Excavations administered by the State Administration of Cultural Heritage have discovered a fortified settlement complex from the Datuotou Culture in the Fengtai District of Beijing, China.
The Datuotou Culture, named after the type-site of Datuotou, was an ancient culture that emerged during China’s Bronze Age. The culture was roughly distributed in the south of the Yanshan, reaching the Zhangjiakou region and Huliuhe Valley to the west, the Yanshan to the north, Bohai to the east, and the Laishui and Jumahe in the south.
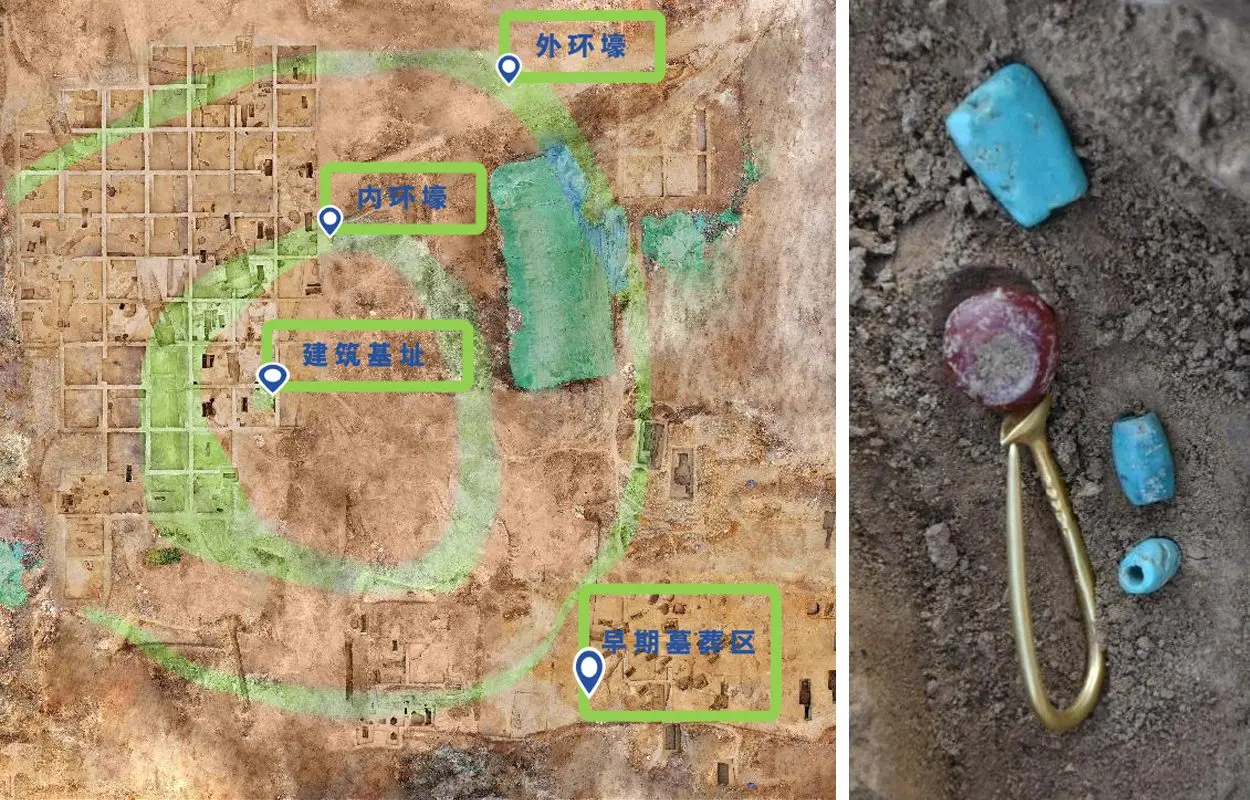
Since 2021, excavations have revealed a large, fortified settlement designated as Xingong, which dates from between 1500 BC to 1300 BC, in addition to archaeological remains from the late Shang Dynasty (1600 BC–1045 BC) and the Western Zhou Dynasty (1045 BC – 771 BC).
The settlement consists of numerous dwellings which are protected by an outer ring moat and inner ring ditch. To the southeast of the settlement are 27 vertical high-status pit tombs, where archaeologists have found painted ceramics, boot-footed pottery, jade rings, turquoise necklaces, gold earrings, and red agate beads.
An isotope analysis conducted on the human remains has revealed that the settlement inhabitants mainly lived on a diet of millet, with little variation in the dietary habits between the low status and high-status individuals.
According to the State Administration of Cultural Heritage: “The Xingong site is an important Datuotou cultural site, and it is also one of the earliest Bronze Age settlement sites found in Beijing. It represents the cultural and human exchanges, and the blending between the north and south of Yanshan Mountain and the northern grasslands in the Bronze Age.”
The cemetery also provides a unique insight into the dietary habits and burial customers of the Datuotou culture, and how they changed into the Shang Dynasty and the Western Zhou Dynasty.
State Administration of Cultural Heritage
Header Image Credit : State Administration of Cultural Heritage