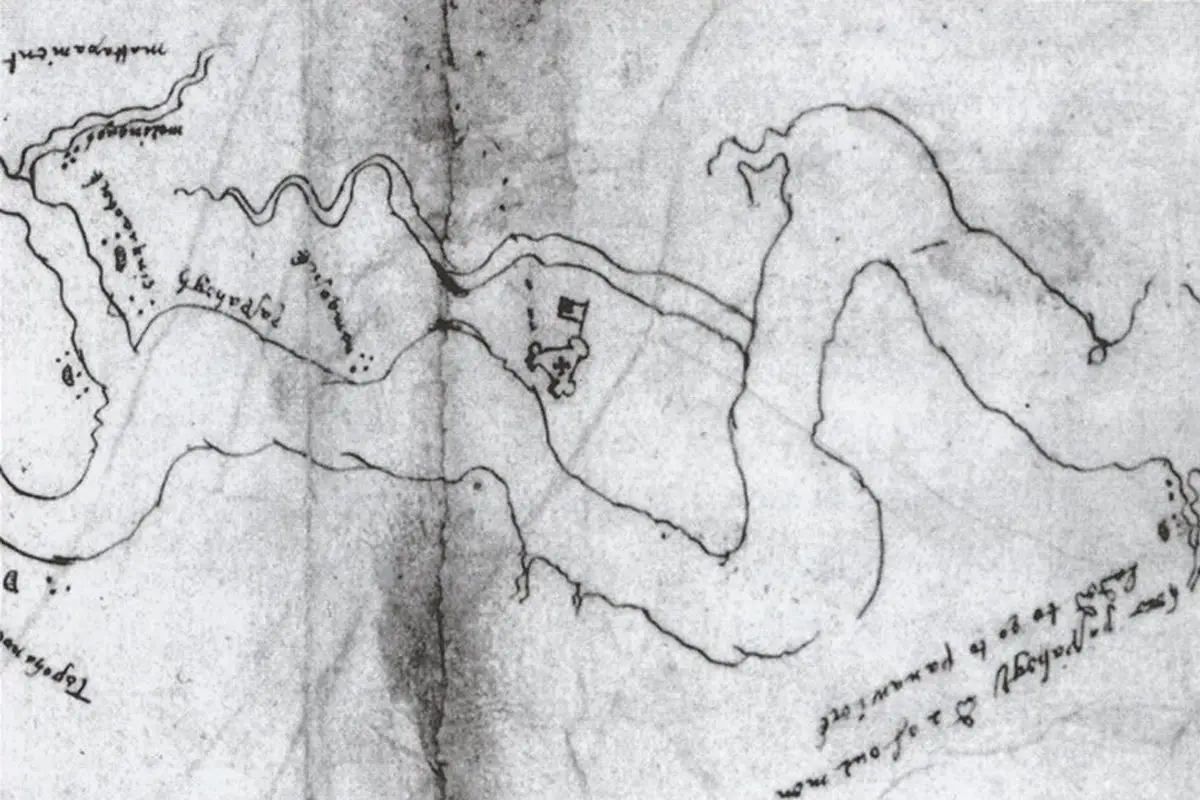
A map known as the Zuñiga Map may lead to further discoveries at James Fort, the first permanent English settlement in the Americas.
The Zuñiga Map is a manuscript depicting the Chesapeake Bay and Tidewater Virginia, which is a copy of a map probably drawn by Captain John Smith, who played an important role in the establishment of the colony at Jamestown.
The map is named after Don Pedro de Zúñiga, a Spanish ambassador to England who sent the map to Philip III of Spain in 1608. The map is significant for noting the location of native villages, the location of Jamestown, and the architecture of James Fort, which is used in the logo for the Jamestown Rediscovery Project.
A letter from Zuñiga to Philip III, housed in the British Library, reads: “I have thought proper to send Y.M. a plan of Virginia and another of the Fort which the English have erected there, together with a report given to me by a person who has been there. Still, I am trying to learn more, and I shall report about it.”
A closer examination of the map shows a feature that looks like a flag extending from the north bulwark of the fort, which has led to new excavations on a previously unexplored area of Jamestown Island.
According to former Jamestown curator, Bly Straube, the flag may have been incorrectly interpreted and could indicate an enclosure or garden that supported the fort inhabitants.
Back in 2019, researchers from the Jamestown Rediscovery Project conducted a ground penetrating radar (GPR) survey on the area indicated by the flag. The survey revealed a large ditch that archaeologists believe dates to 1608.
Excavations in 2022 found a Confederate moat from 1861 which cut into the ditch, in addition to a brick-lined well from 1617 north of what was once Fort Pocahontas. Fort Pocahontas was a Civil War-era Confederate fort that was built on top of James Fort shortly after Confederate troops arrived at the island in 1861.
Excavations are planned in the autumn of 2023 to reveal the entirety of the well and further investigate the area indicated by the flag feature on the Zuñiga Map. John Smith wrote of more than 50 houses at Jamestown in 1608, and archaeologists have yet to uncover any of these houses in the vicinity of the fort.