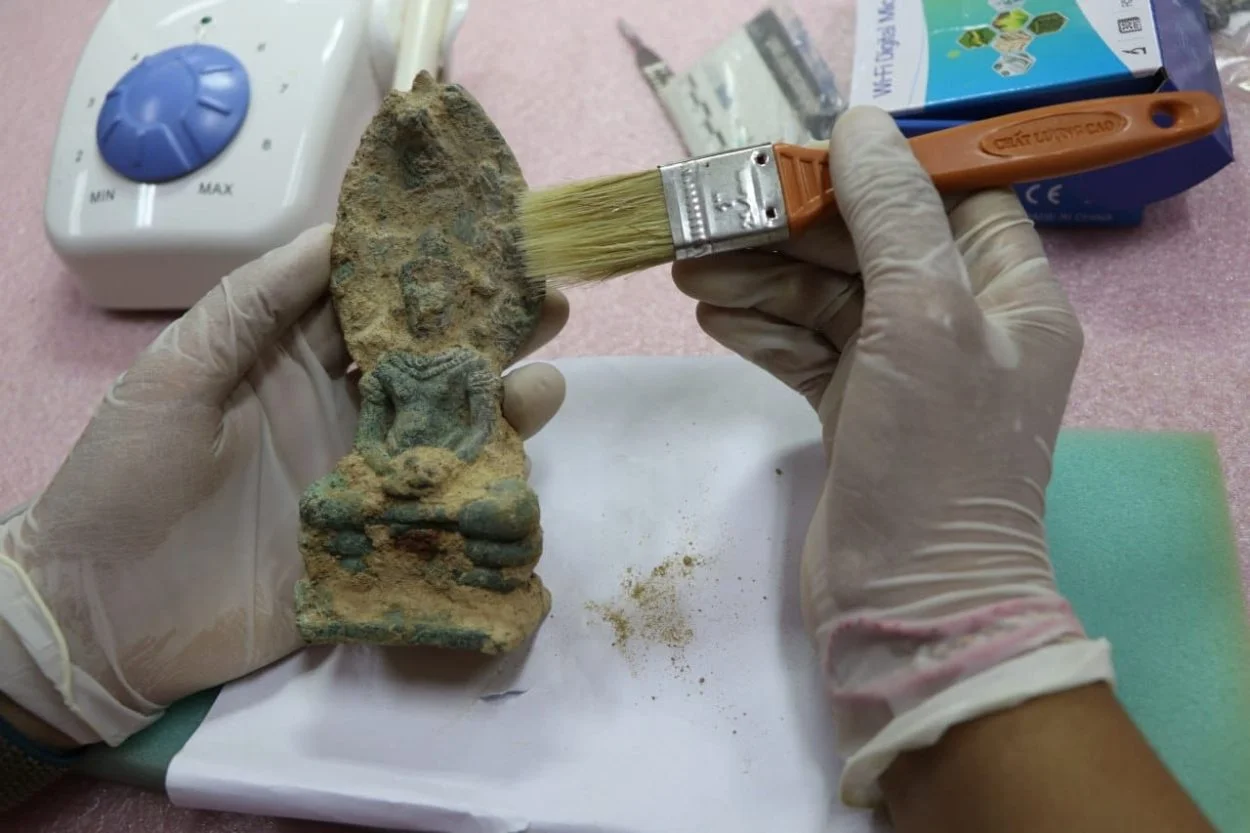
Archaeologists conducting excavations at an ancient temple near Srah Srang, a baray or reservoir constructed during the mid-10th century, has led to the discovery of 1,055 artefacts, including 103 contemporary works of art made from metal and Buddha statues.
Long Kosal, an ANA spokesman, said: “The ancient statues were a metallic development around the 12th century, but we need to study more for a better understanding of the objects. Even though the excavations at the site have been completed, the artefacts are in a state of disrepair and need to be preserved carefully. Therefore, the ANA team is still cleaning and repairing them.”
Apsara National Authority (ANA)
Header Image Credit : Apsara National Authority (ANA)





