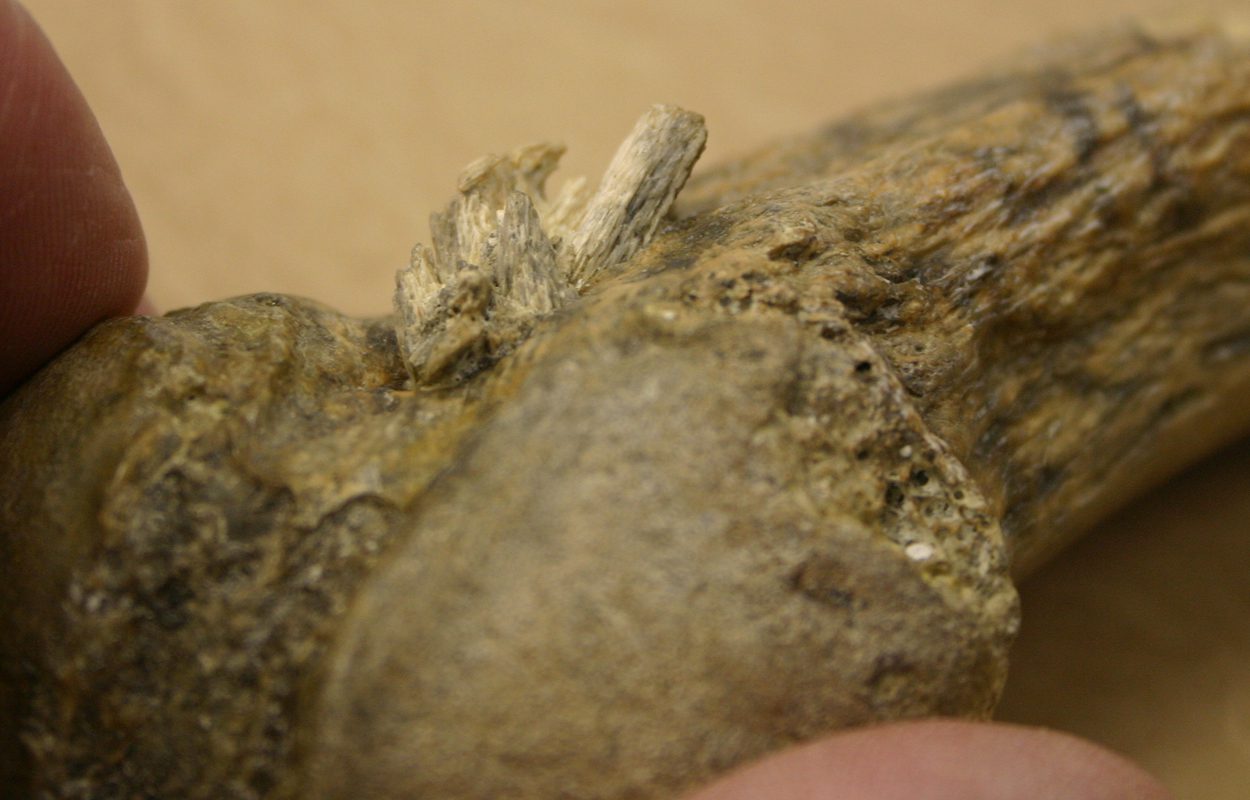
A team of researchers from the Texas A&M University have found the oldest bone projectile point in the Americas.
The projectile point is made from bone and dates from 13,900-years-ago, predating other projectile points found to be associated with the Clovis people by 900 years.
