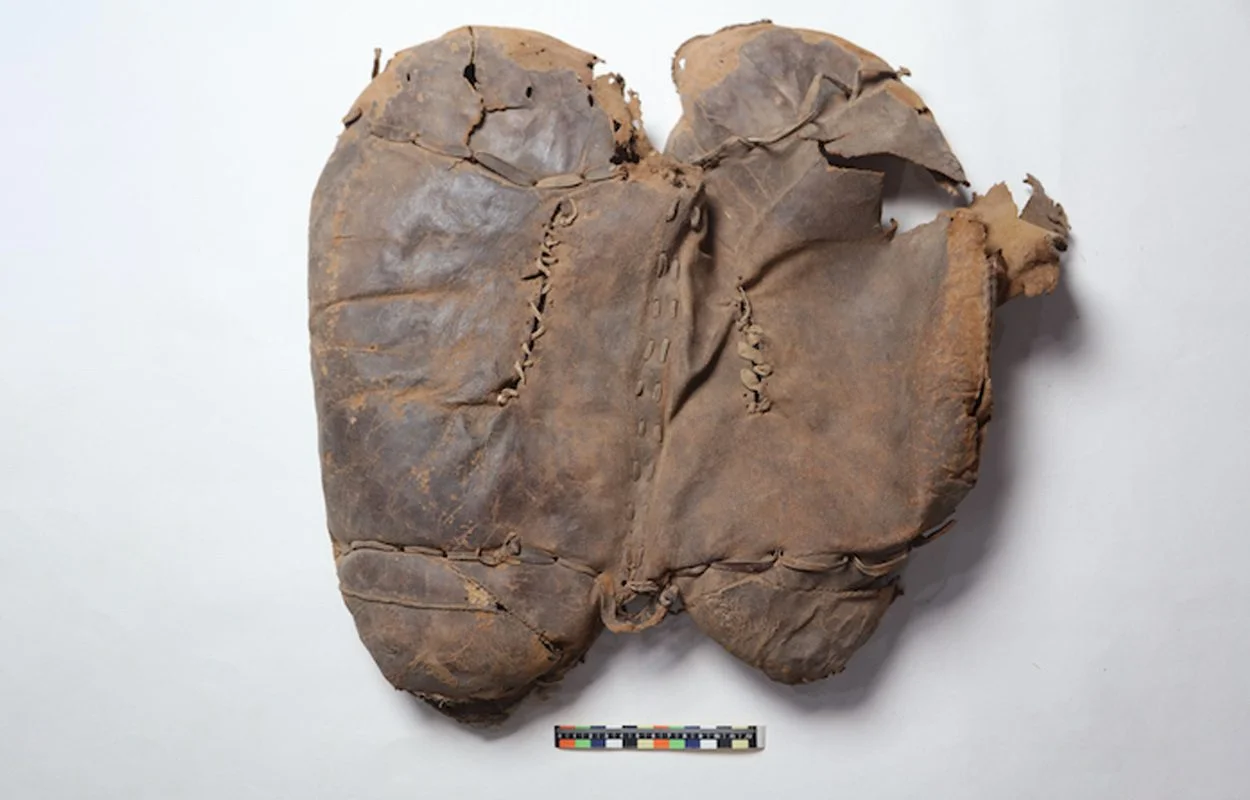
Archaeologists excavating a tomb at the Yanghai cemetery in the Turfan Basin, located in the eastern end of the Tian Shan mountains in the Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang, China, have found a well-preserved soft leather saddle associated with the Subeixi Culture.
The emergence of the saddle brought about a significant enhancement to horseback riding, leading to a revolutionary impact on warfare and facilitating swift long-distance travel throughout Eurasia.
The tomb contains the burial of an adult female in a flexed position, who was buried with a hide coat, leather boots, a pottery cup, a braided woollen band, remains of woollen fabric, and the leather saddle that was placed at her buttocks.
According to the excavation report, the saddle is formed of two oval shaped cushion pads made of cow hide and is filled with a mixture of deer and camel hair. The upper side of the saddle is made up of five pieces of hide sewn together with fine running stitches using sinew thread that forms the seat and the front supports.
Based on the tomb construction and burial items, the Turfan Administration of Cultural Relics dates the burial to between the 7th and 4th century BC.
A recent carbon dating analysis, the results of which are published in the journal Science Direct, has dated the saddle to a range of 727–396 BC with a 95.4% probability. This supports the assigned typologically age previously suggested and is oldest saddle datedin China.
According to the study authors: “The saddle and other equestrian paraphernalia in the Yanghai grave assemblages further illuminate the role of horsemanship in sedentary communities in eastern Central Asia during the first half of the first millennium BC”.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ara.2023.100451
Header Image Credit : P. Wertmann; M. Yibulayinmu