Archaeologists from the Goethe-Universität Frankfurt am Main have uncovered two Roman military camps near the town of Bad Ems, in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Evidence of subsurface features were first identified in 2016 from a series of crop marks, leading to a drone photography survey of the site and geomagnetic prospecting.
The survey revealed a military camp covering an area of 19.7 acres, that could house up to 3,000 garrisoned soldiers living in tents during the duration of when the camp was occupied.
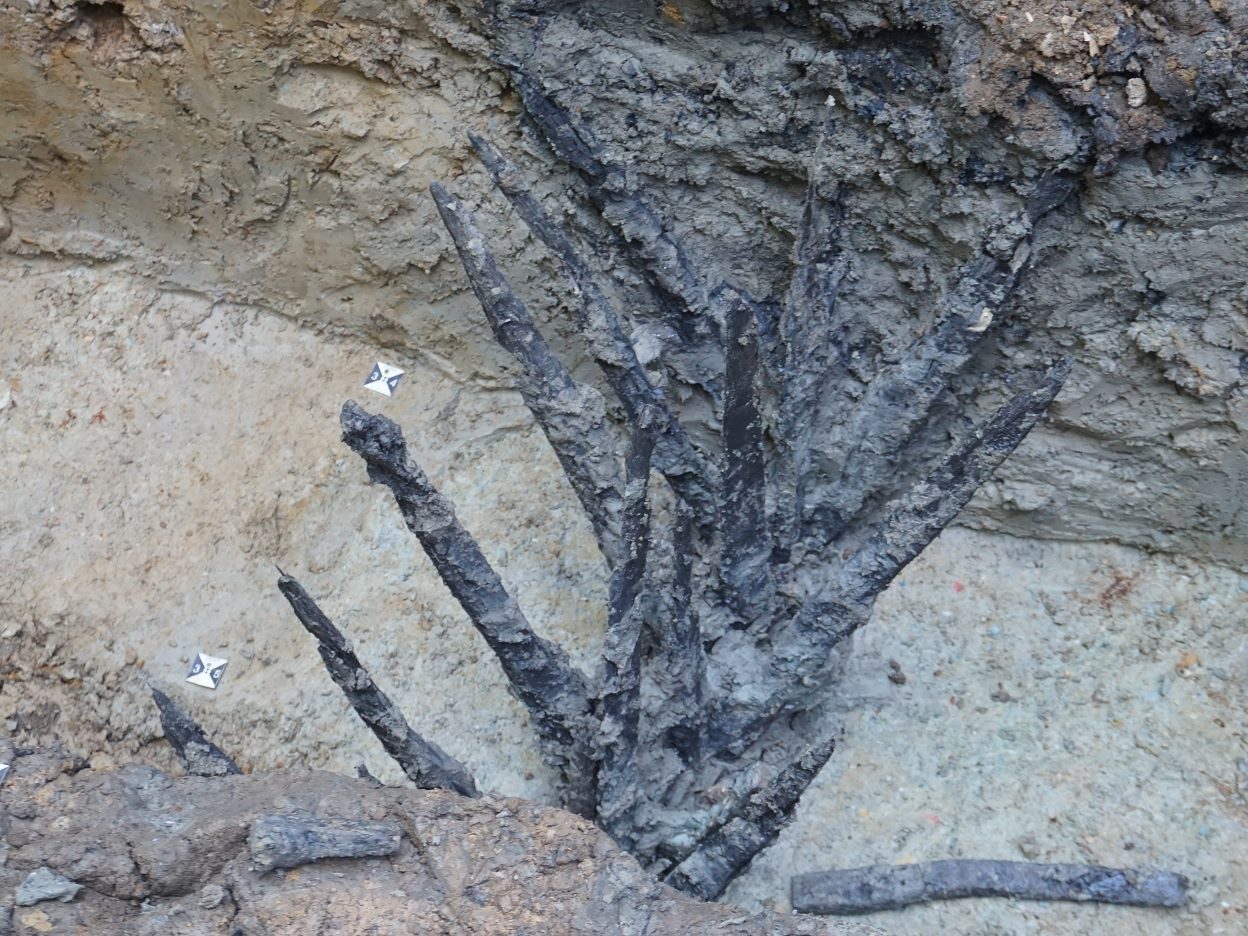
Within the interior is a building consisting of a warehouse and storeroom intended as a solid build, however, evidence of burning suggests that the site was only occupied for a few years and was never completed.
The researchers have also identified a second camp 1.2 miles away on the opposite site of the Emsbach Valley, which has a defensive construction of sharpened wooden stakes surrounded by a tapering perimeter ditch.