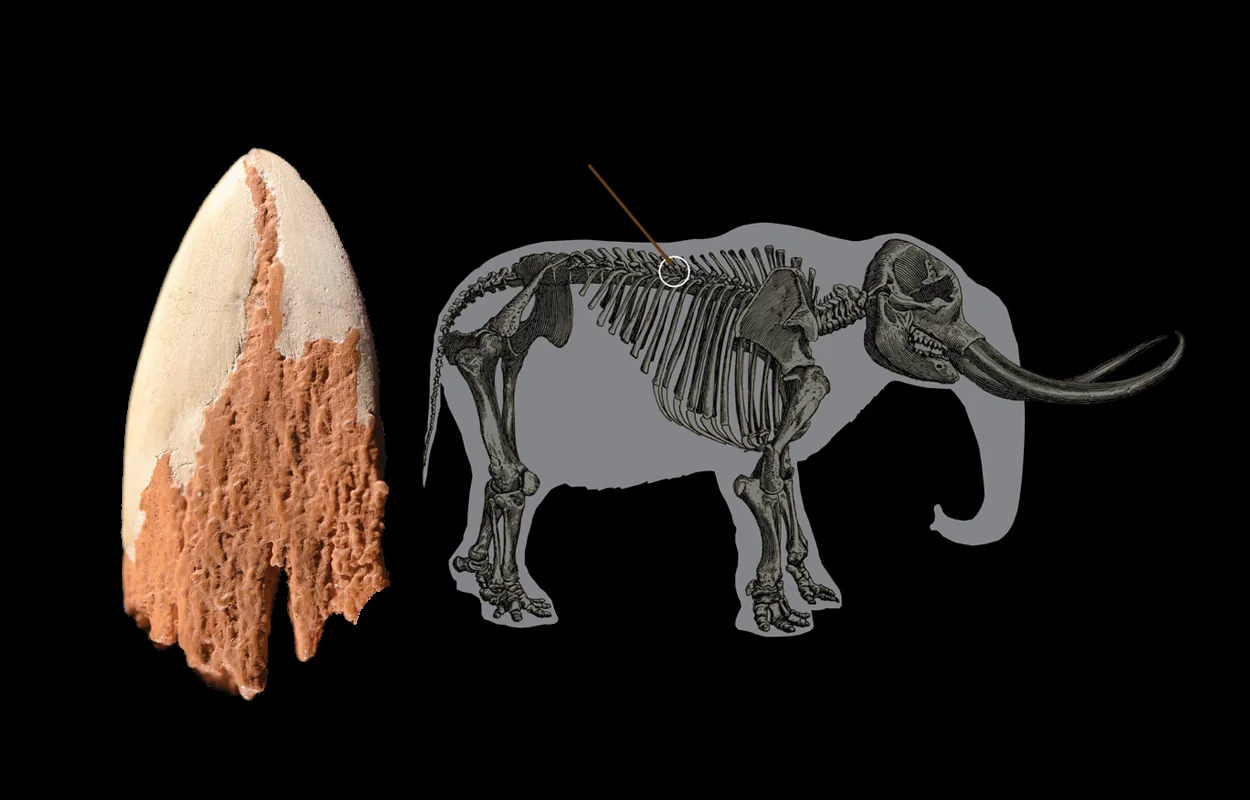
The team were studying bone fragments embedded in a mastodon rib bone, previously excavated by archaeologists at the Manis site in Washington state from between 1977 to 1979.
A study, published in the journal Science Advances, conducted a CT scan and 3D models on the bone fragments, revealing the tip of a projectile point made from the bone of a Mastodon from the extinct genus Mammut.
Mastodons inhabited North and Central America during the late Miocene or late Pliocene, until their extinction at the end of the Pleistocene 10,000 to 11,000 years ago. Modern reconstructions based on partial and skeletal remains suggest that mastodons were very similar in appearance to elephants and, to a lesser degree, mammoths, though not closely related to either one.
Dr. Michael Waters, Director of Texas A&M’s Centre for the Study of First Americans said: “We isolated the bone fragments, printed them out and assembled them,” Waters said. “This clearly showed this was the tip of a bone projectile point. This is this the oldest bone projectile point in the Americas and represents the oldest direct evidence of mastodon hunting in the Americas.”
“What is important about Manis is that it’s the first and only bone tool that dates older than Clovis. At the other pre-Clovis site, only stone tools are found. This shows that the First Americans made and used bone weapons and likely other types of bone tools,” added Waters.
The projectile point is made from a mastodon’s leg bone and was intentionally shaped into a projectile point form. When it was thrown, the hunter’s intention was to get between the ribs and impair lung function, however, the hunter missed and it became lodged in the mastodon’s rib.
Not much is known about the people who used the Manis spear point other than they were some of the first Indigenous people to enter the Americas.
“It is looking like the first people that came to the Americas arrived by boat,” said Waters. “They took a coastal route along the North Pacific and moved south. They eventually got past the ice sheets that covered Canada and made landfall in the Pacific Northwest.”
“It is interesting to note that in Idaho there is the 16,000-years-old Coopers Ferry site, in Oregon is the 14,100-year-old site of Paisley Caves. And here we report on the 13,900-year-old Manis site. So there appears to be a cluster of early sites in the Northwestern part of the United States that date from 16,000 to 14,000 years ago that predate Clovis. These sites likely represent the first people and their descendants that entered the Americas at the end of the last Ice Age.”
https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ade9068
Header Image Credit : Centre for the Study of the First Americans, Texas A&M University





