A WW2 treasure map has been released by the National Archives, part of the annual Open Access Day in the Netherlands for 2023.
The Open Access Day is an unveiling of former classified or confidential documents.
This year, 1300 pages of archived documents have been made public, including minutes from meetings by senior ministers, WW2 files from the Intelligence Bureau of the Ministry of War, personnel files of spies and the resistance movement, and documents investigating abuses in the internment camps where collaborators were imprisoned after the war to await trial.
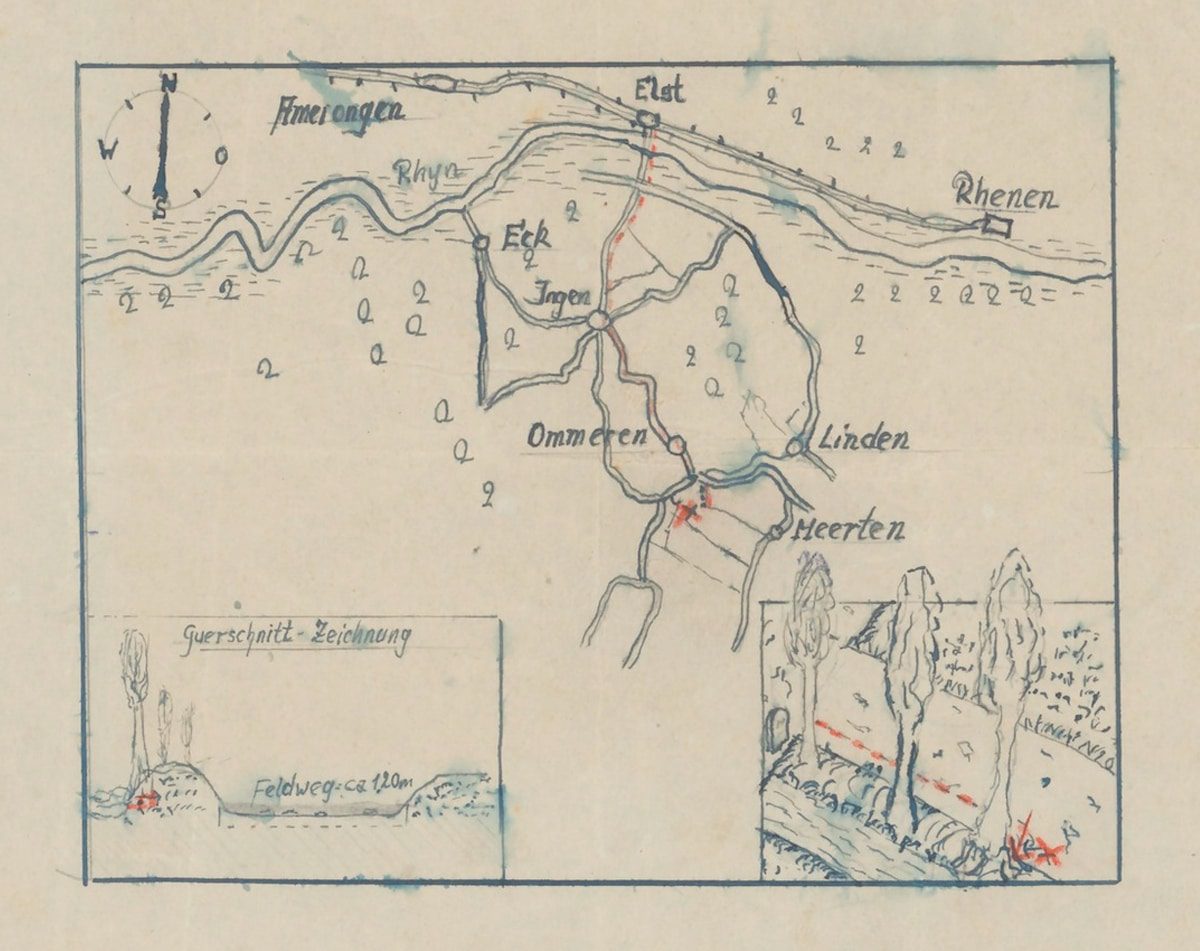
Among the released documents is a map from the archives of the Netherlands Management Institute, which is said to indicate the location of a treasure stash looted from the Arnhem bank vault by German soldiers in 1944.
According to contemporary accounts by a German parachutist who served in Velp near Arnhem, the treasure contains jewellery, watches, and gems, buried in four zinc ammunition boxes in a field near Ommeren, Lienden and Meertenwei.
The map is a crude drawing of the region, marking a route in red from the village of Elst on the northern banks of the Nederrijn (the Rhine), heading south to the village of Ingen.
The route then heads further south to the village of Ommeren and a road junction, adjacent to what could be interpreted as two fields where an “X” marks the spot.
Since the map was made public on Tuesday 3rd January, Ommeren has been enveloped by metal detectorists in search of the treasure, where Dutch laws states that a treasure belongs to the finder and the landowner in equal shares.
Header Image Credit : National Archives – Netherlands Management Institute