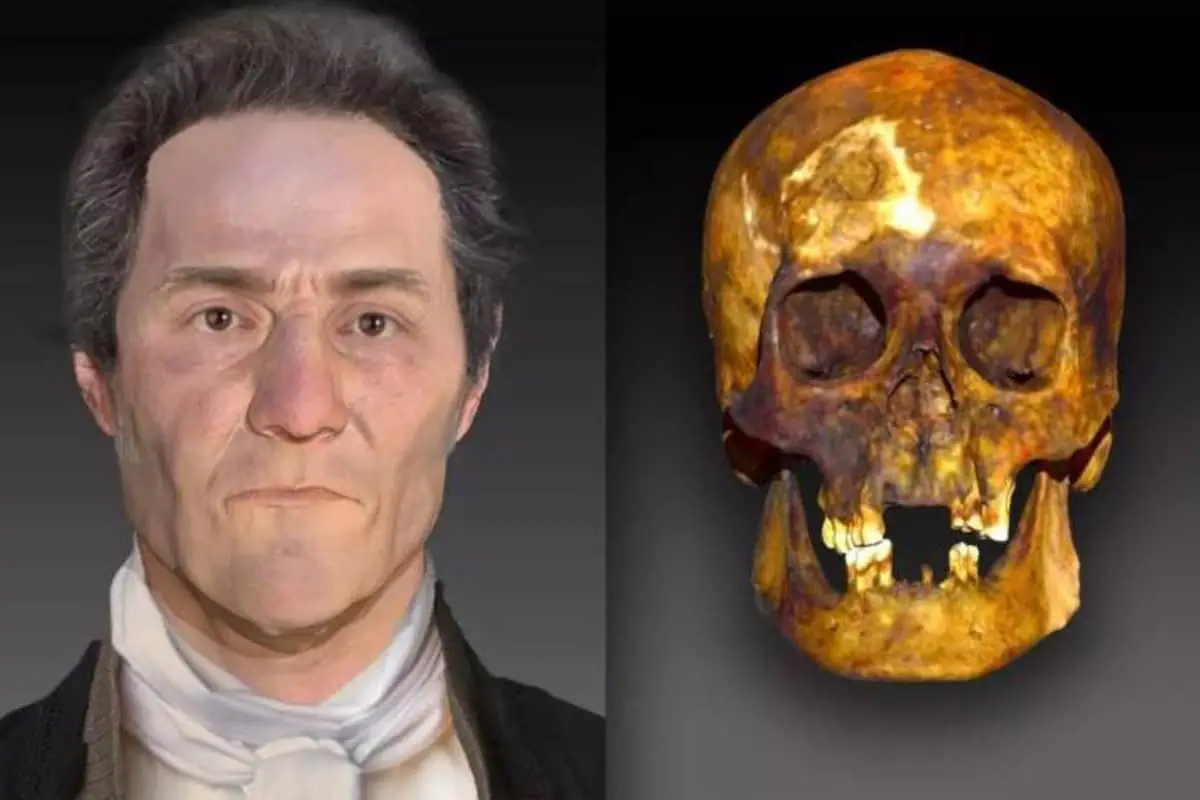
Researchers have revealed the face of the ‘Connecticut vampire’ using forensic facial reconstruction.
In 1990, archaeologists excavating a 19th century grave in the town of Giswold, located in Connecticut, United States, found that the human remains were arranged to form skull and crossbones, a practice performed during The New England Vampire Panic to prevent a suspected vampire from rising from the grave.
The New England Vampire Panic was a period of terror and mass hysteria during the 19th century, caused by an outbreak of consumption that was blamed on vampires.
Consumption, known today as tuberculosis (TB), is an infectious disease caused by the Mycobacte-rium tuberculosis (MTB) bacteria. The disease generally affects the lungs, causing a chronic cough with blood-containing mucus, fever, night sweats and weight loss.
Across the states of Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont, outbreaks of tuberculosis spread amongst family members and households. So severe was the epidemic, that it claimed around 2 percent of the region’s population from 1786 to 1800.
When a tuberculosis sufferer died, it was assumed that they consumed the life of their surviving relatives who also became ill from tuberculosis due to their close proximity to those already infected. To protect the survivors and ward off the symptoms of consumption, the bodies of those who died were exhumed to examine for traits of vampirism.
Vampiric traits were determined by how fresh the corpse appeared, especially if the heart or other organs still contained evidence of liquid blood. After a vampiric corpse was identified, the remains were either turned over in the grave, the corpse decapitated, or their remains reburied in the form of a skull and crossbones.
For decades, the “Connecticut vampire” was known only as “JB55,” based on the coffin’s brass tacks which had the initials of the deceased and the age of death. In 2019, researchers used genealogical DNA methods to identify JB55 as John Barber, a 55-year-old farmer who died from tuberculosis.
Researchers from the Parabon NanoLabs and the Armed Forces DNA Identification Laboratory, working with the Virtual Curation Laboratory at the Virginia Commonwealth University, have revealed the face of the ‘Connecticut vampire’ using forensic facial reconstruction.
In the Virtual Curation Lab, the team used a laser 3-D scanner and a structured light scanner to capture the skull, then applied photogrammetric software to assemble a 3-D digital model.
Forensic anthropologist, Simmons-Ehrhardt said: “This case allowed us to examine the geometric detail and degree of photorealism that can be captured with 3D surface scanning and photogrammetry, enabling us to demonstrate a 3-D workflow for both forensic and historical facial approximation casework.”
VCU students, Maddie Martin, and Emily Pitts, contributed to the project by painting 3-D replicas of the skull. One of the replicas is being provided to the National Museum of Health and Medicine for teaching and public outreach, while the other will stay at VCU for similar purposes.
Header Image Credit : Parabon Nanolabs/Virginia Commonwealth University