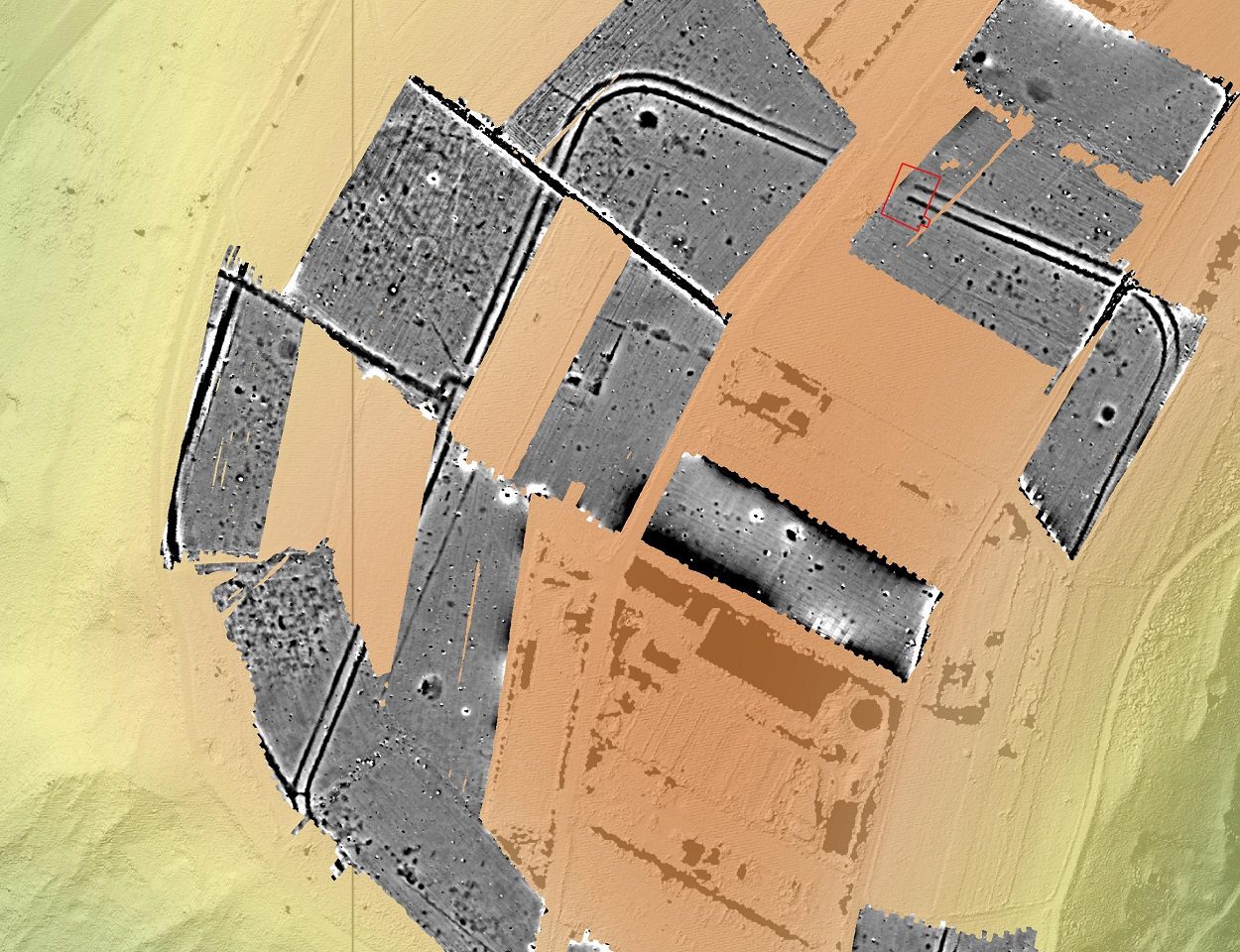
The site of the second camp was first explored in 1897, revealing evidence of processed silver ore, wall foundations and metal slag, that led to the assumption that a Roman smelting works was once located there.
New excavations have determined that the supposed furnace is actually a watchtower, belonging to a small military camp that could hold a garrison of around 40 soldiers.
In the writings of the Roman historian, Tacitus, he describes how the Roman governor, Curtius Rufus, had failed in an attempt to mine silver ore in the area around AD 47, possibly because the yield returns of silver were far too low to warrant the mining operations.
The researchers have confirmed the historical narrative by the discovery of a shaft-tunnel system for exploratory mining. The tunnel falls short of the Bad Ems passageway by only a few metres, a large deposit that in modern times has yielded 200 tons of silver.
The proximity of the camps to the mine suggests that they were constructed to provide security to the mining operations of the region, but once all mining was abandoned, the camps were burnt and the soldiers stationed elsewhere.
Goethe University in Frankfurt am Main





