Archaeologists are one step closer to solving the mystery of Stuarts Town, the missing 17th century Scottish settlement in Port Royal, South Carolina, United States.
Stuarts Town was an initiative by the Carolina Company, founded to secure colonies in America that were exempt from English trade restrictions, and as a venture to boost Scotland’s struggling economy.
Stuarts Town was also meant to serve as a refuge for presbyterians facing religious persecution in Scotland, due to new restrictive liturgy introduced by Charles II.
On a reconnaissance trip to the South Carolina region in 1682, a site at Port Royal was chosen and settled in 1684, squeezed between the English colony of Charlestown and the Spanish colonialists of Northern Florida.
Spanish privateers attacked the colony in 1686, killing all the town’s livestock and burning all the structures to the ground. With Stuarts Town abandoned, the Carolina Company was unable to raise new revenue from investors and their initiative in the New World was dead.
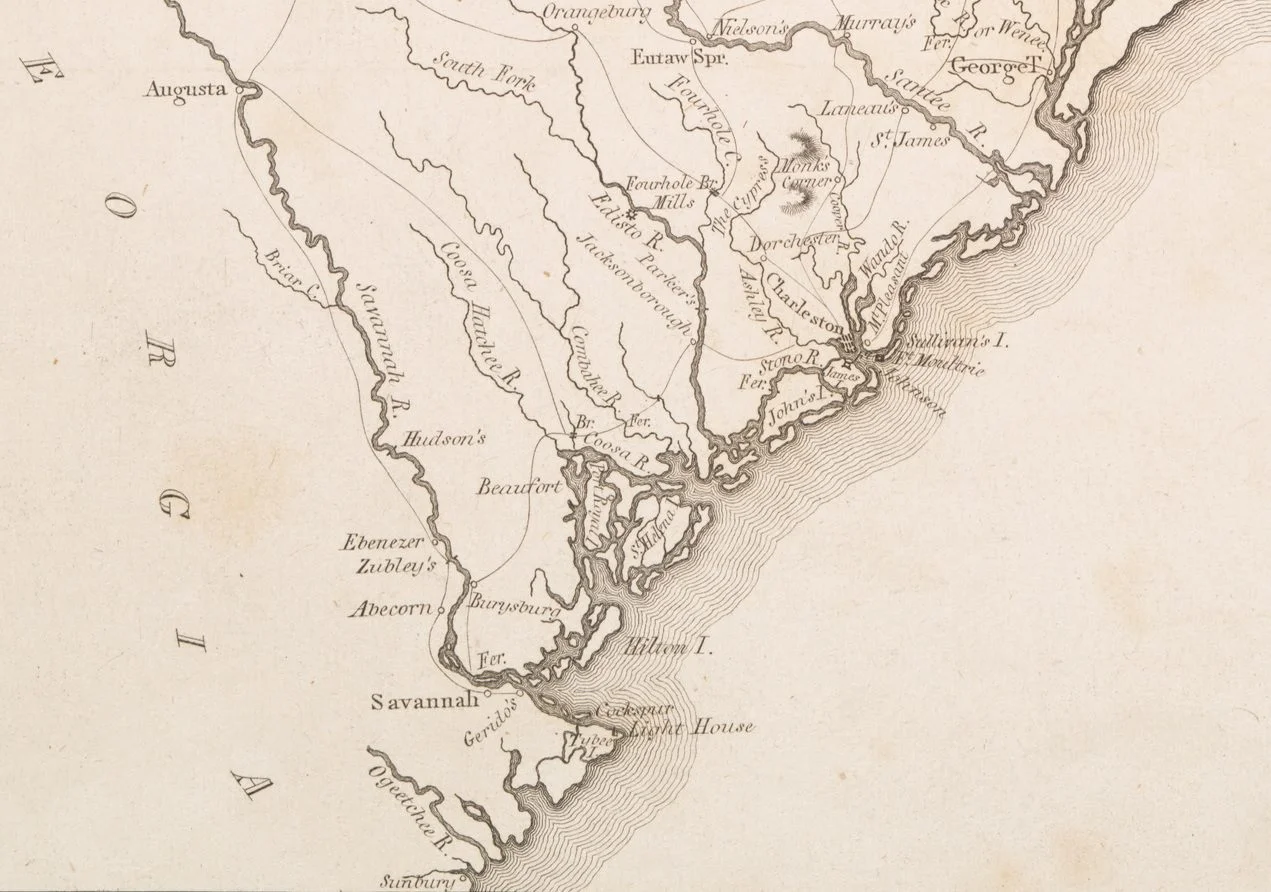
The exact location for Stuarts Town has since been lost, with the generally accepted theory previously pointing to Spanish Point, a piece of land that juts into the Beaufort River about 3 miles north of the Port Royal Sound.
However, archaeologists from the University of South Carolina (USC), believe that the town is located further north where downtown present-day Beaufort is located.
This is partly based on an 18th century land deed which the researchers believe was misinterpreted, instead suggesting the document points to Beaufort and not Spanish Point.
Excavations by the USC team on 11 properties in Beaufort have found shards of what is likely 17th century pottery.
Although no evidence of structures have yet been identified, the ceramic evidence suggests that the team are one step closer to finding Stuarts Town in Beaufort, especially when you consider that no comparable evidence has been found in Spanish Point.
Header Image Credit – NYPL’S Public Domain Archive